In fast-moving financial markets, recognising when a trend is about to reverse can give traders a crucial edge. Reversal indicators are essential tools that help traders anticipate these pivotal turning points, allowing for timely entries and exits that can protect profits and limit losses.
Whether you're trading stocks, forex, or commodities, understanding how to use reversal indicators can greatly enhance your trading strategy.
What Is a Reversal Indicator?
A reversal indicator is a technical analysis tool or pattern that signals a potential change in the direction of a market trend. Rather than following the current trend, reversal indicators aim to identify when a bullish trend may turn bearish, or when a bearish trend may shift to bullish. This early warning system allows traders to capitalise on new trends from the start, maximising profit potential and reducing risk exposure.
Reversal indicators come in many forms, including chart patterns, candlestick formations, and mathematical indicators. Each serves the same purpose: to provide evidence that the prevailing trend is losing momentum and a new trend may be emerging.
Why Are Reversal Indicators Important?
Spotting reversals early can be the difference between a winning and losing trade. By using reversal indicators, traders can:
Capture Trend Shifts Early: Enter new trends at optimal points for greater profit potential.
Reduce Risk: Exit positions before a trend reverses, protecting gains and limiting losses.
Avoid False Signals: Filter out market “noise” by relying on proven indicators rather than guesswork.
Improve Trading Discipline: Make informed decisions based on objective signals, not emotions.
Common Types of Reversal Indicators
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. Readings above 70 indicate overbought conditions (potential bearish reversal), while readings below 30 suggest oversold conditions (potential bullish reversal). Divergence between price action and RSI can also signal an impending reversal.
2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The MACD uses two moving averages to identify changes in trend momentum. A bullish reversal is signaled when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, while a bearish reversal is indicated when it crosses below. Watching for divergence between MACD and price action can further confirm reversal signals.
3. Stochastic Oscillator
This indicator compares a particular closing price to a range of its prices over a set period. Readings above 80 suggest overbought conditions, while readings below 20 indicate oversold. Crossovers between the %K and %D lines in these zones often signal potential reversals.
4. Candlestick Patterns
Certain candlestick formations, such as the hammer, doji, engulfing, and shooting star, are classic reversal signals. For example, a hammer at the end of a downtrend may indicate a bullish reversal, while a shooting star at the end of an uptrend could signal a bearish reversal.
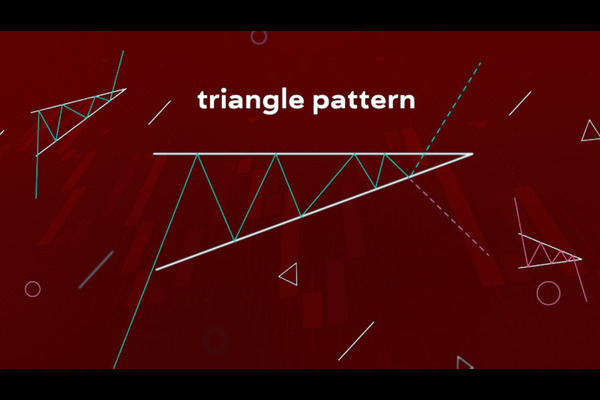
5. Chart Patterns
Patterns like the Head and Shoulders, Double Top, and Double Bottom are well-known reversal patterns. A Head and Shoulders pattern at the peak of an uptrend often signals a bearish reversal, while a Double Bottom after a downtrend can indicate a bullish reversal.
6. Volume Analysis
A spike in trading volume during a price move can confirm the strength of a reversal. For example, if a breakout from a reversal pattern is accompanied by high volume, the new trend is more likely to be sustained.
How to Use Reversal Indicators Effectively
1) Combine Multiple Signals
No single indicator is foolproof. The most successful traders combine several reversal indicators—such as RSI, MACD, and candlestick patterns—to confirm signals and reduce the likelihood of false positives.
2) Watch for Divergence
Divergence occurs when price action moves in the opposite direction of an indicator. For example, if prices are making new highs but the RSI is making lower highs, this negative divergence can signal a weakening trend and an impending reversal.
3) Confirm with Support and Resistance
Breaks of key support or resistance levels, especially when confirmed by reversal indicators, provide strong evidence of a trend change. Always pay attention to these critical price zones.
4) Use Proper Risk Management
Reversal trading can be highly rewarding but also risky due to the potential for false signals. Always use stop-loss orders and manage your position size to protect your capital.
Pros and Cons of Reversal Indicators
Pros:
Early identification of trend changes
Improved entry and exit timing
Can enhance profitability when used correctly
Cons:
Risk of false signals, especially in volatile markets
Requires confirmation from multiple sources
May not perform well in strongly trending markets
Practical Example
Imagine a stock in a steady uptrend. The RSI rises above 70 (overbought), and a bearish engulfing candlestick forms at a key resistance level. At the same time, the MACD line crosses below the signal line. These combined signals suggest a potential bearish reversal, prompting a trader to exit long positions or consider short trades.
Conclusion
Reversal indicators are powerful tools for traders seeking to capitalise on market turning points. By learning to read and combine these signals, you can make more informed trading decisions, manage risk, and enhance your overall strategy.
Remember, no indicator is perfect — always confirm signals and practice sound risk management.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.