With the substantial upward trend in the prices of gold and silver, people are becoming more and more enthusiastic about investing in Precious metals. Although most investors value the value-preserving attributes of precious metals, that is, the choice of physical holding investment, But according to the data, the choice of non-physical holding investors is greater. Among other things, the trading market for paper silver has seen a substantial increase because silver has seen its first breakout in nearly two decades. Now, let's take a look at the risks and rewards of paper silver.

What does paper silver mean?
It usually refers to silver that is traded in the form of financial instruments rather than actual physical silver. Investors buy and sell these financial products to participate in the silver market and try to earn a return on their investment without having to hold or deliver physical silver directly. This form of investment is usually more flexible and convenient, and trading is more liquid, allowing investors to buy and sell at any time.
When investing in silver, there are two broad directions to choose from: physical silver or paper silver. Physical silver investments are generally used as a means of preserving value and will have the same preservation as well as higher costs if used for investment. Therefore, as a non-physical silver trade, it came into being.
Compared to physical silver, it is more convenient and flexible, and investors can trade through stock exchanges, trading platforms, or financial institutions without having to physically hold and store physical silver. This makes it easier for investors to participate in the silver market and trade in a timely manner according to market changes, while also reducing the custodial and security risks associated with holding physical silver.
Moreover, paper silver trading is more liquid in comparison. Investors can buy and sell at any time during the trading day without the limitations of buying and selling physical silver or access time restrictions. This means that investors can adjust their investment strategies more quickly to market changes and enter or exit the market as soon as they need to, resulting in greater flexibility in managing their investment portfolios.
At the same time, its prices are more transparent and open because they are influenced by market supply and demand and exchange rules. Investors have easier access to price information, and the real-time quotes and market-depth information provided by the exchanges enable them to make more accurate trading decisions.
By investing in paper silver, investors can more easily diversify their assets. They can allocate their funds to different types of investments, including stocks, bonds, real estate, etc., thereby reducing the overall risk of their investment portfolios. This diversification strategy helps investors maintain a more stable investment return during market volatility and reduces the impact of a single asset or sector's risk on the portfolio.
And it also allows investors to trade with leverage, which can magnify an investor's investment returns. Through leveraged trading, investors can control larger positions with smaller amounts of capital, resulting in greater returns during market volatility. Of course, it should be noted that this also increases the risk of investment losses.
Paper silver also contains a wide variety of trading options, including silver futures, silver options, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and Securities, which investors purchase to profit or take risks. The liquidity of these products in the market is usually higher, allowing investors more flexibility in their buying and selling operations.
One such product, silver futures, is a standardized contract that allows an investor to buy or sell a certain amount of silver at a price at a specific point in time in the future. This can be traded through futures exchanges. An investor can buy or sell silver at an agreed price at an agreed time in the future through a futures contract. Futures trading usually requires the payment of a margin and bears the risk of delivery at the expiration of the contract.
Silver options, as a financial derivative, provide the buyer with the right, rather than the obligation, to buy or sell silver at an agreed price at a specific time in the future. This means that the buyer can participate in the silver market at a lower cost and profit from price fluctuations.
A silver ETF (exchange-traded fund) is a fund traded through a stock exchange with silver as the underlying asset. It is designed to track movements in the price of silver, thereby allowing investors to capture the performance of the silver market by purchasing shares of the ETF without having to hold physical silver directly.
Silver securities may include stocks, bonds, or other financial assets related to silver. These assets may include stocks related to silver mining companies or other businesses associated with the production, mining, processing, trading, etc. of silver. Investors can indirectly participate in the silver market by purchasing these stocks, thereby earning a return on their investment related to fluctuations in the price of silver.
A silver futures options portfolio strategy is an investment strategy that combines silver futures contracts and options contracts to capitalize on fluctuations in the price of silver. This strategy usually involves buying or selling both silver futures contracts and options contracts to hedge or profit from different scenarios in the market.
Investing in paper silver is more flexible and convenient than holding physical silver outright, and it offers greater liquidity and trading transparency. It is also more diversified, allowing investors to make better portfolio decisions. However, investors also need to be aware that there are some risks associated with it, such as market volatility, liquidity risk, and the risk of manipulation by hedge funds and financial institutions.
Is paper silver safe?
