What is the Parabolic SAR Indicator?
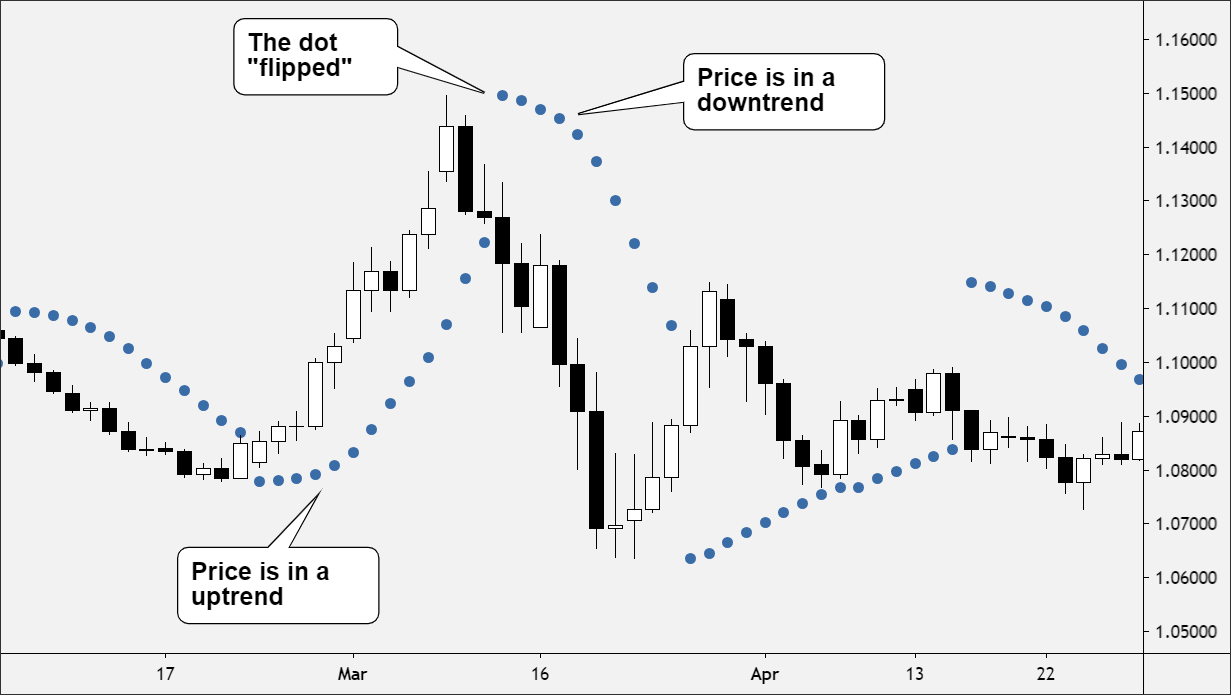
The Parabolic Stop and Reverse (SAR) Indicator is a popular technical analysis tool traders utilise to identify trends, reversals, and entry/exit points.
Developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr., the Parabolic SAR is designed to help traders determine entry and exit points in a market by plotting dots above or below the price action.
For instance, when the dots are below the price, the asset is in an uptrend (bullish trend). On the flip side, when the dots are above the price, the asset is in a downtrend (bearish trend). A trend reversal occurs when the dots flip from one side to the other.
Calculation Formula for Parabolic SAR
The calculation of the Parabolic SAR is somewhat complex and involves several steps in its formula:
SAR_current = The current SAR value
SAR_previous = The previous SAR value
AF (Acceleration Factor) = A value that starts at 0.02 and increases by 0.02 each time a new extreme high or low is reached, up to a maximum of 0.20
EP (Extreme Price) = The highest high or lowest low during the trend
The Acceleration Factor (AF) helps the indicator adjust to price movements:
In strong trends, the dots move closer to the price.
In weak trends, the dots move further away.
It makes the Parabolic SAR adaptive to different market conditions.
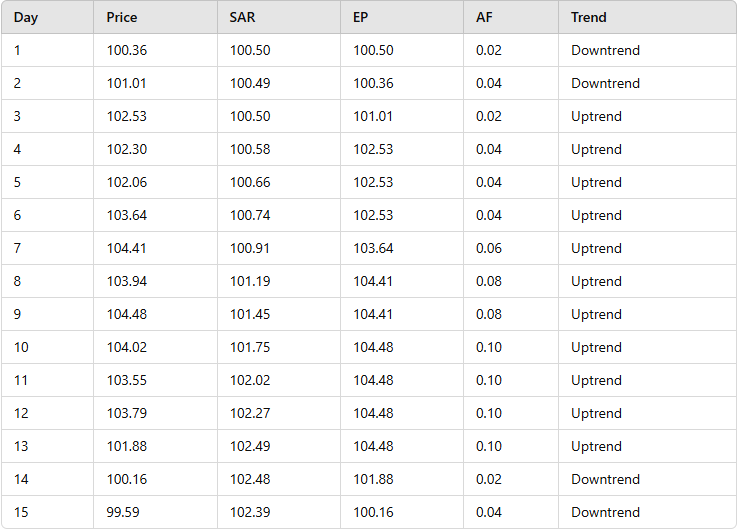
Important Remark: The Parabolic SAR table is generated using a simulated dataset, but the calculations follow the actual Parabolic SAR methodology as developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr.
How to Use Parabolic SAR for Trend Identification
The Parabolic SAR appears as a series of dots above or below the price chart. For example, when the Parabolic SAR dots are below the price, the market is trending. Traders use this signal to enter long positions (buy signal). However, beware that the trend is intact only when the dots remain below the price.
As for identifying downtrends, when the Parabolic SAR dots are above the price, the market is in a downtrend. Traders usually use this signal to enter short positions (sell signal). The trend continues until the dots flip to the opposite side.
