While the international community is discussing when the U.S. will cut interest rates after the end of the rate hike, China is still continuing its policy of cutting interest rates. The continuity of this policy has not only attracted the attention of investors but also the general public. This is because interest rate cuts often have a direct impact on deposit rates, which affects everyone's financial situation. Now, let's take a good look at the impact of falling deposit rates and strategies to deal with them.
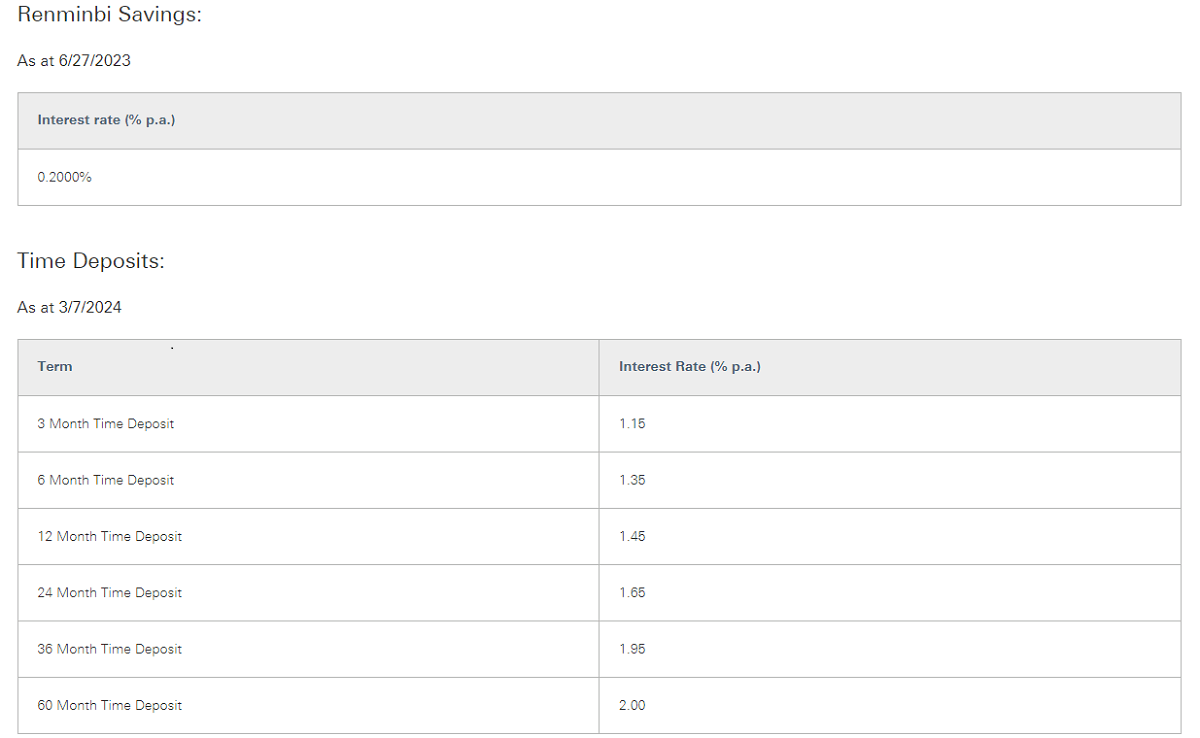
Overview of Deposit Interest Rates
It is the rate of interest paid by banks and other financial institutions to their deposit customers, and it is the rate of return that depositors receive for depositing their funds in the bank. It is usually determined according to the type and term of the deposit; for example, demand deposits, time deposits, and time deposits with different terms (e.g., three months, one year, five years, etc.) will have different interest rates.
The interest rate on demand deposits is the interest earned on funds deposited in a bank account. Demand deposits are deposits that can be accessed at any time and have a lower interest rate, usually between 0.1% and 0.3%. Time deposit interest rates, on the other hand, are the interest rates earned on funds deposited for a certain period of time. A time deposit is a deposit made by a customer for an agreed period of time that can only be withdrawn upon maturity, and the interest rate is usually relatively high.
Common time deposit terms include three months, six months, one year, two years, three years, five years, etc. The longer the term, the higher the interest rate usually is. For example, the interest rate for a one-year time deposit may range from 1.5% to 2.5%, while the interest rate for a five-year time deposit may range from 2% to 3%.
