Although people have seen the term IPO on the internet and are not unfamiliar with h it,But what exactly it is is vague to many. Those who are a little familiar with it will know that it is related to the IPO, but it is not possible to make it completely clear. For this reason, we will talk to you about the process and advantages of IPO listing.

What does IPO mean?
The full name is Initia Public Offering, which means Initial Public Offering, and refers to the first time a company makes its shares available to investors so that the company's shares can be listed and traded on a stock exchange. Through it, a company can raise money and make its shares available in the public market. This is usually an important step for a company to grow and expand its business or to increase its visibility.
When a company needs to grow and expand, especially when it needs money, there are so many ways to do it. One is to earn it on its own, but of course not every company earns enough money. The second way is to go to the bank and borrow money. Borrowing money comes with interest, and not every company can afford to pay it back.
So there is a third way, which is to raise money by selling some of the company's stock, which simply means asking someone for money. One way to do this is to tell people that you are a publicly traded company. Becoming a publicly traded company is a dream for many companies, and one of the most popular ways to do this is called an IPO.
The process of going public in an IPO is simply to first pick a stock exchange where you want to go public, such as NASDAQ in the United States. Then a counterpart investment bank has to be chosen as the underwriter. It is the one responsible for valuing and assisting in selling the stock, similar to a sale. After that, once the stock price is determined, marketing is done, such as roadshows, to increase the company's visibility through media hype. When the process is completed, you can get the financing funds.
It's worth noting that investment banks, as underwriters, have a big stake in this. There are also early investors, like venture capitalists and other organizations that raise money, who hold a lot of stock in their hands. Once a company completes its IPO and its shares go public, these organizations can cash in through the secondary market, the stock market.
A company planning an IPO usually starts its preparations months or even years in advance. This is because it needs to ensure that the management of financial information and internal processes, etc., are in line with the relevant rules of the stock exchange chosen for the listing. The company will prepare a prospectus based on the advice of a stockbroker, a Securities firm, or an investment bank engaged in listing business. The document will list all the details of the company, after which the company will announce the listing in newspapers or on the internet through an advisor.
Shares are usually sold to institutions such as pension funds, insurance companies, and investment funds. These institutions and investment banks may also underwrite these shares, meaning that the securities operators use their credibility in the securities market to sell the securities within the stipulated period of validity of the issue.
This means that these institutions agree to buy back all the shares that have not been sold during this period. Of course, the company's advisors will conduct sufficient research to set a price for the shares that will ensure that they can be sold so that the underwriters do not have to buy them again.
The company then lists the shares on a chosen exchange, which means that the company is also subject to wider public scrutiny and media attention. If the business is successful, the stock will appreciate in value, and all shareholders will receive a capital gain. Shareholders usually include company executives and start-ups, and sometimes employees, since they bought or acquired the stock in the initial public offering.
In the case of smaller companies, investors have little interest in buying and selling stock in that company. Then these stocks are considered illiquid, and thus the stock price falls. This is a risk that every public company has to take.
The three stages of IPO listing
| Stage |
Description |
Important StEPS |
| Preparation |
Company chooses IPO with underwriters and exchange. |
Select investment bank and exchange |
| Submission |
Prospectus is filed, awaiting review and approval |
File documents and wait for regulatory review |
| Listing |
Company's shares listed, entering public market. |
Initial transaction, company becomes listed |
What is the difference between an IPO and a listing?
They are two related but different concepts. An initial public offering refers to the process by which a company sells its shares publicly on a stock exchange for the first time. Prior to this, the company's shares were usually privately traded and held by only a few investors. By conducting an IPO, a company can offer its stock to the public in order to raise capital and increase the company's visibility. The process includes steps such as filing a prospectus, offering shares, and determining the offering price.
A listing means that the company's shares are officially listed and traded on the stock exchange. After listing, investors can trade on the exchange by buying and selling shares. After a company completes its initial public offering, it can apply for listing if its shares meet the listing requirements of the exchange. Listing makes it easier to circulate the company's shares and improves the company's transparency and ability to raise capital.
Overall, an IPO is a process, while listing is a state. A company achieves listing through an IPO, and once successfully listed, its shares can be listed and traded on the stock exchange.
