In the world of quantitative trading, few strategies are as widely discussed—or as misunderstood—as statistical arbitrage. Known for its data-driven nature and rapid-fire execution, this approach is a staple in hedge funds and algorithmic trading desks across global markets.
But while it sounds complex, the concept is rooted in a surprisingly simple idea: taking advantage of temporary price inefficiencies between securities based on statistical relationships. This article breaks down the top five things every trader, investor, or financial enthusiast should know about statistical arbitrage.
5 Things Traders Must Know About Statistical Arbitrage
1. What Is Statistical Arbitrage?
At its core, statistical arbitrage refers to a class of trading strategies that rely on mathematical models and historical data to identify pricing anomalies between related assets. Unlike traditional arbitrage, which involves guaranteed profit from pricing differences across markets, statistical arbitrage is based on probability, not certainty.
It usually involves a large number of trades, executed at high speed, and aims to profit from small pricing divergences that are expected to correct over time. The expectation of mean reversion is key—meaning prices that deviate from their historical norm are likely to move back toward it.
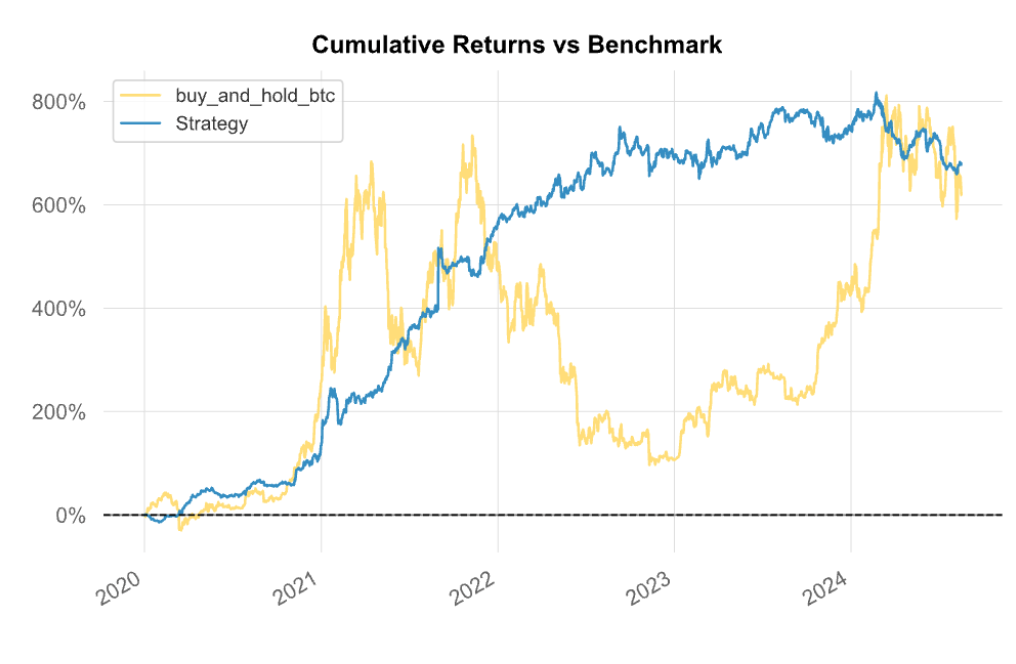
Pairs trading is a classic example of statistical arbitrage, where two historically correlated stocks diverge in price, and the strategy involves going long on the underperformer and short on the outperformer.
2. It's All About Data and Models
Successful statistical arbitrage hinges on data—lots of it. Traders build quantitative models using historical price series, volatility patterns, correlation matrices and other statistical indicators. These models identify relationships between assets that, while not necessarily causal, tend to hold over time.
A typical model may screen thousands of stock pairs, filter them based on cointegration tests or correlation coefficients, and flag potential trades when relationships deviate beyond a defined threshold.
But not all data-driven strategies are created equal. A key challenge in statistical arbitrage is overfitting—building models that work perfectly on past data but fail in live markets. That's why rigorous backtesting and stress testing are essential before committing real capital.
3. It Requires Speed, but Also Discipline
Many assume statistical arbitrage is just about speed, especially with the rise of high-frequency trading. While latency and execution timing can matter, particularly in intraday strategies, discipline is just as important.
These strategies often operate on small profit margins per trade. That means losses can mount quickly if a statistical relationship breaks down or fails to revert. Traders must stick to predefined entry and exit rules and avoid emotional responses to temporary drawdowns.
In modern implementations, statistical arbitrage is often executed through automated systems that remove human bias and allow for thousands of trades per day. But even with automation, human oversight is needed to monitor model performance and adjust parameters when market conditions shift.
4. It's Not Without Risk
Despite its sophisticated appeal, statistical arbitrage carries several risks. First, the assumed relationship between assets may not hold in the future. Correlations can break down during periods of market stress or due to structural changes in an industry.
Second, the strategy often involves leverage, which amplifies both gains and losses. A small deviation that doesn't correct as expected can lead to outsized losses if positions are too large.
Third, competition is fierce. Many institutional players deploy similar models, which can erode profit opportunities or lead to crowded trades. The infamous collapse of Long-Term Capital Management in the 1990s was partly due to failed statistical arbitrage bets that went against them during market shocks.
Understanding these risks is essential for anyone interested in exploring statistical arbitrage, whether through self-managed strategies or by investing in quant-driven funds.
5. It's Still Relevant—If You Adapt
You may wonder whether statistical arbitrage is still viable in today's market, given the rise of machine learning, AI and alternative data sources. The answer is yes—but only if you adapt.
Modern statistical arbitrage has evolved to include more complex signals, nonlinear models and high-dimensional data. Techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA), Kalman filters and even neural networks are increasingly used to refine signal quality.
Moreover, new asset classes like cryptocurrencies offer fresh ground for statistical relationships, especially in markets that are still maturing in terms of efficiency.
Retail traders can also participate, albeit on a smaller scale. While institutional quants enjoy faster access to capital and infrastructure, retail platforms now offer tools for backtesting, portfolio construction and data analytics. If you understand the principles, statistical arbitrage is no longer out of reach.
Final Thoughts
Statistical arbitrage blends quantitative analysis, disciplined execution and a deep understanding of market behaviour. It is not a set-and-forget strategy, nor is it immune to risk. But for traders willing to invest the time to understand its principles—and the effort to manage its complexities—it remains a powerful tool.
From identifying price inefficiencies to navigating volatile conditions with a rules-based system, statistical arbitrage offers a distinct approach to modern trading. Whether you're a professional quant or a curious newcomer, understanding these five core ideas can help you engage with this strategy more effectively.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.








