The Japanese yen (JPY) has experienced significant depreciation in recent years, raising concerns among policymakers, businesses, and investors.
As of October 2025, the Japanese yen (JPY) continues to trade in a relatively weak zone against the U.S. dollar, with USD/JPY around ~147.03.
Historically, JPY strength has been a go-to safe haven in times of turmoil, so its current weakness has attracted scrutiny. In this article, we examine the fundamental factors, regional variations, and potential influences that could change this trend.
Current USD to JPY Exchange Rate (October 2025)
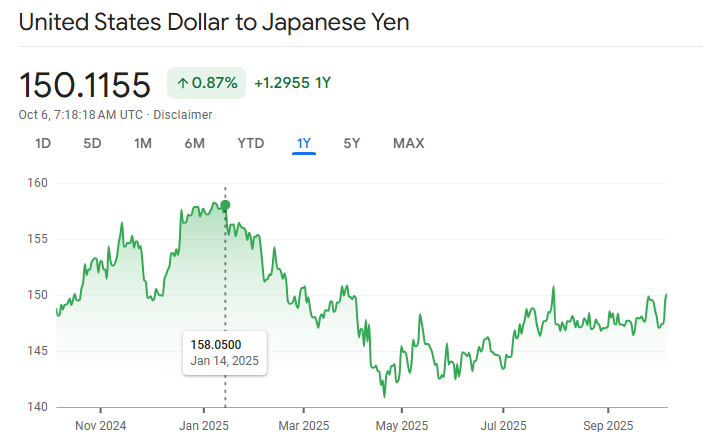
Note: The highest USD/JPY of 2025 exceeded 158.80, and the lowest dipped to ~139.80 in April. [1]
Why Is the Yen So Weak? Key Drivers Explained
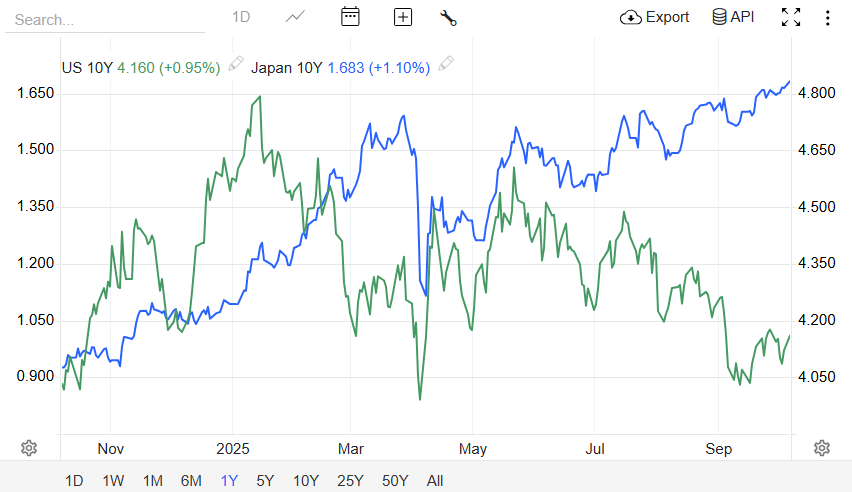
1. Monetary Policy Divergence & Yield Differentials
The Bank of Japan remains cautious and has yet to embark on aggressive rate hikes, while U.S. yields, especially on 10-year Treasuries, remain significantly higher.
As of October 2025, Japan's 10-year government bond yields around 1.6%, compared to the U.S. 10-year Treasury near 4.1%, a gap that keeps capital flowing toward the latter.
This yield differential is the single biggest driver of yen weakness today.
2. Strong U.S. Dollar / Safe-Haven Flow Reversal
USD strength in 2025 is driven by yield, macroeconomic attractiveness, and capital flows.
The dollar's rally has put general pressure on emerging, export, and "carry trade" currencies, including the yen.
3. Fiscal & Political Signals (New Leadership, Stimulus Bias)

Japan may lean toward more fiscal stimulus under new leadership, weakening JPY expectations.
Following Sanae Takaichi's victory in the LDP leadership, markets reported USD/JPY dropping below 150, attributing the move to expected fiscal loosening and diminished hawkish influence on the BOJ. [2]
4. External Trade & Current Account Pressures
Japan's import-heavy structure (energy, raw materials) hurts the JPY when trade conditions worsen. With energy and commodity prices volatile, Japan's import costs rise, reducing net exports and putting the JPY under pressure.
5. Investor Risk Premium & Capital Flows
Foreign and domestic capital flows favour dollar or higher-yielding currencies. If JPY assets yield less or growth looks weaker, capital may depart, especially in volatile global regimes.