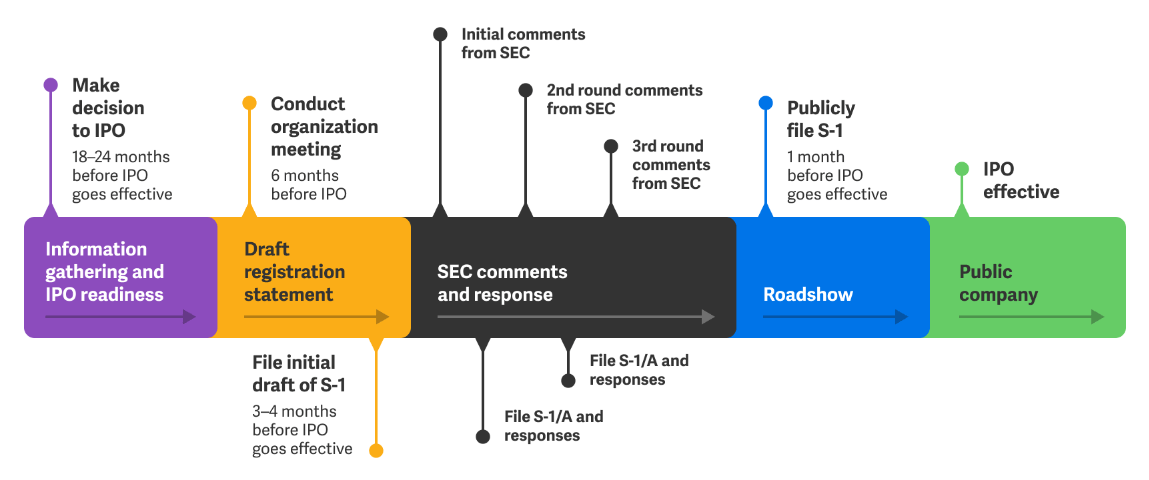 How long does it take from an IPO to a listing?
How long does it take from an IPO to a listing?
This time will vary depending on the company, market conditions, and regulatory procedures, and in general, the entire IPO process can take anywhere from a few months to a year.
The first step is during the preparation period, which takes several months. This is when the company needs to start preparing relevant documents, including financial statements, business plans, legal documents, etc. This includes, among other things, selecting underwriters and exchanges, which usually takes 1-2 months. The investment bank is chosen as the underwriter, and the stock exchange on which the listing will take place is chosen.
And to conduct due diligence and valuation, which takes 2-3 months. During this period, the company needs to conduct due diligence with the underwriters to determine the valuation of the company and the issue price.
Next is the application period, which also takes several months. Typically, it takes 2–3 months, during which the company needs to submit IPO application documents to the relevant securities regulators for review and further information. For example, filing a registration application with a regulator (e.g., SEC in the US), including detailed financial information and business operations.
Once again, there is a review period, which is anywhere from a few weeks to a few months. The securities regulator reviews the company's financials, business model, etc. and asks questions. The company needs to respond positively and may need to revise its documents. The regulator reviews the company's application for registration to ensure that the disclosures are adequate and compliant and ultimately approves the company for an initial public offering.
This is followed by the promotion phase, commonly referred to as a roadshow. This takes 1-2 months, during which the company markets with underwriters and conducts roadshows to attract investors. The shares are marketed to potential investors. Then comes the offering phase, which takes a few days to a few weeks. It is used to determine the final offering price, conduct the stock offering, and allocate the shares to investors. Determine the offering price and the number of shares to be allocated to investors.
Finally, there is the listing and trading, which is the first trading day of the company's stock. This is the day the company's stock is listed on the stock exchange, and investors can begin trading on the open market. Through the official listing on the stock exchange, the shares begin to be traded on the secondary market.
Overall, the entire process from IPO to listing can take anywhere from six months to a year, but the specifics will vary depending on the size of the company, market conditions, and regulatory procedures. This is the reason why many companies do not choose to go public in an IPO; it is indeed more time-consuming and labor-intensive, as well as expensive.
IPO Audit
This is when a company undergoes an audit process by a professional auditor to ensure the accuracy, compliance, and transparency of its financial statements prior to an IPO. This audit process is a key component in the preparation phase of an IPO and typically includes a financial statement audit, an internal control audit, a legal compliance audit, and a business compliance audit.
A financial statement audit is a comprehensive audit of a company's financial statements by the auditor to ensure that they truly and accurately reflect the company's financial position, performance, and cash flows. An internal control audit, on the other hand, refers to the auditor's assessment of the company's internal control system to ensure that it is effective in preventing errors and fraud and providing reliable financial reporting.
Legal compliance auditing is where the auditor assists the company to ensure that its business activities and financial reporting comply with relevant regulations and legal requirements and to guard against potential legal risks. Business compliance auditing, on the other hand, is to ensure that the company's business activities are in compliance with industry norms and relevant standards and to guard against possible operational risks.
The objective is to provide the company with an independently verified financial report, which increases investors' trust in the company and prompts more investors to participate in the IPO. It also helps to protect the rights and interests of public investors and ensure the health and transparency of the IPO market.