Deposit rates are affected by a number of factors, including the combined effect of macroeconomic indicators such as inflation rates and economic growth rates. Monetary policy adjustments by the central bank are the main influencing factor, which affects the level of market interest rates by adjusting the policy rate. In addition, competition among banks also affects it, and banks may adjust their interest rates in order to attract more deposit customers. The amount of demand for funds in the market is also an important factor. If there is an increase in the demand for loans in the market, banks may increase interest rates to attract more deposits.
Specifically, when economic growth slows down, central banks promote economic recovery by lowering interest rates to encourage businesses and individuals to borrow and spend. This can lead to lower interest rates and lower returns for depositors. And when inflationary pressures increase, the central bank raises interest rates to curb excessive money circulation and demand, which can cause interest rates on deposits to rise, increasing the attractiveness of savings.
And when the central bank raises the benchmark interest rate, the interest rates on deposits and loans at commercial banks also rise, which makes savings more attractive and increases the cost of borrowing, thus discouraging excessive consumption and investment and helping to control inflation. Conversely, when the central bank reduces the prime rate, deposit and lending rates at commercial banks fall, which makes savings less attractive while reducing borrowing costs, aiming to stimulate consumption and investment and promote economic growth.
Different banks may adjust their deposit rates in order to compete for market share, especially if competition is intense. This competitive mechanism leads to differences in interest rates on deposits among different banks, with smaller banks likely to offer higher interest rates to attract customers, while larger banks may maintain a lower level of interest rates by virtue of brand trust and stability.
When the demand for loans increases, banks may raise interest rates to attract more deposits in order to meet the demand for funds; conversely, when the demand for loans decreases, banks may lower interest rates to minimize taking in too many deposits. This adjustment mechanism helps banks balance the supply and demand for funds, maintain liquidity and profitability, and guide depositors to adjust their savings and investment strategies in response to changes in interest rates.
Deposit interest rates are usually expressed in terms of annualized interest rates, and the following formula can be used to calculate interest: Interest = principal x annualized interest rate x deposit term (in years). For example, if the deposit principal is 10.000 yuan, the annual interest rate is 2%, and the deposit period is 1 year, then the interest is calculated as follows: Interest = 10.000 × 0.02 × 1 = 200 yuan.
Generally speaking, interest is the return that the depositor gets from depositing it in the bank. Depositors usually choose a bank with a higher interest rate because it means they get more interest earnings. This choice takes into account the impact of interest rates on depositors' earnings, so the interest rate on bank deposits is critical to attracting and retaining customers.
As for investors, although deposits have a lower rate of return relative to other investment products, they will still compare them with the returns of other investment programs because of their relatively low risk and high liquidity. In addition, it may be an ideal choice for investors who need short-term capital reserves or have a low risk tolerance.
In conclusion, the deposit rate is a key indicator in the financial market and has a significant impact on both individual depositors and investors. Changes in it directly affect the yield on deposits, which in turn affects depositors' financial position and investment decisions. Therefore, an understanding of it and its changes can help people better plan their personal finances, choose the right deposit products, and make informed choices in their investment decisions.
Self-regulatory mechanism for deposit rates
| Self-Regulatory Mechanisms |
Description |
| Central Bank Monetary Policy |
Policy rate changes impact market and deposit interest rates. |
| Bank Competition |
Competition adjusts rates, creating interest rate gaps. |
| Market supply and demand |
Deposit rates adjust based on market demand for funds. |
Understanding Lower Deposit Interest Rates
It means that banks are paying less interest to depositors, which can reduce the returns on savings for individuals and businesses. This may affect people's spending and investment decisions, as they will not be able to get the same returns on their savings as before. In search of higher returns, people may save less and instead spend more or look for other investment opportunities, with implications for overall economic activity.
At the same time, businesses may also reassess their capital management strategies and invest more in business expansion and investment in the face of falling deposit rates. This change may stimulate economic growth to some extent, but it may also increase risks in the financial markets.
It may also encourage individuals and businesses to borrow more, as the cost of borrowing may decrease. This situation makes individuals and businesses more inclined to borrow to obtain funds, thus boosting consumption and investment activities. Increased borrowing activities can help boost economic growth because they can drive consumer spending and capital investment, boosting production and employment growth.
And they can compress banks' profits because their lending rates are not necessarily reduced immediately, leading to a reduction in bank spreads. In order to maintain profitability, banks may take other measures, such as cutting costs or finding alternative sources of income. This may include cutting services, raising fees, or seeking new investment opportunities.
It may also lead to lower returns on fixed-income investment products (e.g., bonds), which may affect investor interest in these products. In the search for higher returns, investors may turn to other more attractive investment options, such as equities, real estate, or other investment markets, for higher yields.
