The chip industry is widely recognized as one of the most lucrative sectors in the U.S. stock market. With the surge in artificial intelligence, the industry is poised for significant growth in the coming years. As technology advances and market demands evolve, new companies may rise, while some established players could face challenges. Investors interested in this sector should proceed with caution due to its highly competitive nature. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the chip industry's outlook and offers an in-depth investment analysis.
What is Chip?
It is a kind of integrated circuit, a kind of tiny and complex electronic component. Usually made into a thin sheet, it is only the size of a fingernail. In this small area, a large number of electronic components are integrated, such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, etc., as well as the connecting lines between them. These components and lines are fabricated on a piece of semiconductor material (usually silicon) to form a fully functional circuit.
Their use is mainly to realize the functions of various electronic devices, such as computers, cell phones, televisions, and automotive electronic systems. They can perform a variety of tasks, from simple logic operations to complex data processing and control tasks. Due to its small size and high integration, it makes electronic devices more compact, efficient, and powerful.
It has a wide range of types and functions, including microprocessors (CPUs), storage (memory), graphics processors (GPUs), communications, sensors, and more. As technology advances, its manufacturing process and performance continue to improve, enabling electronic products to achieve more functionality and higher performance.
As a result, we often hear numbers about chip processes, such as 14 nanometers or 7 nanometers, which actually refer to the size of the transistors. However, the pursuit of miniaturization and densification also brings with it a set of challenges, as the process involves constantly pushing the limits of technology and processes.
It is important to realize that its production process is an extremely complex, systematic project that requires multiple stages of design, raw material preparation, and manufacturing. Moreover, in this industry, each link is interdependent and constrained, and each segment has its own unique challenges and opportunities.
First, design software maps the layout and structure of billions of tiny transistors to ensure that each one works properly. Then, high-temperature processing and purification transform silica into high-purity silicon wafers, which are cut, ground, and polished to form flat, smooth silicon wafers.
In the field of design, CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) are two types of chips that are of vital importance. The CPU can be regarded as the brain of an electronic product, is responsible for performing a variety of computational tasks and control operations, and is one of the core components of a device. GPUs, on the other hand, specialize in performing a large number of repetitive operations at the same time and are particularly suited to areas such as graphics processing, parallel processing of data, and artificial intelligence.
This is an area where Intel and AMD are the major players in the CPU market, while NVIDIA dominates the GPU space. There are also companies that specialize in other types of design, such as analog, automotive electronics, and autonomous driving, and they have a significant presence in their respective fields.
The next step in manufacturing is the key link in transforming the design drawings into actual chips. The designed circuit diagrams are etched on special boards, photoresist is applied to the silicon wafers, the circuit patterns are irradiated onto the silicon wafers by photolithography to form the circuit structure, and then special substances are stacked on top of each other layer by layer until all the circuit layers are complete. The whole process needs to be highly precise and error-free, as any small mistake may cause it to be scrapped.
Photolithography, in particular, is one of the key pieces of equipment with amazing internal complexity and precision. For example, the assembly process of an EUV (extreme ultraviolet) lithography machine is so complex that it takes more than a year and requires materials and components from thousands of suppliers around the world. The light source technology for the lithography machine is also extremely complex, such as the use of liquid antimony drops and lasers to produce extreme ultraviolet light.
Chip manufacturing is highly technical and complex and comes with huge costs. Foundries play a key role in the entire manufacturing process, and they, such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, provide advanced manufacturing technologies and large-scale production capabilities.
Final package testing is the process of packaging, testing, and validating the manufactured chip. While there are no established players in this phase as there are in design and manufacturing, equipment and material suppliers such as ASML, Lam Research, and Applied Materials play a vital role in supporting the entire package testing process.
Knowing how complex and technically demanding its manufacturing is, it's clear that the industry, while vibrant, is full of challenges. Factors such as increasing costs and continued technical difficulty make the barrier to entry into the field extremely high. As a result, the industry has shown an oligopolistic pattern, with a few foundries such as TSMC and Samsung dominating the market and having a profound impact on the development of the industry as a whole.
And nowadays, chip technology has widely penetrated all aspects of modern society, including electronic devices, communications, automotive, medical, industrial control, smart homes, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and finance. As a core component of electronic devices, it plays an important role in improving the convenience of life, enhancing work efficiency, strengthening security, etc., and has become one of the key pillars for the development of modern society.
