History is always strikingly similar! In order to promote economic exchanges between regions, in ancient times, Qin Shi Huang had the same railroads and coins, and now the countries in the euro zone use a unified currency. Unlike the dollar, which is considered the safest currency in the world, it is considered a risky investment by investors. However, this does not affect it since its birth immediately made it the world's second-most important currency. Since it is widely favored by investors, trading volume is very large. Why is this so? This article will focus on the special features of the euro.
Special Features of the Euro
The currency's symbol is the "€," designed by the European Monetary Union. In the standards of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the currency code usually consists of three letters in order to uniquely identify currencies on a global scale. The currency code is EUR, and there are 5 to 5007 banknote denominations.
Its history can be traced back to the 1992 Maastricht Treaty, which laid the foundation for the monetary and economic integration of the member states of the European Union (EU). At the same time, in order to promote its establishment, the European Monetary Union (EMU) was created.
In 1994. EU member states adopted a set of conditions known as the "Maastricht criteria," including the requirement for member states to meet certain inflation rates, debt levels, interest rates, and other economic indicators. These are the requirements for the founding members of the eurozone, whereby a monetary union was formed, sharing the same monetary policy.
In 1998. the European central bank (ECB) was established, headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany, to implement monetary policy in the region. On January 1. 1999. the currency was introduced as an e-money for non-cash transactions such as bank transfers and electronic payments. However, banknotes and coins were not officially introduced into circulation until 2002.
On January 1. 2002. its banknotes and coins officially began circulating in the region's member countries, gradually replacing the original national currencies. And as the only common currency legally in circulation, it is the common currency within the European Union, managed by the European Central Bank (ECB).
Over time, the region gradually expanded to include more member states. Initially, there were 11 member states, which later increased to 12.16. and now there are 19. These include Austria, Belgium, Femen, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Malta, Cyprus, Slovakia, Essanilla, Lasoviari, and Anglo-Australia.
In addition to these nineteen European Union countries, the currency is also used in the foreign territories of these member states, such as French Guiana, Thiénévang, and so on. In addition to this, there are four European microstates: Andorra, Monaco, the Vatican, and San Marino. These countries are not nominally members of the EU, but their neighboring countries are members of the EU, so for convenience, they also use the bill.
While the pre-Brexit UK used the pound sterling, Sweden and Denmark have adopted their own currencies as most of their domestic populations are not opting to join for the time being. However, outside of Europe, many special territories of EU member states also use it as their currency, such as the Kosovo region of Montenegro.
As of 2019. about 343 million people use the currency. More than 200 million people globally use the currency pegged to it, which is why the euro is said to be the second most traded currency in the world, after the US dollar. So although it is only twenty years old now, it holds an important place in the field of foreign exchange investment.
What was the lowest euro exchange rate
|
Convertible
|
Lowest
|
Supreme
|
Average
|
|
US Dollar
|
1.0723 |
1.1123 |
1.0918 |
|
Chinese Yuan
|
7.6792 |
7.9435 |
7.7982 |
|
Japanese yen
|
153.24 |
162.96 |
157.63 |
|
British Pound
|
0.8547 |
0.8699 |
0.862 |
|
Australian Dollar
|
1.6140 |
1.6609 |
1.6330 |
|
Canadian Dollar
|
1.4549 |
1.4950 |
1.467 |
|
Swiss Franc
|
0.9336 |
0.9658 |
0.9459 |
|
New Zealand Dollar
|
1.7379 |
1.8005 |
1.7572 |
Special Features of the Euro fundamentals
Its special feature is mainly that it is the common currency of 19 member countries because they share the same monetary policy and are all controlled by the European Central Bank (ECB), which is responsible for its implementation. Make its monetary policy decisions relatively consistent, unlike other countries that have independent monetary policy.
Therefore, the financial situation of some of the member states will also have an impact on the common currency. For example, countries with high debt levels and excessive fiscal deficits may raise investor concerns about the overall stability of the common currency.