Besides identifying uptrends and downtrends, the Parabolic SAR helps indicate trend reversal when the SAR switches position. For instance, if the dots move from below to above the price, it suggests a potential bearish reversal. If the dots move from above to below the price, it suggests a potential bullish reversal. When it occurs, traders tend to exit existing positions and prepare for a new trade in the opposite direction.
Trading Strategies Using Parabolic SAR
As mentioned above, the Parabolic SAR works best in a trend-following strategy. For example, when the dots flip below the price in an uptrend, enter a long position. Vice versa, when the dots flip above the price in a downtrend, enter a short position. Once more, beware of exiting the trade when the dots switch directions again.
While trend reversal signals are often terrible, you can enter counter-trend trades cautiously when the dots flip to the opposite side. However, we recommend using the Parabolic SAR with other trend indicators, such as Moving Average (MA) and Relative Strength Index (RSI).
For instance, a common strategy when using Parabolic SAR with a Moving Average is to buy when the Parabolic SAR flips below the price and the price is above the 50-day Moving Average and sell when the Parabolic SAR flips above the price and the price is below the 50-day Moving Average.
Parabolic SAR vs. Other Trend Indicators
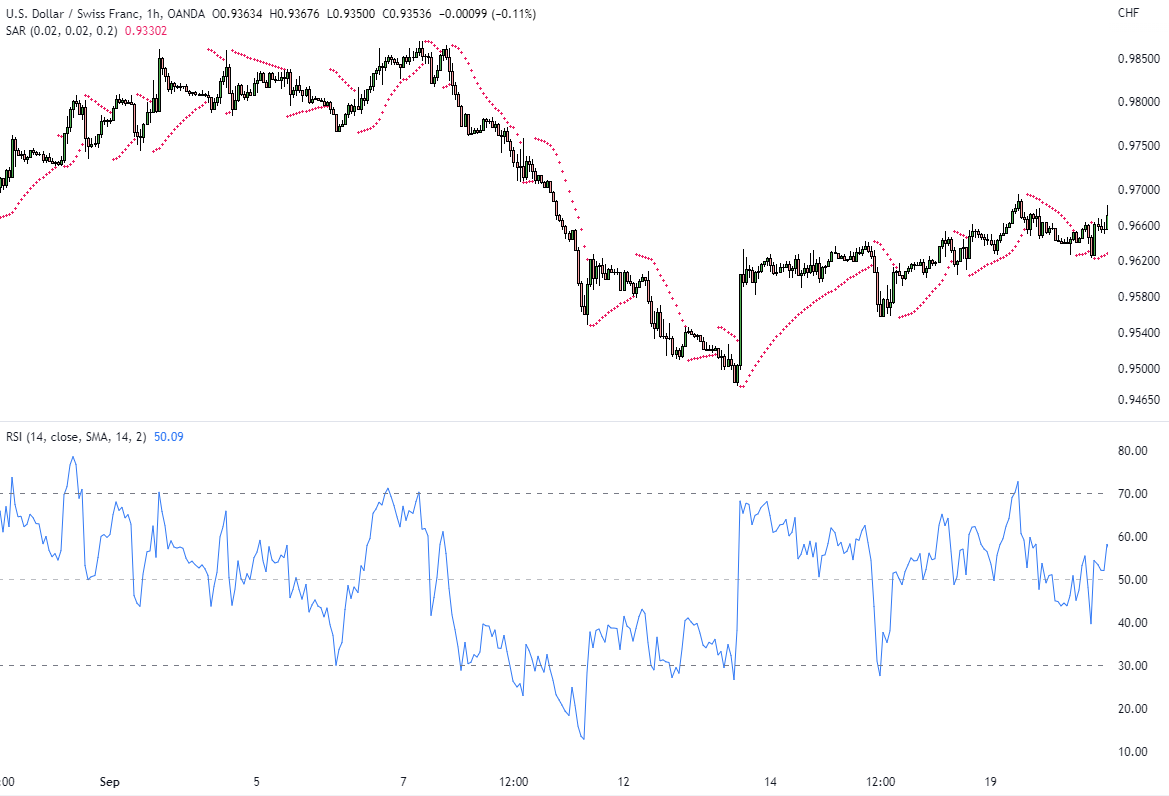
Despite its usefulness, the Parabolic SAR has limitations, such as ineffectiveness in Sideways Markets and Choppy Markets whipsaws. For example, the Parabolic SAR reacts faster to price changes, making it useful for short-term trading, while the Moving Average provides a smoother trend.
Moreover, the Parabolic SAR performs poorly in ranging markets, giving false signals. Thus, we suggest combining it with other indicators like RSI for better accuracy, as the latter confirms trend strength and avoids whipsaws.
For example, if EUR/USD SAR flips below the price and RSI is above 50, we recommend entering a buy trade. If SAR flips above the price and RSI drops below 50, the trader exits the position. You can refer to our Bull Flag vs Bear Flag article for more information on how RSI can help flag trading.
Conclusion
With everything considered, the Parabolic SAR is a powerful trend-following indicator that helps traders identify trend direction, potential reversals, and dynamic stop-loss levels.
However, like any technical indicator, Parabolic SAR is not foolproof. It works best in strong trending markets but can produce false signals in sideways or choppy conditions. To improve accuracy, we recommend combine Parabolic SAR with other indicators, such as Moving Averages and RSI to confirm trends and reduce whipsaws.
By understanding how to interpret Parabolic SAR signals, adjusting its settings for different market conditions, and using it alongside other technical tools, you can make more informed trading decisions and maximise your chances of success. While it is an excellent tool for spotting trends and reversals, careful analysis and risk management are key to using it effectively in real-world trading.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.