 Current State of Chip Industry
Current State of Chip Industry
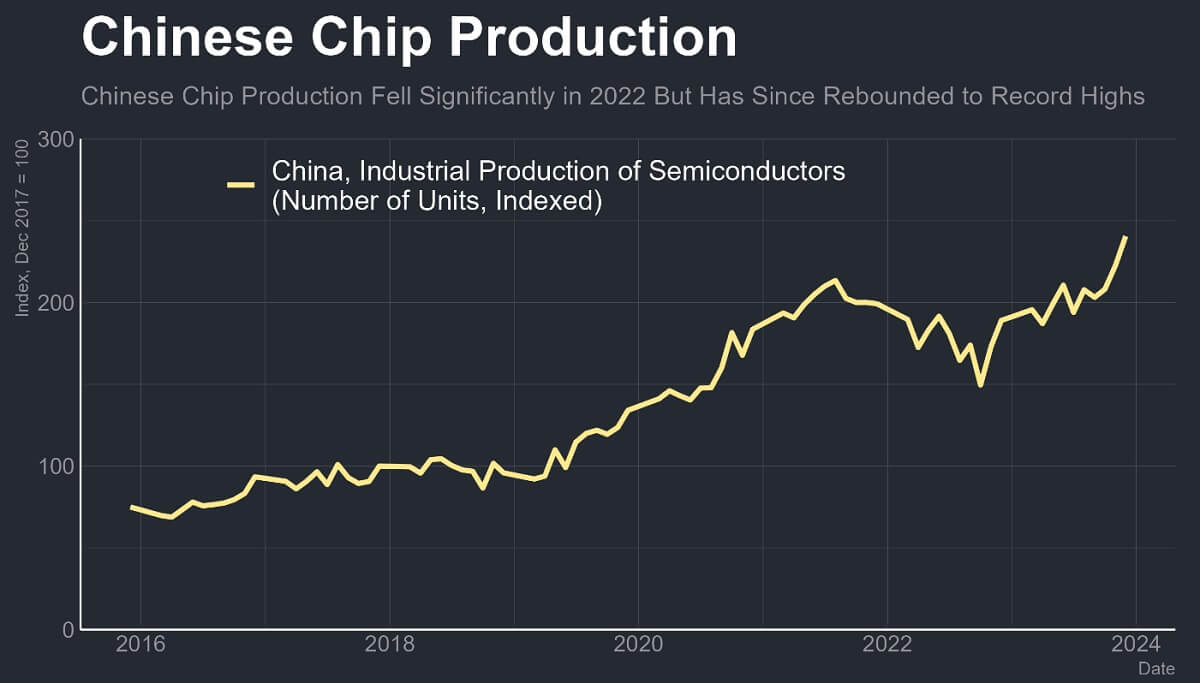
Currently, the chip industry is in the midst of rapid development and change. Globally, its technology continues to innovate, especially in the fields of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, 5G communication, automatic driving, cloud computing, and other areas of rapid development, to promote the increasing demand for it. The continuous expansion and deepening of these fields has led to their increasingly widespread application in modern society and has become one of the key drivers of technological progress and social development.
At the same time, supply chain relationships are evolving globally. Some emerging markets, such as China and India, are increasing their investment in the industry, becoming an important force in global manufacturing and R&D. China, in particular, has raised nearly $48 billion of its own money to create a chip technology research fund because of U.S. investment restrictions.
This worldwide evolution of the supply chain and the rise of emerging markets are changing the landscape and competitive dynamics of their industries, bringing more opportunities and challenges to the industry. These include rising R&D costs due to accelerating technological advances, complexity in manufacturing processes, supply chain vulnerabilities, and global shortages.
In addition, international trade frictions, geopolitical tensions, and epidemics may adversely affect the industry. Moreover, because of the critical importance of technology in modern society, countries are therefore engaged in a series of actions and competitions in order to compete in the field of technology.
Because of the strategic importance of the industry, some countries have adopted various means to control or influence the supply chain. These may include policy support, investment programs, tax incentives, etc., aimed at promoting the development and competitiveness of their chip industries. Such practices can help countries secure their position in key technology areas and reduce their dependence on other countries.
In some cases, reliance on foreign-produced chips may pose a threat to national security, so some countries may take measures to ensure that they have sufficient independent production capacity. These measures may include government funding, technological research and development, and regulatory policies to enhance the competitiveness and autonomy of their industries.
At the same time, considering its importance in the field of national defense and security, some countries will also strengthen the regulation and management of its safety and reliability, including measures to restrict the transfer of sensitive technologies and strengthen supply chain control, so as to safeguard their national security interests.
As it is a core component of the global industrial chain, trade frictions and tariff policies among countries may also have an impact on its industry. In international trade, some countries may take restrictive measures, such as limiting exports to specific countries or imposing tariffs, to protect their industrial interests.
Besides, the chip industry itself is also very risky. First of all, technology risk is an important factor because technology is constantly developing and market demand is changing. If a company is unable to keep up with the development of technology or meet market demand, it may face the risk of losing market share or even being eliminated.
