An indispensable role in the U.S. economic arena is the U.S. Federal Reserve System,commonly known as the Federal Reserve. As the central bank of the United States,it bears the important responsibility of formulating monetary policy,supervising financial institutions,maintaining financial stability, and promoting economic growth. Its decisions and policies not only have a far-reaching impact on the U.S. economy but also have a wide-ranging influence on the global financial markets. Now we will have a good understanding of the pillars of financial stability in the United States—what kind of institution is the Federal Reserve?

What is the Federal Reserve?
Its full name is the Federal Reserve System,which translates to the U.S. Federal Reserve System,the central banking system of the United States. It is an official institution established by federal law with an independent legal personality responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy,supervising financial institutions,maintaining financial stability,promoting economic growth and employment,and managing the money supply.
The central bank and our daily banks, such as HSBC and so on, are not the same thing; they are taking deposits and issuing loans to make money for commercial banks. Instead,a central bank is an issuing bank,a government bank,and its function is to issue money and formulate a national or regional monetary and credit policy.
It can be said that each country can have hundreds of commercial banks,but the central bank of a country or region is generally only one. For example,the central bank of China is the People's Bank of China (PBOC), and the yuan it issues has the PBOC printed on it.
The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States,in charge of the issuance of the dollar and responsible for the development of the dollar's monetary policy. Its main responsibility is to formulate and implement monetary policy that affects economic activity and inflation levels by adjusting interest rates and the money supply. It regulates and supervises the U.S. financial system to ensure the sound operation of banks and financial institutions,protect consumer rights,and maintain financial stability.
And manage and operate the U.S. payment system,including clearing and settlement systems,to ensure smooth and secure payments. And then conduct economic research and analysis,collect and disseminate economic data,and provide advice and guidance on economic and financial policies. And then issuing and managing the U.S. money supply,including regulating the issuance and withdrawal of currency.
And to fulfill these responsibilities,it relies on three tools for setting monetary policy:the discount lending window,the reserve ratio,and open market operations. U.S. monetary policy is mainly implemented through these three tools. These three words may sound a bit awkward, but in fact, they are not complicated.
The discount lending window is actually a kind of emergency lending policy to banks in order to prevent and deal with economic crisis and set up.It is a lifesaver in case of a crisis when banks are unable to turn around,and banks will not apply to use this loan as long as they can carry on easily.
The reserve ratio stipulates that commercial banks must pay a certain percentage of the deposits they take in to the U.S. Federal Reserve System in order to prevent banks from lending too aggressively. Since this ratio relates to the overall stability of financial markets,it is usually not changed frequently.
Its most important and routine policy tool is still the third tool,open market operations. Usually in the news report, you can see the U.S. Federal Reserve System open market meeting,also called the interest rate meeting. Discussion is the discussion of the discussion; interest is the interest rate of interest. The interest rate discussed at this meeting is called the federal funds rate.
This interest rate is critical, and it can be considered one of the most important indicators of interest rates in the United States financial markets. The Federal Reserve will hold eight open market meetings each year. The purpose of the only meeting is to decide the rise and fall of the federal funds rate. And its rise and fall will directly affect the level of market interest rates and the cost of borrowing,which in turn has an impact on economic activity,investment, consumption, and inflation.
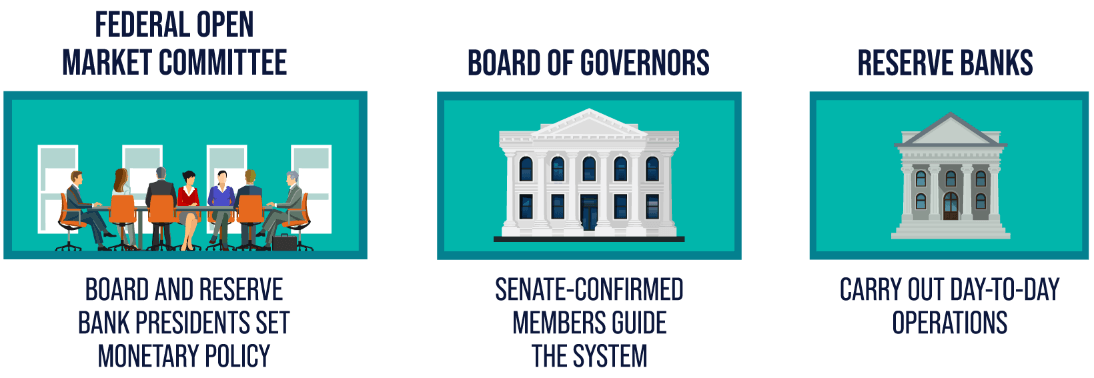
Though its role is the same as that of many central banks in the world,such as the People's Bank of China and the Bank of England in the United Kingdom, the organization of the U.S. Federal Reserve System is not quite the same as that of these central banks,which are basically government agencies in other countries around the world. Whereas it was formed as a system, it was divided into two parts,adopting a dual structure of government departments plus non-profit organizations.