It is also closely related to the economic integration of member countries in the region as well as to political stability among them. This is because of the relatively strong trade and financial links between member countries, which make the economies within the region interconnected. As a result, the performance of the currency is usually influenced by the state of the region's economy as a whole. At the same time, factors such as political events, election results, and government formation can have an impact on the currency, especially when political uncertainty increases.
There is also the fact that countries joining the region are required to meet a series of so-called "Maastricht criteria," which include conditions such as reasonable inflation rates, sound fiscal policies, and low inflation expectations. These criteria are designed to ensure that member countries have a relatively healthy economic base when introducing a common currency.
Something else to keep in mind is economic data, which in the Eurozone has a direct impact on the exchange rate of the common currency. These include gross domestic product (GDP), inflation, employment data, trade data, and more. Strong economic data is usually supportive of the currency, while a weakening economy could lead to its depreciation.
Meanwhile, the monetary policy of the European Central Bank (ECB) plays a key role in the movement of the common currency. The ECB's decisions and policy statements, especially regarding the level of interest rates and quantitative easing, as well as the regulation of the financial system, affect investors' expectations.
And as one of the global reserve currencies, its fundamentals are also of interest to international investors and central banks. Global economic and financial conditions have an impact on its international standing and performance. For example, a slowdown or acceleration in global economic growth may affect exports and imports in the common currency region, which in turn has an impact on the value of the currency.
The state of trade within the common currency region, as well as international relations with other countries and regions, may also have an impact on the value of its common currency. Trade surpluses or deficits and relations with major trading partners are important considerations. External factors, such as commodity price fluctuations, natural disasters, and public health events, may also have an impact on the fundamentals of the currency.
Geopolitical events and tensions may trigger demand for safe-haven assets and influence their movement. Investor sentiment and market expectations have an impact on the fundamentals of the currency. market sentiment can be influenced by a variety of factors, including volatility in the global financial markets, geopolitical tensions, and so on.
Overall, the fundamentals of the common currency are a complex combination of factors. Investors and analysts usually focus on these factors to assess the future movement of the currency.
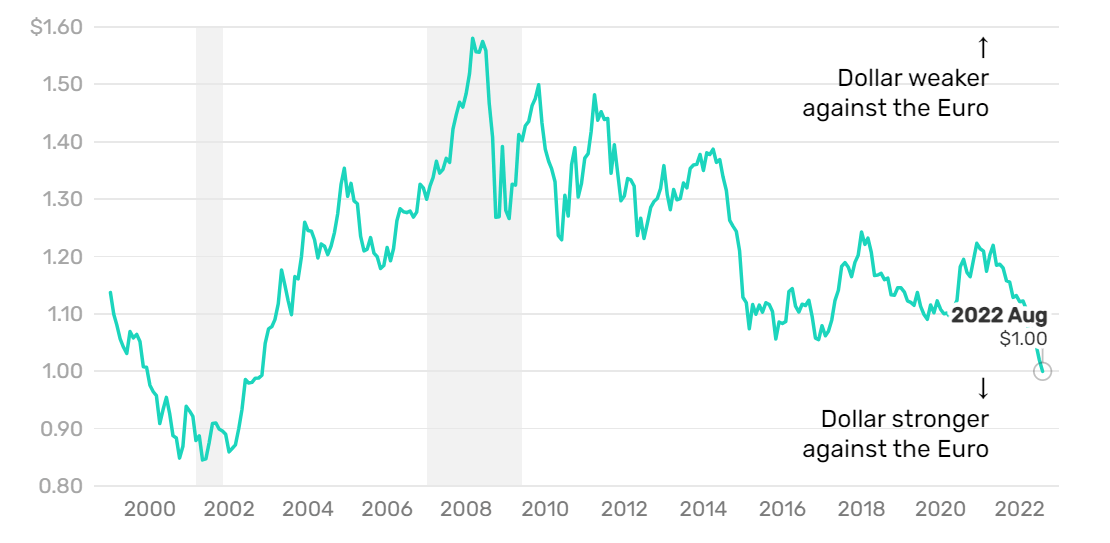
Special Features of Euro to Dollar
As the two most commonly used currencies, they are both reserve currencies among central banks around the world. As a result, the euro to dollar is the most popular and is currently the most traded currency in the global forex market. And its huge trading volume makes it difficult for individuals or institutions to manipulate it; trading is relatively fair and reliable. In addition, its exchange rate trend of short-term fluctuations is small, and occasionally there is a rule to follow, which is very conducive to investor judgment to protect earnings.
