Many people feel that they should use ROA when using indicators to pick stocks. After all, it is an indicator that the stock god Warren Buffett is using, so it is naturally very high and valuable. However, most people do not utilize it very effectively. Many people cannot figure out why some good companies returns on equity will obviously decline year after year, but the market is too blind to continue to be bullish. This article will now tell you about stock selection, the application, and the analysis of return on equity.
Return on net assets reflects the ability of what enterprises?
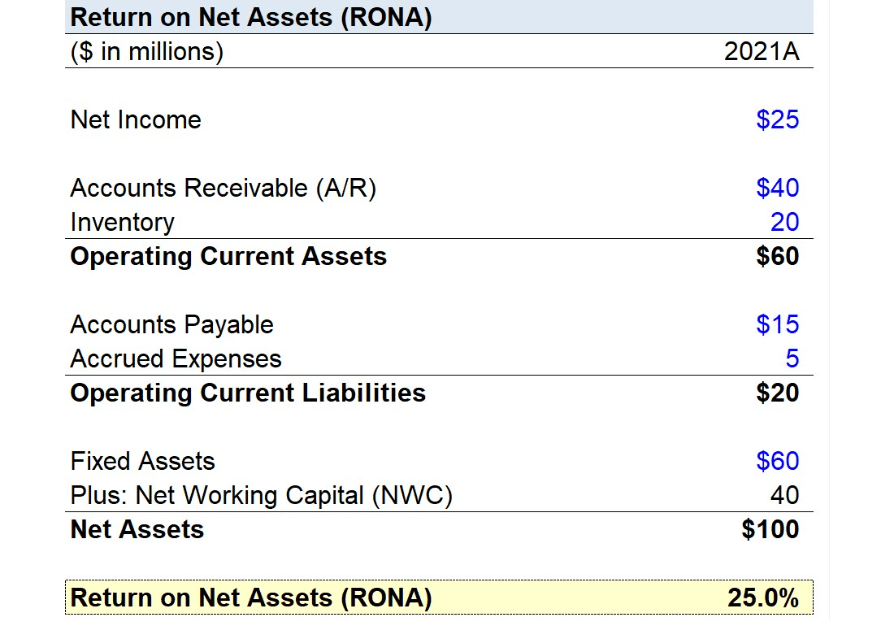
Its full English name is Return on Net Assets, also known as return on net assets. Abbreviated as RONA, it is an important indicator of a company's profitability. It indicates the net profit that a company is able to generate from the net assets invested by shareholders (i.e., shareholders' equity) over a given period of time (usually one year). In other words, ROE reflects the rate of return on shareholders' investments and indicates how much net profit each dollar of net assets can generate.
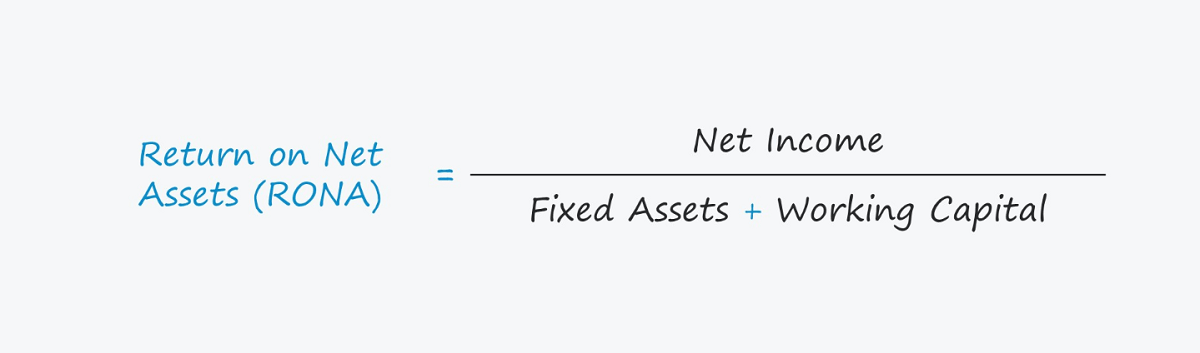
The ROE formula equals net profit divided by net assets, reflecting the net profit that a company generates each year from its net assets. And since net assets are actually shareholders' equity, representing the portion of shareholders' equity in the business, it is also known as return on shareholders' equity, or ROE, as it is popularly known.
Therefore, ROE can reflect the situation of a business from two perspectives. One is to measure the profitability of the enterprise from the perspective of the enterprise's assets; the other is to measure the return to investors from the perspective of shareholders' equity. In addition, the level of return on net assets can also help investors assess the competitive advantage and management efficiency of a company.
By looking at ROE, it is possible to understand how efficient a company is in utilizing its net assets (shareholders' equity), i.e., how much net profit it is able to generate from its net assets each year, showing how efficiently and profitably it manages its assets. A high ROE implies that a company has performed well in its resource allocation and investment decisions and is able to create value in its long-term operations.