One part is the Federal Reserve,which is often referred to as the Federal Reserve Board,and this part is a government agency. The other part is the Federal Reserve Banks, which are located in 12 different cities throughout the U.S. These 12 Federal Reserve Banks are non-profit organizations by nature.
Each of these 12 reserve banks has its own jurisdiction and is responsible for managing all the commercial banks within that region. Each Reserve Bank is owned by thousands of member banks in the region,meaning that the Federal Reserve is essentially a private bank holding organization.
Of course,although the U.S. Federal Reserve System has a certain private sector component,it operates under the supervision and control of the federal government,and its goal is to achieve the country's monetary policy objectives,such as maintaining price stability,promoting full employment, and maintaining financial stability. And because of the world currency status of the U.S. dollar,the Federal Reserve,which is in charge of the issuance of U.S. dollars,has been one of the most highly regarded financial institutions in the world. As a core institution in the U.S. economy and financial system,its policy decisions have a wide impact on the global economy and financial markets.
Is the Fed private or state
| Characteristics |
Private nature |
Public nature |
| Control |
Partially privately held |
Regulated and controlled by the federal government |
| Leadership |
Shareholders elect board members. |
The president nominates; the Senate approves committees. |
| Objective |
Private shareholders, monetary goals. |
Achievement of national monetary policy objectives |
Composition and shareholders of the Federal Reserve
Unlike other countries whose central banks are government-controlled,in essence, the U.S. Federal Reserve System employs a special organizational structure consisting of a central institution,the Federal Reserve Board,and 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks. This dual structural system is designed to achieve a balance between centralized monetary policy decision-making and local financial regulation.
The entire territory of the United States is divided into 12 regions,each of which establishes a regional Federal Reserve Bank. The shareholders of these regional Federal Reserve Banks are mainly local commercial banks. Commercial banks are required to hold a certain number of shares in the regional Federal Reserve Banks in order to become member banks of the United States Federal Reserve System. The amount of these shares held depends on the size and operations of the individual commercial bank.
In addition to commercial banks,some private banks and other financial institutions may also hold shares in regional Federal Reserve banks. However,private shareholder holdings are relatively small and do not significantly influence the decisions of the US Federal Reserve System.
The Federal Reserve Board is the central agency of the US Federal Reserve System and is headquartered in Washington,DC. The Board is responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy,supervising the U.S. banking system,and maintaining financial stability. The members of the Board are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate for a 14-year term,with broad powers and responsibilities.
Decisions in the U.S. Federal Reserve System are made by members of the Federal Reserve Board (FRB), who are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. In turn,the members of the board of directors of each regional reserve bank are appointed by the Federal Reserve Board (FOMC), half of whom are appointed by the federal government and the other half of whom are elected by the private shareholders of the regional reserve banks.
The FOMC is the most important policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System,responsible for setting and implementing monetary policy. It consists of seven members of the Federal Reserve Board and five bank chairmen from the 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks. The FOMC meets regularly to discuss the economic situation and monetary policy and to decide whether or not to adjust monetary policy tools such as the federal funds rate.
In this open market meeting,on the other hand,only seven executive members from the central Federal Reserve Board and 12 bank presidents from local Federal Reserve Banks are authorized to attend. That is to say that these 19 people are the highest decision-makers to decide the federal funds rate; these top decision-makers do not have to consult the President and Congress in the process of voting,with complete independence.
There are a total of 12 votes in the meeting. The central side of the seven Federal Reserve Board executive members each has one vote. The local side has a total of 5 votes,of which the President of the New York Federal Reserve Bank has a fixed vote because the New York Fed is so important. The other 11 Federal Reserve Banks rotate the remaining 4 votes in accordance with a one-year period.
