In the dynamic world of forex trading, managing risk is paramount. Forex hedging, a strategy traders use to offset potential losses, is crucial in safeguarding investments against adverse market movements.
For context, while forex trading offers lucrative opportunities, it also comes with inherent risks due to the volatile nature of currency markets. To navigate these uncertainties, traders employ hedging strategies like direct hedging, multiple currency hedging, forward contracts and more.
What Is Forex Hedging?

At its core, forex hedging involves opening one or more positions to offset the potential losses of an existing position. This means that if the market moves against the original trade, the hedge; whether it's a direct offsetting position or a related currency trade — can limit or balance out the loss.
Hedging is not about maximising profits but reducing risk exposure, stabilising potential outcomes, and preserving capital during periods of volatility or uncertainty.
Remember: While hedging doesn't eliminate risk, it serves as a buffer, reducing the impact of adverse price movements.
When to Hedge in Forex Trading
Hedging isn't meant to be used constantly but strategically during certain market conditions or trading scenarios where risk exposure needs to be minimised. One of the most common situations to consider hedging is during heightened market volatility. It could be due to massive economic announcements like interest rate decisions, non-farm payroll reports, or geopolitical events that could cause sharp and unpredictable movements in currency pairs.
Traders also hedge when managing long-term positions and want to protect profits or limit losses without closing their trades prematurely. For example, if a trader holds a profitable long position on GBP/USD but anticipates short-term market weakness, they might hedge by opening a temporary short position. Doing so will protect against a pullback while maintaining their original investment thesis.
Another time to hedge is when there is uncertainty in correlated currency pairs or when a trader is exposed to multiple positions involving the same base or quote currency. In such cases, a hedge can act as a buffer, preventing a significant loss across all open trades due to one unexpected currency move.
Hedging is also appropriate when traders deal with large position sizes, where even a small price movement can result in significant losses. In these cases, hedging becomes a tool for financial insurance, ensuring that adverse moves don't completely wipe out gains or capital.
5 Simple Forex Hedging Strategies Traders Should Know
1) Direct Hedging
Direct hedging, also known as simple hedging, is one of the most straightforward approaches. It entails opening a position opposite an existing trade on the same currency pair. For instance, if a trader holds a long position on EUR/USD, they might open a short position of equal size on the same pair.
This strategy locks in profits or losses, providing a safety net against market volatility. However, not all brokers permit direct hedging, so traders should verify this capability with their chosen platform.
2) Multiple Currency Hedging
This strategy involves taking positions in correlated currency pairs. For example, if a trader is long on GBP/USD and wants to hedge against potential losses, they might take a short position on EUR/USD, assuming a positive correlation between the two pairs.
By doing so, adverse movements in one pair may be counterbalanced by favourable movements in the other. However, this method requires a deep understanding of currency correlations and market dynamics.
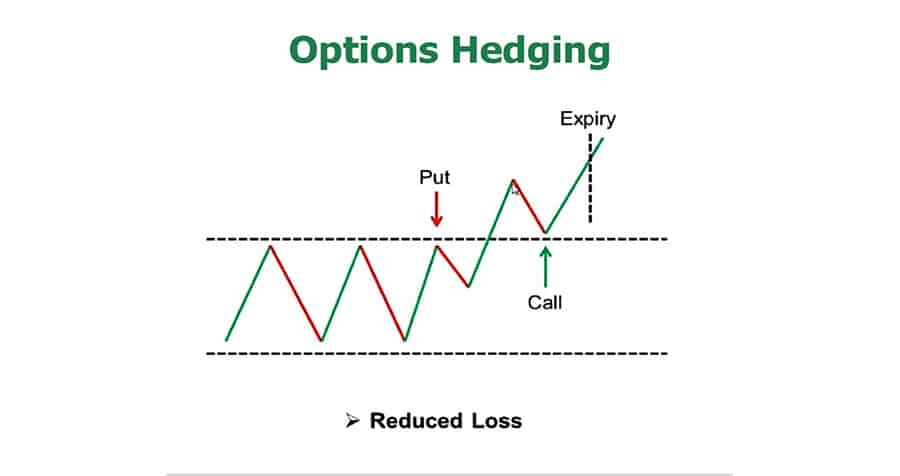
3) Using Options for Hedging
Options allow traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price within a specific timeframe. By purchasing put options, traders can hedge against potential declines in currency value, while call options can protect against increases.
Options offer flexibility, allowing traders to manage risk without committing to a position unless it's favourable. However, options come with premiums, which are costs that traders must consider when employing this strategy.
4) Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell a currency at a specified rate on a future date. These contracts are customisable, allowing traders to tailor the amount and settlement date to their specific needs.
By locking in exchange rates, forward contracts provide certainty, shielding traders from unfavourable market movements. However, they also require a commitment to the agreed-upon rate, which might be disadvantageous if the market moves favourably.
5) Stop-Loss Orders
While not a hedging strategy in the traditional sense, stop-loss orders serve as an essential risk management tool. By setting a predetermined exit point, traders can limit potential losses on a trade. This method ensures that losses are contained, even in volatile market conditions.
Is Forex Hedging Legal?
As for legality, forex hedging is entirely legal in most parts of the world. Countries like the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, and many members of the European Union allow various forms of hedging and even support it through advanced trading platforms and tools.
However, in the United States, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA) have placed certain restrictions on hedging practices — particularly within retail forex accounts. For example, direct hedging, where a trader holds long and short positions on the same currency pair simultaneously, is generally prohibited in the U.S. Instead, U.S. brokers follow a "first in, first out" (FIFO) rule, which requires traders to close the oldest positions first.
Despite regional differences in regulation, forex hedging remains a globally accepted and commonly used risk management strategy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective forex hedging requires a clear understanding of one's exposure and risk tolerance. Traders should assess their positions, determine potential risks, and choose appropriate hedging instruments.
By employing direct hedging, multiple currency hedging, options, and forward contracts, traders can safeguard their investments against market volatility. While hedging doesn't guarantee profits, it provides a structured approach to managing potential losses, ensuring long-term trading success.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.