The shareholder perspective allows for an examination of the level of return on investment a company provides to its shareholders, i.e., how much net profit shareholders receive for each dollar of net assets invested. This perspective focuses on the investor's equity and earnings in the business and can be used to assess the return and risk of the investor's investment in that business. A high ROE usually means that the company is performing well in utilizing the capital invested by the shareholders and is able to generate more net profit.
It can also be broken down into three elements through DuPont analysis: net sales margin, asset turnover, and equity multiplier. This approach helps to understand the specific factors that affect the profitability of a company, such as profitability, asset utilization efficiency, and debt levels, thus providing a more in-depth perspective for further analysis.
Net sales margin is the ratio of net profit to sales revenue, which reflects the profitability of a company, specifically the percentage of profit a company earns after deducting all costs and expenses from the sale of its products or services. The higher the net sales margin, the more profit a company makes from its sales activities, the more profitable it is, and the more it reflects its ability to sell expensively.
Asset turnover is the ratio of sales revenue to total assets, reflecting the operational capacity of a business. Specifically, asset turnover measures the efficiency with which a business utilizes its total assets to generate sales revenue over a given period of time. The higher the asset turnover ratio, the more sales revenue a company generates per unit of assets, indicating that the company is operating more efficiently and is able to effectively utilize its assets for sales, thus achieving the goal of “selling more.”.
The equity multiplier is equal to total assets divided by net assets, reflecting the degree of indebtedness of the enterprise. A higher equity multiplier indicates that a relatively large proportion of total assets come from liabilities, i.e., a higher level of indebtedness. By increasing liabilities, an enterprise can magnify the return on shareholders' equity, but at the same time, it also increases financial risk. Therefore, the level of equity multiplier is one of the most important indicators of an enterprise's liability risk and financial structure.
Return on net assets not only reflects the profitability of the current year but also allows you to understand the profitability level of a company in its long-term operation by observing its long-term trend. A stable or growing ROE over a long period of time usually indicates that the company has a stable profit model and competitive advantage with strong business operation efficiency and asset management capability.
Over the long term, a firm's long-term return on net assets is very close to the long-term average return on the firm's stock. This is because it reflects the profitability of a business generated on the basis of its net assets, and the stock price of a business is often closely related to its profitability and net asset growth.
Therefore, by analyzing the long-term return on net assets, investors can make predictions about a company's long-term profitability and potential investment returns. Understanding this information can help investors make more comprehensive and rational investment decisions, ensuring better returns on long-term holdings.
 What does a high Return on Net Assets indicate?
What does a high Return on Net Assets indicate?
Generally speaking, a higher ROE indicates that a company generates more revenue per unit of net assets, meaning that it is more efficient in its use of capital. This provides a higher investment value to shareholders as it indicates that the company is able to efficiently convert shareholders' investment into profit.
A high return on net assets usually reflects that the company is performing well in terms of asset management and capitalization. A company's ability to generate higher net profits by effectively utilizing shareholders' equity (net assets) indicates a competitive advantage and a higher level of profitability in the industry. For existing shareholders and potential investors, this means that the company is providing a higher return on investment to its shareholders.
A high return on net assets means that the company is able to effectively utilize shareholders' equity (net assets) to generate income. This indicates that the company is performing well in asset management and capital operations and has high profitability and operating efficiency. At the same time, a high ROE is usually a sign that a company is performing well in its industry and has a competitive advantage.
A higher ROE usually implies that the company has provided shareholders with a higher return on investment, indicating strong profitability and excellent management. In addition, such performance may also suggest that the company has a competitive advantage in its industry and is able to create value for shareholders on a sustainable basis.
In general, companies with a return on equity of 15% or more are usually regarded as excellent companies, which suggests that the company is performing well in terms of profitability and shareholder returns. Companies that reach 20% or above are considered top-tier, showing that the company possesses extremely strong profitability and excellent management. It means that the company has a competitive advantage in the industry and can continue to create value for shareholders. And this is a positive sign for both existing shareholders and potential investors, indicating that it is a good company worth investing in.
And if a high return on net assets is maintained over a long period of time, such as 15% or more for more than five years, it is an important criterion for selecting a quality company. This indicates that the company is efficiently utilizing its shareholders' equity while making steady profits. Such companies usually demonstrate operational excellence, sound management, and a durable competitive advantage.
These factors provide investors with a high margin of safety and the company's ability to continue to grow and protect investors' equity even when the market is volatile. This stable and high ROE reflects the quality of the company's earnings and the efficiency of its asset management, providing investors with long-term, sustainable returns.
However, investors should not just look at a higher figure and invest impulsively, as it may come with some risks. For example, a company may increase its return on net assets by increasing leverage (borrowing debt), which may increase the company's financial risk. If the company's debt level is too high, it may adversely affect the company's financial position and solvency in the event of a change in the business environment.
In addition, the company may seek to enhance its return on net assets through short-term or one-time gains rather than through sustained and stable business growth. Therefore, investors also need to focus on the sustainability of the company's long-term earnings model and strategy to ensure that a high ROE is not based on an excessively risky or unsustainable approach to profitability.