As a matter of fact, silver has a high industrial value and is in high demand in the market. However, compared to its demand, its price has been highly suppressed. This has led many to suspect that the price of silver has been manipulated, and as a result, the price of silver is more volatile and risky, and as a result, the safety of paper silver is also questionable.
Therefore, when investing, one must be careful of the risk of price manipulation. Certain financial institutions may use high-frequency trading and misrepresentation of trades to manipulate the price of their products, thus affecting the fairness of the market. Such behavior may result in investors not being able to access fair market prices, which in turn may result in investment losses.
In addition to this, its price is affected by a variety of factors, including supply and demand, economic data, and geopolitical situations. Changes in these factors may lead to market volatility, which in turn affects the price, leading to capital losses. Investors should pay close attention to these factors and consider their impact when making investment decisions in order to minimize investment risks.
Certain products may also involve transactions with financial institutions, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or silver derivatives. When choosing to invest in these products, investors should assess the creditworthiness and stability of the financial institution to ensure the safety of their investment. Choose a financial institution with a good reputation and regulatory compliance to minimize investment risk.
It also has the important risk of being exposed to illiquidity, which means that investors may experience difficulties in buying and selling contracts or securities when market demand falls or prices fluctuate sharply. Because buy-and-sell orders in the market become scarce, counterparties may become rare. This may result in investors not being able to sell their holdings of contracts or securities in a timely manner or only being able to trade at undesirable prices.
Then there are management fees and rollover risks to be wary of. Management fees are fees that investors pay to hold a product, usually at a percentage less than the amount invested. And futures-based ETFs may involve regular contract rollover operations, which may result in additional transaction costs and may cause losses if not done properly.
Finally, exchange risk is also a major concern. Since such products are usually not secured by actual silver but in the form of a financial instrument, investors may face difficulties in exchange and incur losses under extreme circumstances, such as a financial crisis or currency reset. This may occur when an investor attempts to convert the product to physical silver, and due to market volatility or problems with the financial institution, the investor may not be able to convert the product to physical silver in a timely manner or at all.
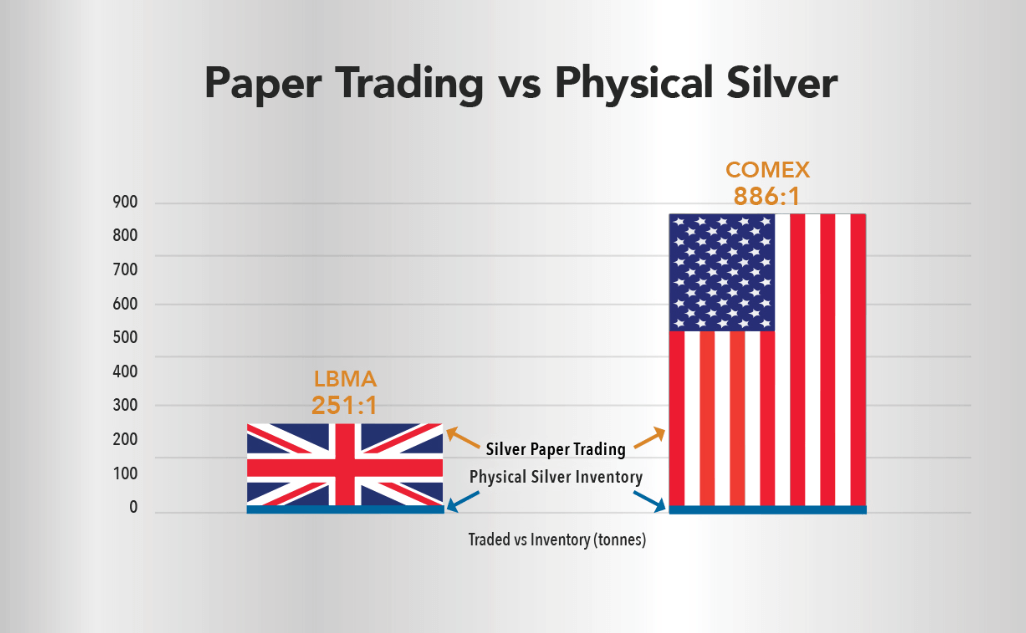
After all, as of today's data, the paper silver market is two to three hundred times larger than the physical silver market. As shown in the chart above, this ratio illustrates the enormous leverage and speculative nature of the market. That is to say that the amount of physical silver actually traded in that market far exceeds the amount of physical silver that actually exists.