6. Structural Constraints & Demographic Trends
Japan's ageing population, low productivity growth, and high public debt issues had dampened confidence as weak structural growth limits Japan's ability to "outgrow" currency pressure.
7. Limited Central Bank Leverage & FX Intervention Constraints
BOJ has constraints in countering the JPY weakness aggressively. Large interventions may be politically constrained or require foreign coordination, and consistent intervention can deplete reserves or invite international criticism.
8. Relative Weakness vs Regional Peers
Some regional currencies are also weaker, but the yen's weakness is sharper due to Japan-specific factors.
For example, the Korean won or Chinese yuan show stress, but not with the same yield crowding and fiscal/political baggage.
Regional & Cross-Currency Perspective

To see if JPY weakness is unique or part of a broader pattern:
In 2025, the Korean won (KRW) and the Indian rupee (INR) have similarly weakened against the USD. However, their causes are more related to trade and capital flows rather than significant policy differences.
The Chinese yuan (CNY / CNH) has experienced a controlled decline. But China's capital regulations and central oversight restrict free float movements.
Historically, during risk-off episodes, the yen typically appreciates. However, its current weakness suggests significant opposing forces at play.
This comparison highlights that yen's weakness isn't just an emerging-market trend; Japan's internal and policy conditions amplify it.
USD/JPY Forecast 2025 & Japanese Yen Outlook 2026
Listed below is an overview of potential trajectories for the yen in late 2025 and moving into 2026, informed by yield spreads, monetary policy, and institutional predictions.
| Scenario |
USD/JPY Range |
Key Conditions |
| Moderate Bearish (Yen Recovery) |
140 - 150 |
BOJ tightens slightly, U.S. yields soften, energy import costs ease |
| Base Case / Range-Bound |
145 - 155 |
Japan maintains cautious policy, global yields moderate, balanced trade |
| Strong USD / Deep Yen Weakness |
150 - 160+ |
Persistent U.S. yield advantage, fiscal stimulus in Japan, weak exports |
According to Goldman Sachs, the yen is expected to remain weak, with forecasts placing USD/JPY at or above ¥150 over the next 12 months under current yield and policy dynamics.
Some Goldman strategists also see room for yen strength toward the low ¥140s under scenarios of U.S. growth slowdown or policy shifts. [3]
MUFG's foreign exchange outlook offers more balanced projections: while they currently favour short exposure on USD/JPY given policy divergence, their forecasts include possible yen rebounds later in 2025–2026.
Markets widely recognise that the yen's direction through 2025–2026 will depend heavily on whether the BOJ normalises monetary policy, how long U.S. yields stay elevated, and whether fiscal and growth conditions in Japan improve.
What to Monitor Next (for Yen Watchers & Traders)
BOJ rate decisions and policy statements
U.S. Treasury yields and forward rate expectations
Japan's inflation data, wage growth, and output gap
Trade balance and import cost pressures
FX interventions and announcements by BOJ / MOF
Political leadership cues (e.g. stimulus plans, tax policy)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why Is the Japanese Yen So Weak Against the U.S. Dollar in 2025?
The yen has weakened due to diverging monetary policies, with Japan's Bank of Japan (BoJ) maintaining an ultra-loose monetary policy.
2. How Does Japan's Low Interest Rate Policy Affect the Yen's Value?
Japan's low or near-zero interest rates make holding yen less attractive for investors seeking yield, leading to capital outflows and a weaker yen relative to currencies with higher yields such as the U.S. dollar.
3. Is the Yen Expected to Weaken Further or Recover?
Most analysts forecast continued yen weakness in the near term, driven by persistent yield differentials and government stimulus policies.
4. What Impact Does Inflation in Japan Have On the Yen?
Recent positive inflation, driven partly by a weaker yen, is helping reduce Japan's budget deficits but eroding consumers' purchasing power and adding complexity to monetary policy decisions, indirectly affecting yen sentiment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, yen's depreciation in 2025 is more than a trend; it's a reflection of policy divergence, macro pressure, investor flows, and structural Japanese constraints. The question is not if the yen will move further, but when key forces shift.
If BOJ pivots to a more hawkish posture, or U.S. yields soften, JPY could regain ground, possibly back toward 140–145. But if current dynamics hold or intensify, USD/JPY 150–160+ cannot be ruled out.
For traders and analysts, the path forward depends on watching monetary cues, fiscal signalling, yield spreads, and trade dynamics; anything from global shocks to domestic surprises could flip the flow.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.
Sources
[1] https://www.poundsterlinglive.com/history/USD-JPY-2025
[2] https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/yen-sinks-takaichi-win-spurs-bets-fiscal-easing-2025-10-06/
[3] https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2025-04-02/goldman-picks-yen-as-top-hedge-against-us-recession-tariff-risk