In contrast, improving ROE by increasing net profit is a positive approach. This usually means that companies increase profits by improving operational efficiency, improving their main business, or optimizing their cost structure. This approach reflects a company's actual operating ability and business potential and helps to enhance its long-term competitiveness.
Investors should pay attention to this focus because it represents the company's true profitability and management level. If a company is able to steadily increase its net profit while maintaining a reasonable growth in net assets, this is usually a positive sign that the company has the potential to provide shareholders with a sustainable return on their investment.
Thus, return on equity is an important financial indicator for assessing a company's operating performance and investment value. However, in addition to that, it is also necessary to analyze the quality of profits, focusing on the source of profits, reasonableness of expenses, authenticity of income, cash flow, and accounts receivable. These analyses help investors to more accurately judge the quality of a company's earnings and financial position so that they can make informed investment decisions.
return on net assets in conjunction with other indicators
Since Warren Buffett became the stock god, many investors have attached great importance to the return on equity (ROE) indicator. Because it is an important basis for judging how well a company is doing, it reflects the level of earnings that shareholders' equity can bring in a year, which directly reflects the company's profitability and efficiency with shareholders' funds.
When selecting investment targets, you should tend to look for companies that have a high and stable ROE in their industry. This usually means that these companies have good competitive advantages, management efficiency, and profitability. In addition, a higher ROE also indicates that the company is able to utilize its resources efficiently and achieve sustainable growth.
However, investors should also carefully analyze whether this high ROE is dependent on short-term factors, such as one-time revenues or high leverage. When evaluating a company, attention should also be paid to the quality of earnings, cash flow, and the company's long-term strategy to ensure that this high ROE is sustainable.
In addition to this, when choosing a stock, investors should also evaluate a number of factors, including the company's price-to-book ratio, growth rate, and valuation, to determine its investment opportunity. A high ROE usually indicates that a company is performing well in terms of utilizing shareholders' equity, but it needs to be analyzed in conjunction with other metrics, such as the growth rate, which can indicate a company's earnings potential, and the valuation, which reflects the market's expectations of a company's future prospects.
For example, a high return on net assets is usually associated with a high price-to-book (P/B) ratio and a high share price, as these metrics reflect the market's perception of a company's value and profitability. A high ROE indicates that a company is doing well in generating profits from shareholders' equity, which the market usually takes as a positive sign, pushing up the share price.
In addition, a high return on Net Assets may also lead to a high price-to-book ratio, as the market is willing to pay a higher premium for companies that are able to utilize their assets efficiently. These correlations reflect the market's confidence in and expectations of a company, but investors should still take care to fully assess a company's financial position and business prospects.
For growth stocks, a high price-to-book ratio (P/B) usually represents a higher ROE for the company and is therefore considered more investable. Growth companies usually excel in business expansion and innovation and may have higher earnings potential and growth prospects. As a result, the market is often willing to pay a higher P/E ratio for these companies because they excel in asset utilization and profit growth.
However, while companies with higher price-to-book ratios (P/B) may be recognized by the market for their high return on Net Assets, this does not mean that the company is reasonably valued. Investors need to assess whether the P/B ratio matches the company's earnings growth potential, as well as the company's stage of development, competitive advantages, and long-term strategic objectives.
It is also important to note that the stage of development of a company (e.g., mature stage, emerging stage, etc.) can have a significant impact on its valuation. For emerging industries or start-ups, NAV may be more volatile, as these companies may be in the early stages of high growth with immature business models and profitability.
Therefore, when evaluating such companies, it is necessary to consider their growth potential, market outlook, and strategic objectives rather than relying solely on the existing return on net assets. Mature-stage companies usually exhibit a more stable ROE, but investors still need to focus on their long-term strategy and market competitiveness to ensure that the company can continue to provide stable returns to shareholders.
All of this suggests that ROE is a valuable metric that can help investors better assess a company's profitability and valuation level. However, investors should use it in conjunction with other metrics and analytical methods to fully assess the potential investment value of a company. In addition, different companies and industries may have different standards for return on Net Assets, and investors need to make judgments on a case-by-case basis.
Normal range of return on net assets
| Industry Name |
ROE (adjusted for R&D) |
| Advertising |
3.25% |
| Aerospace/Defense |
10.36% |
| Air Transport |
20.67% |
| Apparel |
9.11% |
| Auto & Truck |
6.99% |
| Auto Parts |
5.18% |
| Bank (Money Center) |
14.87% |
| Banks (Regional) |
12.14% |
| Beverage (Alcoholic) |
8.70% |
| Beverage (Soft) |
29.60% |
| Broadcasting |
-2.16% |
| Brokerage & Investment Banking |
10.24% |
| Building Materials |
19.82% |
| Business & Consumer Services |
13.32% |
| Cable TV |
19.32% |
| Chemical (Basic) |
8.30% |
| Chemical (Diversified) |
-2.33% |
| Chemical (Specialty) |
13.18% |
| Coal & Related Energy |
28.31% |
| Computer Services |
14.44% |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 What does a high Return on Net Assets indicate?
What does a high Return on Net Assets indicate?