The rising wedge pattern is a significant formation in technical analysis, often signalling potential bearish reversals in financial markets. Characterised by converging trend lines that slope upwards, this pattern reflects a period where the price makes higher highs and higher lows, but the narrowing price action suggests weakening momentum.
Traders and analysts monitor this formation closely, as it can provide insights into future price movements and potential trading opportunities. However, despite its effectiveness, there is potential for false signals.
Formation and Characteristics of the Rising Wedge Pattern
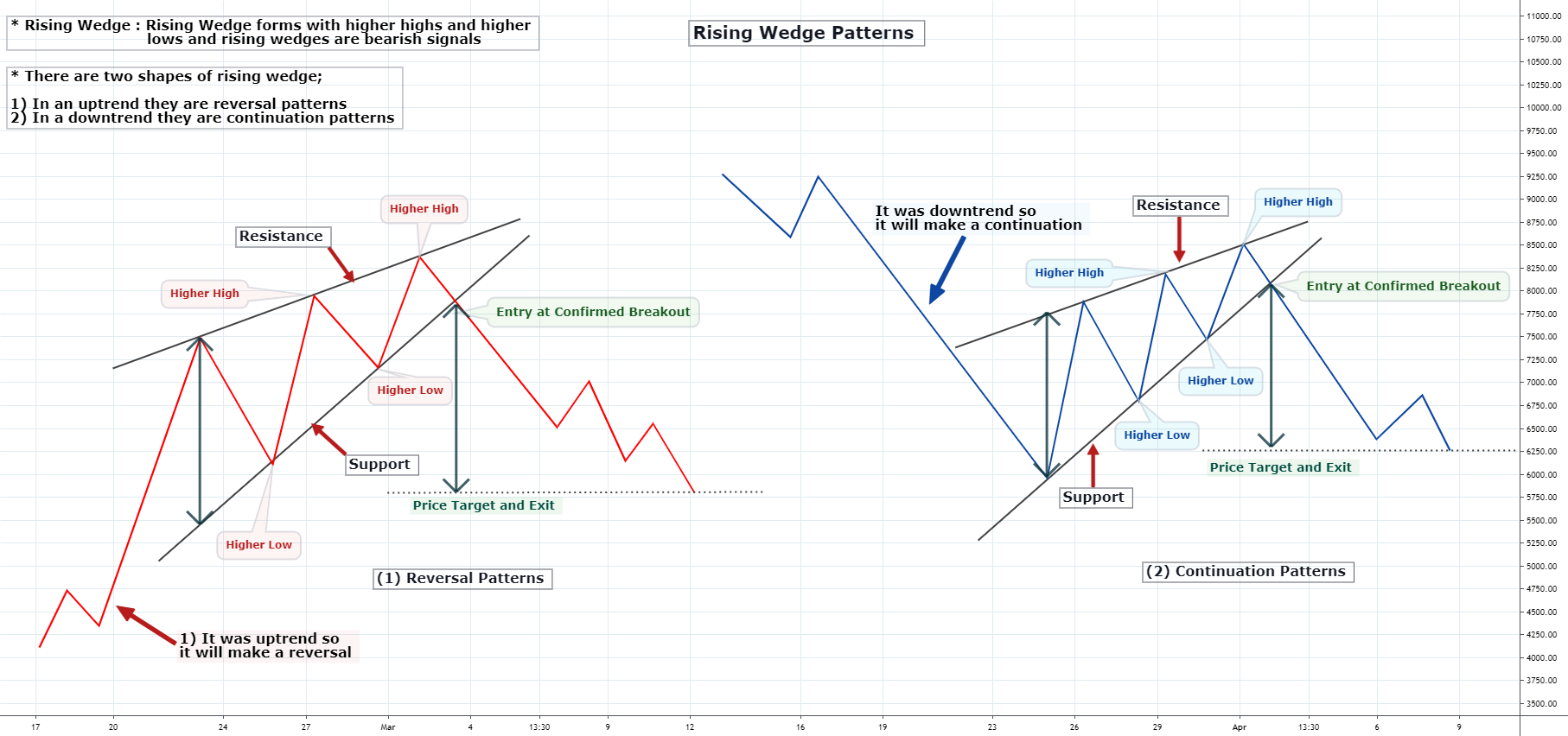
Before we get to its limit, let's understand the pattern's characteristics. Firstly, a rising wedge pattern emerges when the price of an asset consolidates between two ascending trendlines that converge over time.
The upper trendline represents resistance, connecting a series of higher highs, while the lower trendline signifies support, linking a series of higher lows. Notably, the slope of the support line is steeper than that of the resistance line, reflecting a gradual loss of upward momentum.
This pattern can develop over various timeframes, typically formed over three to six months. During its formation, trading volume often diminishes, suggesting weakening buying pressure. The convergence of the trendlines indicates that the price range is tightening, which may precede a breakout.
Implications of the Rising Wedge Pattern
The rising wedge is generally considered a bearish pattern, which implies that an upward trend is losing strength and may reverse downward upon breaking through the lower support line. This bearish reversal is anticipated because the narrowing price range, with declining volume, indicates diminishing buying interest.
Traders often interpret a break below the support line as a signal to enter short positions, aiming to capitalise on the expected price decline. However, it's crucial to recognise that while the rising wedge often suggests a bearish reversal, this is not always so.
For example, the price may break above the resistance line, continuing the upward trend. Such false signals can occur, underscoring the importance of confirming the breakout direction before trading decisions. Confirmation might involve waiting for a daily close beyond the trendline or observing an increase in volume accompanying the breakout.
Real-World Example
In July 2020, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) exhibited a classic rising wedge pattern, indicating a period of uncertainty in its stock price. The stock experienced rallies that met resistance and selloffs that found support, forming a wedge.