Because it will reduce the return on savings for individuals and businesses, it will stimulate demand for borrowing. Since the cost of borrowing is likely to be lower, individuals and businesses are more inclined to borrow funds, thus boosting consumption and investment activities and helping to drive economic growth. Therefore, it is usually used by central banks to stimulate the economy.
However, if market interest rates are already at a low level, then lower interest rates may not be effective in stimulating borrowing and economic activity. With market interest rates already low, banks may not be able to reduce lending rates further, thus limiting the impact of reducing their demand for borrowing.
In addition, if the cost of borrowing is already low, firms and individuals may not increase their borrowing, choosing instead to maintain the status quo or adopt other strategies. Thus, while the central bank's intention in lowering deposit rates is to stimulate economic activity, its effect may be limited when market interest rates are already extremely low.
China has already adopted a prolonged policy of cutting interest rates with the intention of stimulating consumption. In fact, as market interest rates have fallen, bank deposit returns have continued to decrease, so most of the funds have flowed to wealth management products with relatively higher returns. According to the latest data from P&E Standard, the survival scale of bank wealth management products has increased YoY, while at the same time, RMB deposits have decreased significantly, showing the trend of capital flow to the wealth management market.
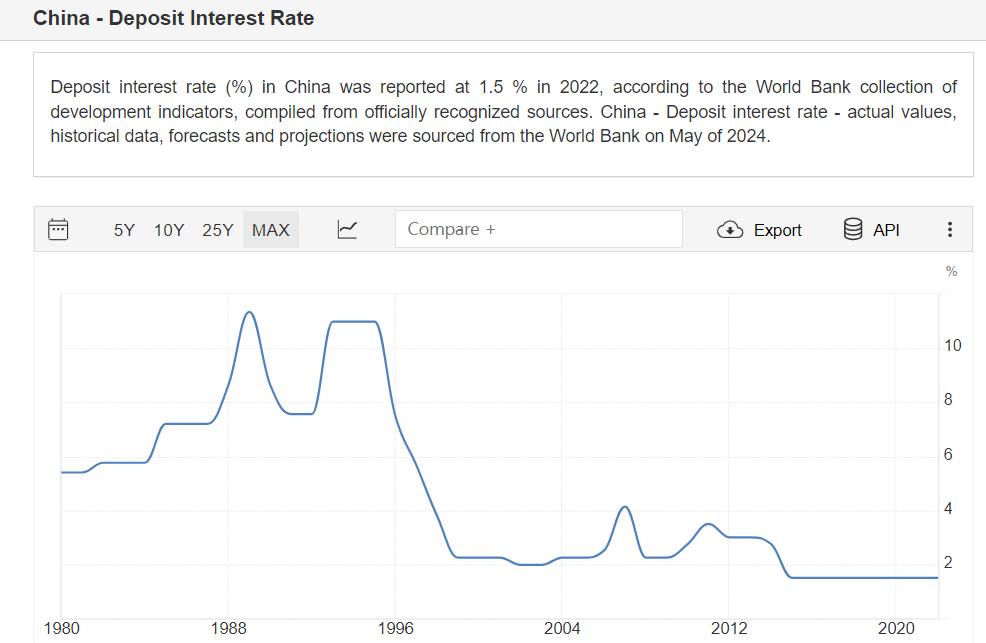
Will Deposits Rates Keep Falling?
The wide variety of financial products available in the market today poses a challenge to ordinary investors in making their choices, as not everyone has the ability or expertise to accurately assess and select the right product for them. In addition, there is also a general concern among investors about the future direction of the deposit interest rate, especially whether it will continue to be lowered or even reach a negative interest rate.
In fact, its future trend is affected by a number of factors, including the monetary policy of the Central Bank, the overall state of the economy, inflationary expectations, and changes in market interest rates. The interaction of these factors will affect the banks' adjustment strategies for interest rates as well as the level of interest rates for deposits in the market.
It is a common monetary policy tool for the central bank to influence the level of market interest rates by adjusting the policy rate. If the central bank decides to adopt an accommodative monetary policy to promote economic growth, they may reduce the policy rate. Such a move to lower the policy rate usually leads to an overall decline in market interest rates, which in turn pushes deposit rates to adjust downward. This is because banks tend to borrow funds at lower interest rates, thereby reducing the interest rates they pay to depositors.