Even in the absence of a vote this year,policymakers attending the meeting still have the right to speak, participate in the discussion, and have an impact on final policy. This means that the rise and fall of the federal funds rate is the result of joint discussion and decision-making by the Federal Reserve Board and local Federal Reserve Banks. This mechanism is part of the system to realize the separation of powers, checks, and balances.
The Federal Reserve uses this dual structure of government departments plus non-profit organizations at first because of the checks and balances between the U.S. federal and local. And then, after a hundred years of development,this set of complex operational mechanisms, because of the influence of the United States central bank, became a guarantee of its independence and its decision-making impartiality.
Independence of the Federal Reserve
The independence of the U.S. Federal Reserve System has existed since its inception. Because the United States has emphasized the separation of powers and checks and balances since the founding of the country,the federal government and the state governments have their own responsibilities in administration and law and collaborate with each other to check and balance each other.
Despite the long history of financial activity in the United States,the Federal Reserve was not formally established until December 1913. after more than 100 years. State governments had feared that the establishment of a national central bank would expand the scope of power of the federal government to the detriment of state interests and therefore delay the establishment of a central bank.
The United States has twice established national banks,but they are still essentially commercial banks and do not have the significance of a modern central bank. These two banks came into being during a special historical period but were established with only a 20-year validity period to prevent excessive concentration of power.
After the closure of the Second Bank of the United States,large-scale financial crises occurred almost every ten years,and the lack of regulation of the financial system made the role of finance in the economy even more important. As financial markets expanded and the risk of financial crises grew,the need for a central bank became urgent.
In 1913. the U.S. Congress passed the Federal Reserve Act,which established a dual structure consisting of both the federal government and non-profit organizations,creating the U.S. Federal Reserve System and realizing the separation of powers and checks and balances. The Act stipulated the organizational structure, duties, and scope of authority of the US Federal Reserve System and gave it a certain degree of autonomy in decision-making.
At that time,in order to avoid centralization of power and,? at the same time, to prevent any one interest group from installing its own faction to manipulate the U.S. Federal Reserve System, the choice to let the Federal Reserve Board and 12 local reserve banks together assume the central bank functions of the United States and its main leadership,including the members of the Federal Reserve Board and the chairman,is nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate appointment.
This system of appointments not only ensures government involvement in the decision-making of the U.S. Federal Reserve System but also safeguards its independence,as these leaders serve longer terms and are less susceptible to political influence. And it creates a system of checks and balances,and it is almost impossible to control the President,the House of Representatives, and the Senate at the same time,and to buy off this chairman of all the districts,as well as the civil representatives,in order to manipulate the U.S. Federal Reserve System behind the scenes.
And the U.S. Federal Reserve System enjoys a high degree of independence in setting monetary policy. Although it is required to report to Congress and the President on its monetary policy measures and the rationale for its decisions,its monetary policy decisions are based primarily on professional economic analysis and data rather than political considerations. Instead of relying on government appropriations to operate,it maintains its operations through its asset holdings and interest income from financial institutions. This model of financial self-sufficiency helps reduce government influence over it.
At the same time,the US Federal Reserve System focuses on transparency, regularly reports to the public and Congress on its monetary policy decisions and implementation,and is subject to public and media scrutiny and evaluation. In addition,it is subject to audits and regularly submits audit reports to Congress to ensure that it is acting in accordance with the law and its responsibilities.
Eventually and then, through the efforts of successive Federal Reserve Chairmen,the U.S. Federal Reserve System is free from political interference or external pressure in the formulation and implementation of monetary policy to ensure professionalism, objectivity, and long-term stability in decision-making. Its independence is also an important safeguard for its ability to ensure the professionalism and stability of monetary policy decisions,which helps to maintain the stability of financial markets and the healthy development of the economy.
The Impact of Fed Independence on Financial Markets
| Implications |
Specific impacts |
| Monetary policy independence |
Prioritize long-term economic stability and job growth. |
| Transparency in policymaking |
Market meetings and reports reduce uncertainty. |
| Economic stability |
Avoid political interference and maintain market stability. |
| Investor confidence |
Reduces interference and boosts confidence. |
| Policy Flexibility |
Flexibility to respond to economic and market changes. |
Disclaimer:This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment,security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.