Technical analysis suggested a likely upward breakout, with an expected movement of approximately $20 per share, translating to a 37% change from its then-current price of $53. Investors awaited a definitive breakout before entering positions to capitalise on the anticipated significant movement.
Potential for False Signals
While the rising wedge is a valuable tool in technical analysis, it is not infallible and can sometimes produce false signals. A false breakout occurs when the price appears to break below the lower trend line, suggesting a bearish move, but then reverses direction and moves upward instead. Several factors contribute to these false signals:
Market Noise: Short-term price fluctuations and volatility can lead to misleading breakouts that do not reflect the underlying trend.
Subjectivity in Pattern Recognition: Identifying a rising wedge can be subjective, and slight variations in drawing trend lines may lead to different interpretations among traders.
Lack of Volume Confirmation: A breakout with low trading volume may lack the necessary momentum, increasing the likelihood of a false signal.
Trading Strategies to Mitigate False Signals
When trading the rising wedge pattern, several strategies can enhance the likelihood of success and mitigate false signals:
Confirmation of Breakout Direction: Before initiating a trade, confirm the breakout direction. A break below the support line, especially with increased volume, suggests a bearish reversal, while a break above the resistance line indicates a potential bullish continuation.
Volume Analysis: Monitor trading volume during the formation of the pattern. Decreasing volume often accompanies the pattern, and a breakout with a surge in volume can confirm the breakout's validity.
Risk Management: Implement stop-loss orders to manage potential losses. For a bearish breakout, place a stop-loss order just above the broken support line; for a bullish breakout, just below the broken resistance line.
Price Target Estimation: Estimate potential price targets by measuring the height of the wedge at its widest point and projecting this distance from the breakout point. This approach provides an approximate target for the ensuing price movement.
Rising Wedge Pattern vs Falling Wedge Pattern
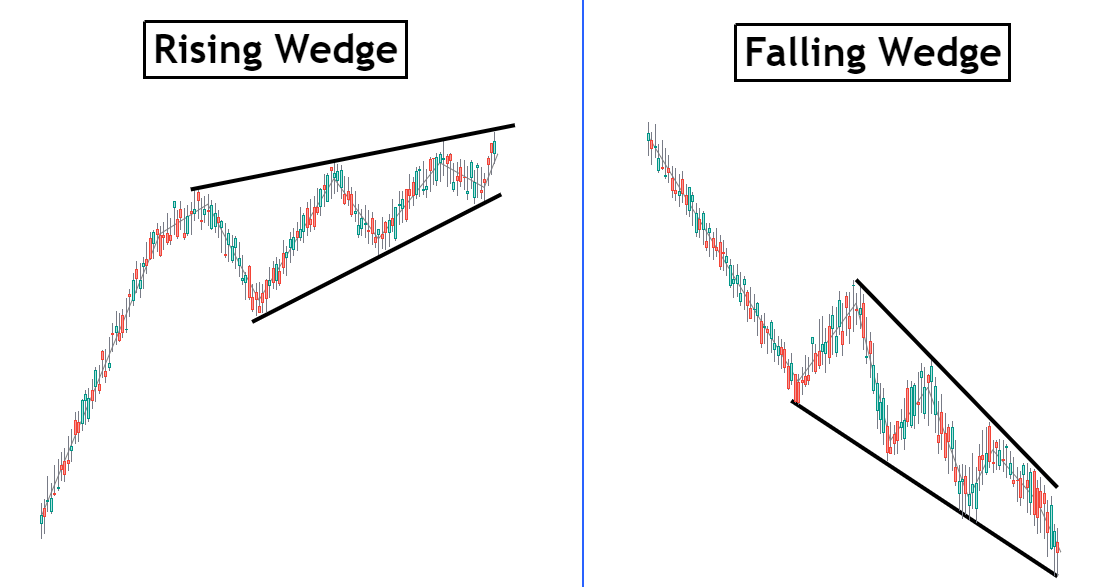
While both are wedge-shaped and signal potential breakouts, they point in opposite directions and occur under different market conditions.
For example, a rising wedge pattern forms when price action is confined between two upward-sloping trendlines that converge over time. It typically appears during uptrends and signals a loss of momentum, often leading to a bearish reversal. In this pattern, the support line (connecting higher lows) rises more steeply than the resistance line (connecting higher highs), reflecting weakening bullish momentum. Breakout usually occurs downward as volume fades and the trading range narrows.
In contrast, a falling wedge pattern forms between two downward-sloping trendlines that converge. It often develops during downtrends and signals a potential bullish reversal or continuation. The falling wedge shows that sellers are pushing prices lower but with decreasing conviction — evident in the slower decline of lower highs and lower lows. When the price breaks above the upper resistance line, especially with rising volume, it signals renewed buying interest and a possible trend reversal to the upside.
Moreover, the psychology behind each pattern differs. A rising wedge reveals growing hesitation among buyers, with the potential for bears to regain control. A falling wedge, on the other hand, signals that sellers are losing momentum, and buyers may soon drive a breakout.
Notably, both patterns can appear as continuation or reversal setups depending on their position in a trend. For example, a falling wedge within an uptrend is often a bullish continuation pattern, while the same pattern in a downtrend may mark a reversal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rising wedge pattern is pivotal in technical analysis, often signalling potential bearish reversals. However, the possibility of false signals necessitates careful analysis and confirmation before executing trades.
By seeking confirmation through decisive breakouts and increased volume, utilising complementary technical indicators, setting appropriate stop-loss orders, and analysing higher time frames, traders can enhance their ability to interpret and respond to rising wedge patterns better.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.