On the other hand, if the economy slows down or falls into recession, the central bank may take measures to stimulate the economy. One common measure is to lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment activities. In this case, the central bank may lower its policy rate, which may trigger a decline in interest rates on deposits as banks pay interest to depositors at lower rates to adjust market conditions and promote economic activity.
The trend in interest rates globally does have a significant impact on the interest rates on deposits in a country. If interest rates in other countries are on a downward trend, this may put downward pressure on interest rates on deposits in the country. In this case, changes in interest rates in other countries may be transmitted to the home country because of the linkages in international financial markets.
The current trend shows that central banks are adopting accommodative monetary policies globally. As the global economy faces uncertainties and challenges, many central banks tend to stimulate growth and boost inflation by lowering interest rates. This trend has led to downward pressure on interest rates globally, resulting in a general decline in deposit rates.
As uncertainty about the economic situation increases, investors are likely to favor conservative investments and shift their funds to safer deposit products, further increasing pressure on central banks to lower interest rates. At the same time, the government is also likely to adopt fiscal stimulus policies to promote economic recovery, which usually requires the central bank to adopt a more accommodative monetary policy to support its implementation. As a result, the trend of interest rates continuing to move downward is likely to continue for some time to come.
As for the future, whether it will continue to fall or reach negative interest rates depends on a number of factors, including the state of economic growth, inflation expectations, central bank monetary policy, and the global economic situation. If economic growth slows down or inflation remains low, the central bank may continue to adopt an accommodative policy, which may lead to a further decline in interest rates or even the emergence of negative interest rates.
However, whether deposit rates will continue to fall in the future depends on other future events and developments and therefore cannot be predicted with certainty. For individuals and investors, an understanding of changes in monetary policy and the economic environment is critical to an understanding of future interest rate movements. Diversified portfolios should also be considered to diversify risk and cope with the uncertain interest rate environment.
Strategies for Coping with Falling Deposit Rates
In China, deposit rates in the banking sector continue to fall. For individuals and investors alike, how to protect and increase personal wealth has become an important topic. In the face of this challenge, there are a number of strategies and recommendations that can be adopted to avoid risk, seek returns, and maintain financial soundness.
For individuals, products with favorable prices are more popular in times of economic downturn. Therefore, one can focus on areas of consumer downgrading, such as the low-cost market and the second-hand market, to get better value for money. In addition, one can also focus on products and services with higher utility, such as daily necessities and basic medical services.
And for those with stable jobs, maintaining current employment may be a wise choice. Despite the uncertain economic situation, a steady source of income can provide security for personal finances. It is also important to keep an eye out for changes in the industry and opportunities in emerging industries so that you can make adjustments if necessary.
At the same time, prudent debt management is especially important in an uncertain economy. Both individuals and investors should avoid over-reliance on borrowing, plan their financial structure rationally, and repay high-interest liabilities in a timely manner to minimize financial risks. At the same time, prudent selection of lending products and institutions should be made to ensure that the terms of borrowing are reasonable and to avoid increasing the financial burden due to high interest rates.
In an environment of declining deposit rates, investors need to consider finding other financial investment channels to generate higher returns. In addition to considering traditional assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, they can also focus on markets such as foreign exchange and commodities. In addition, fintech platforms offer a diverse range of investment products.
You can also focus on medium- to long-term deposits, cash management financial products, and savings bonds, which are relatively sound investment strategies, especially for investors who focus on capital preservation and risk control. These investment varieties usually have lower risks and relatively stable returns and are suitable for capital preservation and appreciation.
Medium- to long-term deposits usually have higher interest rates and lower relative risks and are suitable for longer-term capital reserves and planning. Cash management financial products have better liquidity and lower risk and are suitable for short-term fund management and daily expenses. Savings bonds, as government bonds, have higher security and stable returns and are suitable for the sound allocation of long-term funds.
To summarize, in response to the deposit rate cut, individuals can protect and increase their personal wealth by diversifying their financial investments, focusing on areas of consumer downgrade, maintaining stable employment, prudent debt management, and improving financial education. It is also necessary to pay close attention to changes in the economic situation and adjust one's financial planning in a timely manner to cope with the ever-changing market environment.
The Impact of Declining Deposit Rates and Coping Strategies
| Impact. |
Response Strategies |
| influence personal and business-saving choices. |
Diversify financial investments. |
| increase borrowing and debt risks. |
Manage debt carefully and avoid over-reliance on borrowing. |
| impact bank profits and service quality. |
Explore higher-yield investments like forex, commodities, etc. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.