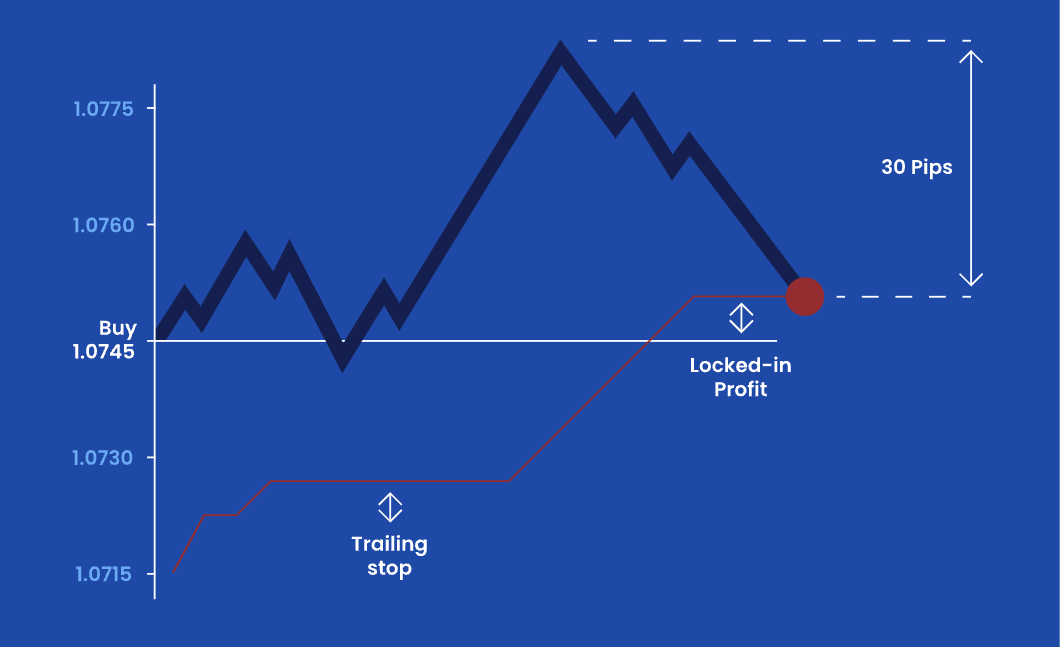
A trailing stop order is an essential tool for traders in the stock and forex markets. It allows traders to lock in profits while minimising downside risk by automatically adjusting the stop-loss level as the price moves in their favour.
Unlike standard stop-loss orders, which remain fixed at a predetermined price level, a trailing stop moves dynamically with the market. This flexibility helps traders capitalise on favourable price movements while ensuring positions are automatically exited if the market moves against them.
Understanding How a Trailing Stop Works

A trailing stop order functions by setting a predefined distance between the stop price and the current market price. As the price moves in the trader's favour, the stop-loss level moves accordingly, maintaining the specified distance. If the price reverses, the trailing stop remains at its last adjusted position and does not move back, ensuring that profits are preserved when the price change goes against the trade.
For example, in stock trading, if a trader sets a 5% trailing stop on a stock currently priced at $100, the initial stop-loss will be set at $95. If the stock price increases to $110, the stop-loss will adjust to $104.50 (5% below the new high). If the stock declines to $104.50, the position will be automatically sold, securing the profit. However, if the stock rises, the stop-loss will continue trailing at 5% below the highest price.
The same concept applies in the forex market. For example, a trader might set a 50-pip trailing stop for a currency pair, meaning the stop-loss moves 50 pips below the highest price reached after entry. If the price increases by 100 pips, the stop-loss moves up by 100 pips minus the 50-pip distance, ensuring that profits are locked in while allowing the trade to continue running as long as the trend remains favourable.
Setting Up a Trailing Stop Order in Stock Trading
When trading stocks, setting up a trailing stop order depends on factors such as volatility, trading strategy, and market conditions. Most brokerage platforms offer trailing stop order functionality, allowing traders to customise their stop parameters based on percentage or fixed price movement.
To set up a trailing stop order for stocks, traders determine the appropriate trailing stop distance first. This can be done using a percentage-based or fixed-dollar approach. A percentage-based trailing stop moves with the price at a set percentage, commonly between 5% and 15%, depending on the stock's volatility. A fixed-dollar trailing stop sets the stop-loss at a specific price difference, such as $2 or $5, which remains constant as the price fluctuates.
Highly volatile stocks require wider trailing stops to prevent premature stop-outs, while less volatile stocks can use tighter stops to capture profits efficiently. For example, if a stock historically experiences daily price swings of 3% to 5%, a trailing stop of 2% may be too tight, resulting in frequent stop-outs. A 7% to 10% trailing stop may be more appropriate, allowing the trade to stay active through normal fluctuations while still protecting profits in case of a sharp decline.
How to Use Trailing Stop Order for Forex Trading
In forex trading, traders used trailing stops to protect profits in highly liquid and volatile currency markets. Unlike stock markets, which have regular trading hours, forex markets operate 24 hours a day, making trailing stops an essential tool for traders who cannot monitor their trades constantly.
Setting up a trailing stop order in forex involves selecting the trailing stop distance based on pips, the smallest price movements in currency pairs. Traders can set their trailing stop in pips, percentage terms, or based on technical indicators such as the Average True Range (ATR).
To determine the ideal trailing stop distance, traders analyse the currency pair's volatility. Major pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD have lower volatility, allowing for tighter trailing stops, typically between 20 to 50 pips. Exotic pairs, which experience larger price swings, require wider stops, sometimes between 70 to 150 pips.
Forex brokers provide built-in trailing stop order options, where traders can specify the trailing stop distance when entering a trade. The stop-loss automatically adjusts as the price moves in favour of the trade. If a trader enters a long position on EUR/USD at 1.1200 and sets a 50-pip trailing stop, the stop-loss starts at 1.1150. If the price rises to 1.1300, the stop-loss moves to 1.1250. If the price drops to 1.1250, the trade is closed, securing a profit.
Pros and Cons of Trailing Stops
Despite trailing stop orders offering multiple advantages such as automated trade management, maximised profit potential and reduced emotional trading decisions, making them a preferred risk management tool for traders, improper use can lead to frequent stop-outs or missed profit opportunities.
Listed is a table providing a clear comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of trailing stops in trading.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Locks in profits automatically as the price moves in favor of the trade. |
Can trigger stop-outs too early if set too tight, especially in volatile markets. |
| Removes emotional decision-making by executing trades automatically. |
Ineffective in sideways or choppy markets, leading to frequent stop-loss triggers. |
| Maximises profit potential by allowing trades to run in strong trends. |
Trailing stop placement requires careful adjustment based on market conditions. |
| Works well in trending markets, ensuring traders capture extended moves. |
Does not protect against overnight gaps or sudden price spikes that may bypass the stop. |
| Reduces the need for constant monitoring, making it ideal for busy traders. |
May result in premature trade exits, missing out on larger potential gains. |
| Adaptable to various trading strategies, including short-term and long-term trading. |
Trailing stop settings can be complex, requiring experience to optimise for different assets. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up a trailing stop order for stocks and forex is a powerful way to lock in profits while limiting risk exposure. By dynamically adjusting to market movements, trailing stops help traders capture extended price trends without having to monitor their trades manually.
While trailing stops offer significant advantages in trend-following strategies, traders must also be aware of their limitations, including market gaps and choppy conditions.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.