This situation leads to dramatic price fluctuations in the market, as it is traded more by speculators and financial institutions than by actual supply and demand. This also increases the instability of the market and exposes investors to greater risk.
Different types of products also have different risk characteristics. For example, trading in silver futures and options is typically riskier because they are derivatives with higher price volatility that can lead to larger losses. In contrast, investing in silver ETFs or silver securities may be relatively stable, but there is still market risk.
In summary, investing in paper silver requires caution with respect to the various risks involved and ensuring that the market is well understood. At the same time, the robustness of the investment portfolio can be improved by diversifying the portfolio, including considering physical investments such as physical gold and silver. By balancing different types of assets, investors can better withstand market volatility, reduce overall investment risk, and achieve long-term investment goals.

Can paper silver make money?
If you hold physical silver, as long as you hold it for a long period of time, you will be able to preserve its value. Then the investors who choose paper silver can get profits in more ways. Generally speaking, a common trading strategy in futures trading is to rely on buying up and selling down to make a profit.
This means making a profit by buying contracts that are priced lower than the expected future price and then selling them when the price rises, or by selling contracts that are priced higher than the expected future price and then buying them back when the price falls. This way of taking advantage of market price fluctuations to make a profit is known as arbitrage trading, which involves buying a low-priced contract or selling a high-priced contract.
For example, the same long-term investment strategy would be to buy paper silver when the price is low, hold it for a long period of time and wait patiently for the market to move, and then sell it when the price has risen to a satisfactory level, which would result in a higher profit. This strategy usually requires patience and conviction, as market volatility can cause prices to fluctuate for long periods of time.
Short-term traders, on the other hand, are usually more concerned with short-term market fluctuations and therefore use methods such as technical and fundamental analysis to find trading opportunities. technical analysis focuses on Chart Patterns and trends in market data such as price movements and trading volumes, as well as the use of various technical indicators to predict future price movements.
Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, focuses more on the impact of economic data, supply and demand, and geopolitical factors on the market, as well as the fundamental value of silver, in order to determine long-term trends and changes in price. Utilizing a combination of these analytical methods, short-term traders can more accurately time their trades and adopt appropriate trading strategies to capture profits.
In fact, whether the price of silver is rising or falling, investors can use fundamental analysis to determine future trends and adopt trading strategies accordingly. By studying factors such as supply and demand, economic data, and geopolitical situations, investors can more accurately grasp market movements and price trends.
Some Trading Products also allow investors to trade with leverage, thereby magnifying investment gains or losses. Through the moderate use of leverage, investors can trade on a much larger scale based on small amounts of capital, thus gaining higher profits. Of course, leveraged trading can amplify investment profits, but it likewise increases investment risk. If the market moves against expectations, leveraged trading can lead to larger losses.
Different trading platforms or products may have different transaction fees and implied costs, which can have an impact on investment profitability. Investors should pay particular attention to transaction costs when choosing a trading platform, including trading commissions, fees, and position costs. In addition, it is important to consider implied costs, such as trade execution prices, slippage, and interest on positions, which can also have an impact on investment profitability.
To minimize trading costs, investors can choose low-cost trading platforms or products and try to avoid frequent trading. Costs can also be reduced by choosing appropriate trading hours and trading strategies, such as avoiding trading during periods of high volatility and adopting long-term holding strategies. A comprehensive consideration of transaction fees and implied costs can help investors increase their profitability.
Investing in paper silver has the potential to make money, but it also carries a certain amount of risk. Like any investment, it is exposed to various risk factors, such as market volatility, price risk, liquidity risk, and so on. Therefore, when deciding whether or not to invest, investors need to fully understand the market situation, formulate appropriate investment strategies, and strictly control risks.
Risks and Rewards of Paper Silver
| Types of risk |
Description |
Type of return |
Description |
| Price volatility |
Price volatility due to market changes |
Price Increase |
Buy low, sell high in a rising market. |
| Liquidity |
A market demand drop hinders trading. |
Long-term holding |
Hold long-term, sell on price rise. |
| Exchange |
A financial crisis hinders trade. |
Short-term trading |
Spot volatility using analysis techniques. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.