Second, supply chain risk is also a challenge. Its manufacture involves a large number of raw materials and components, and if there is a problem in one part of the supply chain, such as an interruption in the supply of raw materials or transportation problems, it could lead to production disruptions or cost increases. In addition, market risk is also one of the challenges facing the industry. Due to factors such as fierce competition in the market, price fluctuations, and unstable demand, companies may face problems such as a lack of sales and inventory backlogs, which affect their profitability and market position.
In addition, policy and legal risks need to be considered. Some countries may introduce restrictive policies, laws, and regulations that affect the development and operation of the industry. Meanwhile, the protection of intellectual property rights is also an important issue, as its technology involves a large number of patents and trade secrets, which may cause significant losses to enterprises in the event of infringement or leakage.
Nevertheless, the industry still has great potential and attraction. Governments and enterprises have increased their investment and R&D efforts in this field in order to seek an advantageous position in global competition. In the future, with the continuous progress of technology and the expansion of application areas, the industry is expected to continue to maintain a sustained and healthy development trend.
In summary, the chip industry is a field full of challenges and opportunities. Understanding the basics of the industry, the key companies, and the challenges it faces is crucial for investors to make informed investment decisions. Although the industry faces many challenges, it is still full of great potential for growth as technology continues to advance and investment continues.
 Investing in the Chip Sector
Investing in the Chip Sector
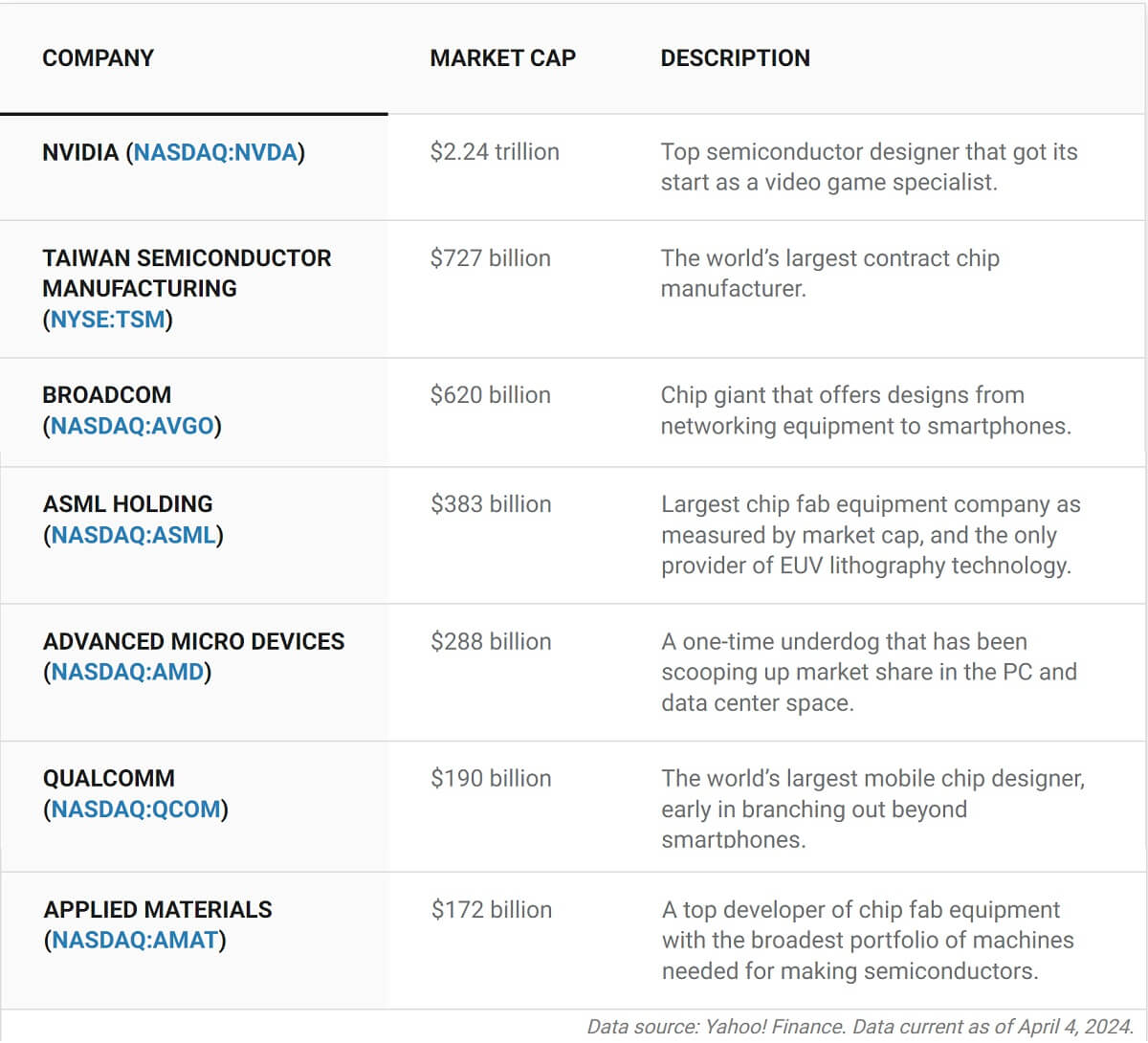
As a highly sought-after area of the technology industry, investments in this sector offer a certain amount of potential and risk. Simply put, it has certain investment opportunities in the short term, driven by artificial intelligence technology. However, in the long run, issues such as price wars and overcapacity may pose challenges to the industry. Investors need to formulate their investment strategies carefully based on market changes and company performance.
