Options trading can first seem complicated, but mastering strategies like the butterfly spread can offer traders a smart way to manage risk while targeting profits in stable markets. Butterfly spreads are designed to capitalise on stocks expected to have little volatility, making them ideal for traders looking for limited-risk, limited-reward scenarios.
It is an advanced strategy often recommended for those who have moved beyond basic calls and puts and want to optimise for limited risk and potentially decent returns.
Therefore, understanding how butterfly spreads work and when to use and manage them is crucial for beginners to build a solid foundation in options trading.
What Is a Butterfly Spread?
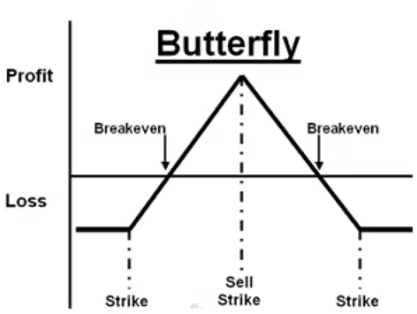
A butterfly spread is a neutral options strategy combining bull and bear spreads. It is created using three different strike prices, all within the same expiration date, and can be set up with either call or put options.
It is constructed by simultaneously buying and selling multiple options contracts with different strike prices but the same expiration date.
The "wings" of the butterfly represent the outer strikes, while the "body" represents the middle strike. A classic butterfly spread involves three different strike prices, and it's often structured with either calls or puts, although call butterflies are more common among beginners.
This strategy limits both potential profit and potential loss, making it particularly attractive to beginners who prefer defined outcomes.
Components
As mentioned, a basic butterfly spread with calls involves:
Buying one in-the-money call (lower strike price)
Selling two at-the-money calls (middle strike price)
Buying one out-of-the-money call (higher strike price)
The distance between each strike price is usually the same, creating the symmetrical "butterfly" shape on a profit and loss chart.
Types
1. Long Butterfly Spread
It is the traditional butterfly setup where you buy the wings and sell the body. It is suitable when expecting low volatility and minimal movement in the stock price.
2. Short Butterfly Spread
In the short butterfly, you sell the wings and buy two middle strikes. This strategy profits if there is a significant movement from the middle strike price. However, it carries a higher risk and is less popular among beginners.
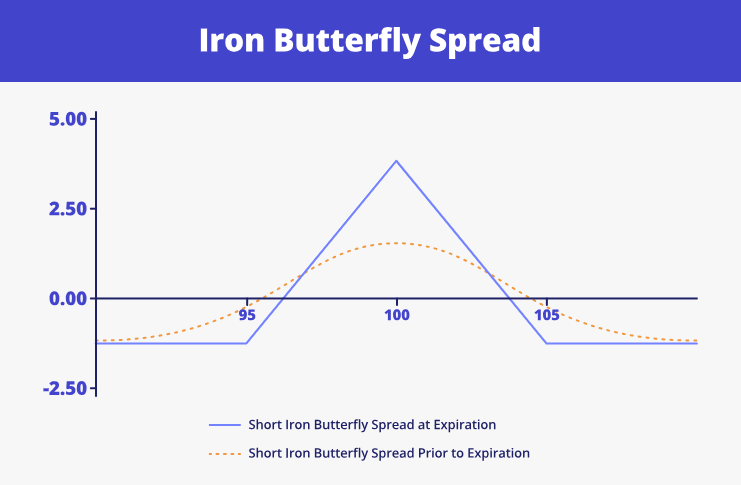
3. Iron Butterfly Spread
An iron butterfly uses both calls and puts. It involves selling an at-the-money call and put while buying an out-of-the-money call and put. The iron butterfly is also neutral but provides more flexibility in risk management.
How a Butterfly Spread Works and Ideal Condition
To set up a standard butterfly spread, you need to:
Buy one option at a lower strike price (higher premium)
Sell two options at a middle strike price (collect premiums)
Buy one option at a higher strike price (lower premium)
All options must have the same expiration date.
The cost to enter the butterfly spread is called the net debit. This net debit is also the maximum possible loss. The maximum profit occurs if the underlying security closes precisely at the middle strike price on expiration.
Ideal Condition
Butterfly spreads work best when:
The trader expects minimal movement in the underlying asset.