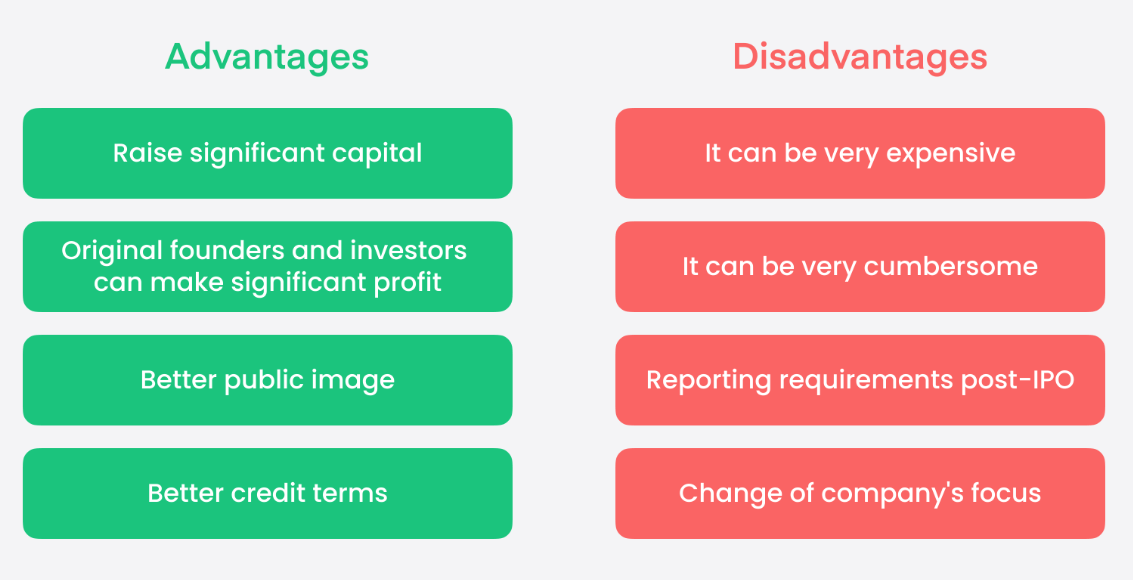 Advantages of an IPO
Advantages of an IPO
The advantage is that once a successful initial public offering is conducted, it can raise a large amount of capital. For example, Alibaba went public on the New York Stock Exchange in 2014 and raised over $20 billion. It also helps the company increase exposure and visibility, which naturally boosts future sales and earnings.
For investors, going public is the best way to buy stock in a company. It is difficult for everyone to buy company stock if the company is not listed. Therefore, an IPO listing is a win-win situation for both the company and the investors.
The downside is that when a company is listed on the stock exchange, it is subject to many rules from the regulators. The company has to publish all the financial information that may be favorable to its competitors. Additionally, the company conducting the IPO must perform well in front of the public, and if the market does not agree with the IPO price, this may result in the need to raise additional funds, causing the share price to fall.
Compared to other ways of going public, IPOs offer several advantages, such as scale of financing, public recognition, increased corporate valuation, and opportunities to cash in on equity.
Initial public offerings provide companies with a diversified means of financing and large-scale capital, which helps to support corporate expansion and growth. It is mainly used to raise large-scale capital by issuing shares to the public, which is then utilized for business expansion, research and development, and marketing.
It is also an opportunity for publicity and marketing, which can increase the visibility of the company and attract more investors and customers. And it enables the company's shares to be listed on the stock exchange, which increases the company's public recognition. Listed companies are more likely to attract the attention of investors and the media, which helps to build a brand image. Then present itself in the stock market to attract more investors and media attention, increasing the company's visibility and exposure.
The shares held by early investors and the founding team can be cashed out through stock trading after the stock market listing to realize the return on investment. This is an opportunity for the company's founders, angel investors, etc. to cash out. It is also possible to incentivize a portion of the equity of employees through stock options and other forms of incentives to increase employee loyalty and motivation and to attract and retain outstanding talent.
After listing, the Market Capitalization of the company will be determined by market forces, and investors will decide the price at which to buy shares based on the company's performance, prospects, and other factors. A successful listing helps to increase the valuation of the company, reflecting the market's recognition of the company's value and providing more favorable conditions for future financing.
The listing of a company's shares on the stock market allows them to be bought and sold in the secondary market, increasing the liquidity of the equity and making it easier for investors to buy and sell the company's shares. It also makes it easier for shareholders to liquidate their investments and provides employees with liquidity for shareholding awards.
A successful IPO is often seen as a symbol of a company's success in the market, helping to increase the company's market recognition and investor confidence. It will also increase the company's corporate reputation and transparency, which will help the company build stronger relationships with investors and partners.
Going public means that a company has passed regulatory scrutiny and meets the criteria for public trading, which can enhance the company's credibility and reputation in the eyes of investors and consumers. And it requires companies to follow more standardized and transparent financial and corporate governance standards, which can help improve corporate governance and enhance the sustainable development of enterprises.
An IPO is a strategic decision for enterprises that brings rich capital, increased visibility, market capitalization, and other benefits to the company and helps to promote the development and growth of the enterprise. However, on top of these benefits, there are some challenges and costs, and they are not applicable to all enterprises. Other listing routes, such as shell listing, Special Purpose Acquisition (SPAC), and direct listing, offer more flexibility.
IPO listing process steps
| Steps |
DESCRIPTION |
| Select underwriters and exchanges |
Identify investment banks and listing exchanges |
| Due diligence and material preparation |
Prepare IPO prospectus for financial transparency. |
| Prospectus Submission |
File with SEC and wait for review and approval |
| Roadshow and promotion |
Interact with investors and conduct marketing |
| Determine issue price and quantity |
Set IPO details based on market demand. |
| Listing and trading |
Company's shares commence trading on listing date. |
| Subsequent market operations |
Meet listing requirements, engage with stakeholders. |
| Ongoing operations and growth |
Maintain public presence, grow market capitalization. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 How long does it take from an IPO to a listing?
How long does it take from an IPO to a listing? Advantages of an IPO
Advantages of an IPO