The industry is a key sector with a wide range of applications, covering a number of areas such as smartphones, computers, automobiles, and artificial intelligence. As these sectors continue to grow, the demand for high-performance, low-power, and reliable chips continues to increase, creating tremendous growth opportunities for the industry. As a result, the industry has a bright future, attracting continued attention and investment from investors.
However, its industry is also subject to cyclical influences. With the continuous emergence of new technologies, the demand for new products in the market will show cyclical growth. This growth stimulates activities upstream and downstream throughout the industry chain, including design, manufacturing, testing, and packaging.
At the same time, such fluctuations in market demand will inevitably lead to an imbalance between supply and demand. During periods of oversupply, companies may face the challenge of falling prices and reduced profitability and may even experience overcapacity and inventory buildup. During periods of undersupply, on the other hand, demand in the market will outstrip supply, driving chip prices up and boosting company performance.
In addition, different types of companies will perform differently during the cycle. For example, companies that focus on new technology development and market leadership may be more likely to gain a competitive advantage during an up-cycle, while companies focusing on low-cost and mass production may be more vulnerable to down-cycle shocks.
While it is true that revenues across the industry may be challenged to some extent during a down cycle, investment opportunities still exist in certain segments. For example, foundries such as TSMC may be relatively unaffected, as they typically have advanced manufacturing technologies and resources to attract more orders and maintain solid profitability.
TSMC's performance in the current cycle is a good example, with its gross margin and revenue performance remaining solid, demonstrating its relatively small scope of exposure. Therefore, even in the face of challenges across the industry, it is still possible to seek returns by investing in a number of relatively stable sectors or businesses.
During an upcycle, the industry as a whole usually shows a better growth trend. In this case, upstream companies such as SML Applied Materials are likely to be the first to benefit, as their capital investment and production increases will precede the industry as a whole. Additionally, companies that directly serve customer endpoints, such as NVIDIA and Qualcomm, will also benefit from increased demand. Therefore, investors can focus on these companies during the upcycle to capture industry growth opportunities.
Although the chip industry is subject to cyclicality, it still offers long-term investment value as a technology-driven industry with sustained demand growth. It is important to realize that its irreplaceable position in modern technology and daily life determines its long-term investment value and certainty.
For the time being, as a leader in the field of AI, NVIDIA does occupy an important position in the market. It has performed well in artificial intelligence, data centers, and other fields. However, its share price may face volatility because the market has some doubts about its high valuation.
Despite Apple's relatively weak performance in artificial intelligence (AI), the launch of its new chip, M2. could open up new opportunities for it. It could bring performance gains, energy efficiency improvements, and other advantages that could enhance its competitiveness in the market and provide investors with new investment leads.
TSMC, as a leader in chip manufacturing, has been leading the way in advanced processes. However, capacity expansion may lead to an oversupply situation, which in turn will affect the company's profitability and share price to a certain extent. However, in the long run, its technological strength and market position remain strong.
Its role as infrastructure is becoming increasingly prominent as technology advances and demand grows. In the long run, the development of technologies such as the Internet of Everything and artificial intelligence will further drive the industry's prosperity. Investors should therefore take a long-term view to capitalize on investment opportunities in the sector's long-term growth rather than being swayed by short-term cyclical fluctuations.
Overall, the chip industry is somewhat cyclical, but as a long-term investor, it is important to understand this cyclicality and control risk. While the presence of cyclicality can affect a company's short-term performance, the industry's technological advances and continued demand growth remain the main source of its investment value in the long term.
Industry Outlook and Investment Analysis of Chips
| Outlook |
Investment Analysis |
| Technology Advancement |
Continuing to drive industry growth. |
| Emerging Applications |
Provide better investor opportunities. |
| Global Markets |
Expanding market size requires attention to geopolitical risks. |
| Policy Implications |
Policy changes may have an impact on the industry. |
| Long-term Investment View |
Long-term investment potential despite risks. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 Current State of Chip Industry
Current State of Chip Industry Investing in the Chip Sector
Investing in the Chip Sector