However, because its birth is built on the basis of the member states, any country in the region has economic and political turmoil that may affect the entire region's economic stability, and the same period of price fluctuations will also be affected. So in the eyes of investors, it is a currency with risky attributes. But the risk is often hidden in the high-yield opportunities, so it is still favored by investors.
As one of the most popular and active currency pairs on the Forex market, EUR/USD is unique in that it is traded on a daily basis in large volumes. This high liquidity makes it easier for traders to move in and out of the market, and the price fluctuations at the time of the transaction are relatively small.
Moreover, they are considered to be one of the major currency pairs, and their exchange rates directly reflect the relative strengths and weaknesses of the two economies, the Eurozone and the United States. Because it involves two of the world's largest economies, this pair has attracted a lot of attention from investors around the world. And since both are among the world's major reserve currencies, their trading is influenced by the global status of both. Any change in one of the two usually causes volatility in global markets, which in turn affects the pair.
The European Central Bank and the Federal Reserve are responsible for the monetary policies of the two currencies' respective countries, and the decisions of the two central banks have a direct impact on their exchange rate fluctuations. For example, interest rate decisions and the direction of monetary policy will trigger the market's interest in buying and selling this currency pair. And it will also be directly affected by the macroeconomic indicators of the two countries and regions, including GDP growth rates, inflation rates, employment data, etc. Investors closely monitor these indicators for information on the health of both economies.
Performance between them is closely linked to global risk appetite. When market risk appetite is high, investors may be inclined to buy high-yielding currencies. And when market risk appetite is lower, they may prefer to buy the relatively safer U.S. dollar. This will have a direct impact on the exchange rate between the two, and market risk pressures may cause EUR/USD to fall.
Geopolitical events and tensions may also have an impact on this currency pair. For example, geopolitical tensions, political uncertainty, and trade disputes between the U.S. and Europe could trigger risk concerns in the market, which in turn could affect the performance of this currency pair.
Overall, these characteristics of the euro on the forex market are attracting more and more investors. Novice traders can also try their hand at forex investing in EUR/USD. Being one of the world's five largest currencies and being favored by forex investors at the same time proves that its influence on the world cannot be ignored. But the link between countries is inextricably linked; smart investors need to pay attention to the new changes between the currencies of the countries and learn to pull the cocoon from the changes in order to provide favorable judgment for their own investment.
Euro To Dollar Forecast 2024
|
MONTH
|
OPEN
|
LOW-HIGH
|
CLOSE
|
|
January
|
1.229 |
1.179–1.229 |
1.197 |
|
February
|
1.197 |
1.196–1.232 |
1.214 |
|
March
|
1.214 |
1.214–1.267 |
1.248 |
|
April
|
1.248 |
1.248–1.304 |
1.285 |
|
May
|
1.285 |
1.277–1.315 |
1.296 |
|
June
|
1.296 |
1.244–1.296 |
1.263 |
|
July
|
1.263 |
1.223–1.263 |
1.242 |
|
August
|
1.242 |
1.193–1.242 |
1.211 |
|
September
|
1.211 |
1.164–1.211 |
1.182 |
|
October
|
1.182 |
1.182–1.221 |
1.203 |
|
November
|
1.203 |
1.149–1.203 |
1.167 |
|
December
|
1.167 |
1.134–1.168 |
1.151 |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.