Implied volatility will fall.
The trader seeks a defined risk-reward structure.
They are often used ahead of earnings announcements or massive news events when a trader believes the actual impact will be lesser than the market anticipates.
Additionally, butterfly spreads can be attractive when volatility is overpriced, allowing traders to collect rich premiums through the two short positions.
Example
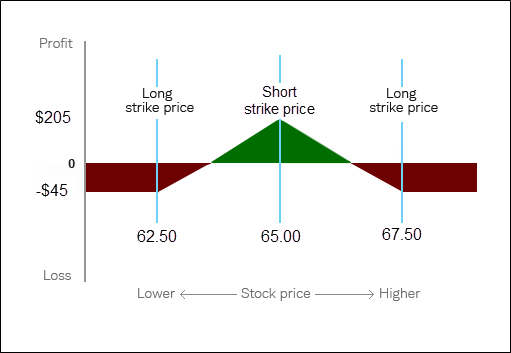
Suppose stock XYZ is trading at $100, and you expect it to remain relatively stable over the next month.
You could set up a butterfly spread like this:
The total cost (net debit) = $7 + $2 - $8 = $1
Thus, the maximum loss is $100 (since 1 contract controls 100 shares), and the maximum gain is $400 if the stock closes precisely at $100 on expiration.
This real-world example highlights how butterfly spreads require minimal capital and offer a high reward-to-risk ratio if conditions are favourable.
Tips for Beginners
To maximise the potential of butterfly spreads, beginners should follow a few best practices:
1) Start with Paper Trading
Before committing real money, practice setting up butterfly spreads on a virtual trading platform. This helps build familiarity with the strategy without financial risk.
2) Choose Stocks with Low Volatility
Butterfly spreads work best when underlying assets are not expected to move much. Look for stocks or ETFs with low implied volatility or those trading in tight ranges.
3) Watch Out for Commissions
Butterfly spreads involve multiple legs, which means more commissions and fees. Select low-cost or commission-free broker options trading for maximum returns.
4) Focus on Liquid Markets
Liquidity is critical for entering and exiting butterfly spreads at favourable prices. Reduce slippage with well-traded options and tight bid-ask spreads.
5) Understand the Greeks
Butterfly spreads are particularly sensitive to gamma and theta. Understanding how delta, gamma, theta, and vega affect your position can help you make better decisions.
6) Use Narrow Strike Widths Initially
Choose narrower strike intervals (like $5 apart rather than $10) to limit risk. As you gain experience, you can experiment with wider spreads.
Benefits and Risks
The butterfly spread has many advantages, especially for traders looking to manage risk while debating where a stock might settle.
Defined Risk: The maximum risk is limited to the initial premium paid, making it an attractive strategy for beginners who want to control downside exposure.
Defined Reward: You know your maximum profit potential from the start.
Low Capital Requirement: Since risk and reward are capped, the margin and capital requirements are much lower than options positions.
Best for Low Volatility: Butterfly spreads can deliver solid returns if you can correctly predict minimal movement in the underlying asset.
Flexibility: The strategy can be adapted with different widths between strike prices depending on how much you want to risk or reward.
Limitations
Despite its advantages, the butterfly spread is not foolproof. It has several risks and limitations traders must be aware of.
Time Decay Sensitivity: The strategy benefits from time decay only when close to expiration. Early in the trade, movements against the middle strike can harm your position.
Volatility Risks: Unexpected increases in volatility can widen trading ranges and push the stock price out of the profitable zone.
Precise Target Required: The closer the final price is to the middle strike, the higher the profit. Significant moves away from this price lead to losses.
Complexity for Beginners: Although the risk is limited, setting up the butterfly spread correctly requires understanding options pricing and execution nuances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the butterfly spread is an excellent options trading strategy for those seeking defined risk and reward. It offers attractive returns if you can correctly predict minimal movement in the underlying asset's price. However, it requires careful planning, understanding of volatility, and precise execution.
Beginners who take the time to master butterfly spreads can add a powerful tool to their trading arsenal. Practising in a simulated environment, starting with highly liquid assets, and maintaining disciplined risk management are all keys to success.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.









