Sometimes in the stock market, less is more—and that's exactly the idea behind a reverse stock split. Instead of creating new shares, companies combine existing ones to lift the share price. It's a move that can confuse even experienced traders at first glance, but understanding how it works can make a real difference to how you view a company's future prospects.
Definition and Basic Concept of Reverse Stock Split
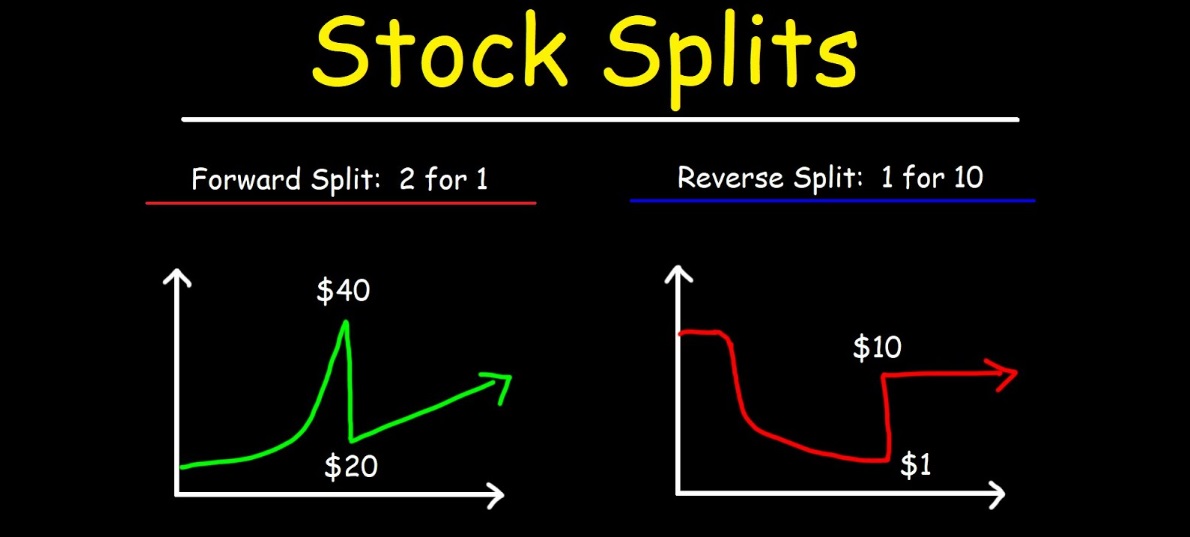
At its core, a reverse stock split is exactly what it sounds like—a stock split, but in reverse. In a regular stock split, companies issue more shares to existing shareholders, usually to lower the stock price and make it more accessible. However, with a reverse stock split, the company consolidates its shares, reducing the number of outstanding shares but increasing the price per share. It's a bit like exchanging several small coins for one larger coin—while the overall value stays the same, the way you see it changes.
For example, in a 1-for-10 reverse stock split, a shareholder with 100 shares at £1 each would end up with 10 shares, each priced at £10. Importantly, the total value remains the same (100 shares at £1 is equal to 10 shares at £10), but the higher price per share may make the stock more appealing to institutional traders or help the company meet certain listing requirements.
How Does a Reverse Stock Split Work?
The mechanics of a reverse stock split are relatively simple. If a company decides to undergo a reverse split, it will announce the ratio (e.g., 1-for-5. 1-for-10) and the effective date. Shareholders don't need to do anything; their shares will automatically be consolidated by the set ratio. For instance, in a 1-for-10 split, each shareholder's 10 shares would be reduced to 1. and the price of each share would increase tenfold.
But the key thing to remember is that while the stock price increases, the total value of the investment remains unchanged. If you had 100 shares at £1 each, after the reverse split, you would have 10 shares priced at £10. It's all about changing the way the stock is presented on the market, not altering its overall worth. In some cases, a company might even issue a cash payment for any fractional shares that result from the split, ensuring that no one is left with less than a full share.
Reasons Companies Choose a Reverse Stock Split
Now that we've got a basic understanding of what a reverse stock split is, you might be wondering why companies decide to go down this road. There are a few reasons for this, and not all of them are negative.
One common reason for a reverse stock split is to meet the minimum share price required for listing on a major stock exchange, like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the London Stock Exchange (LSE). If a company's stock price drops too low, it may be at risk of being delisted, which could limit its exposure to traders and hurt its credibility. By increasing the share price through a reverse stock split, the company can maintain its listing and avoid these negative consequences.
Another reason companies choose reverse splits is to improve their image. A very low stock price can sometimes give the impression of a struggling company, even if that's not the case. By increasing the stock price, a company may make itself more appealing to institutional traders, who often avoid stocks that trade for pennies a share. Essentially, it's a way for the company to improve its perceived value without actually changing the underlying fundamentals.
Impact on Stock Price and Shareholder Value
It's important to note that a reverse stock split doesn't increase the total value of your investment, but it can have an impact on how the stock is perceived in the market. In the short term, the price may rise due to the change in stock price, but that doesn't necessarily mean it's a sign of a company's health. Traders should always look beyond the price tag and assess the company's actual financial performance.
For example, if a company with a stock price of £1 per share undergoes a 1-for-10 reverse stock split, the price will immediately jump to £10 per share. On the surface, this might seem like a positive change, but if the company's fundamentals are weak, the stock price could quickly drop back down. Ultimately, while the reverse split might make the stock more appealing to some traders, it's not a guarantee of better performance going forward.
For shareholders, the real impact is in how many shares they own. After the split, they'll hold fewer shares, but the value of each one will be higher. If they had 100 shares worth £1 each, they would now have 10 shares worth £10 each. While it seems like a simple change, this could affect the way traders approach the stock in the future.
Common Examples of Reverse Stock Splits in History
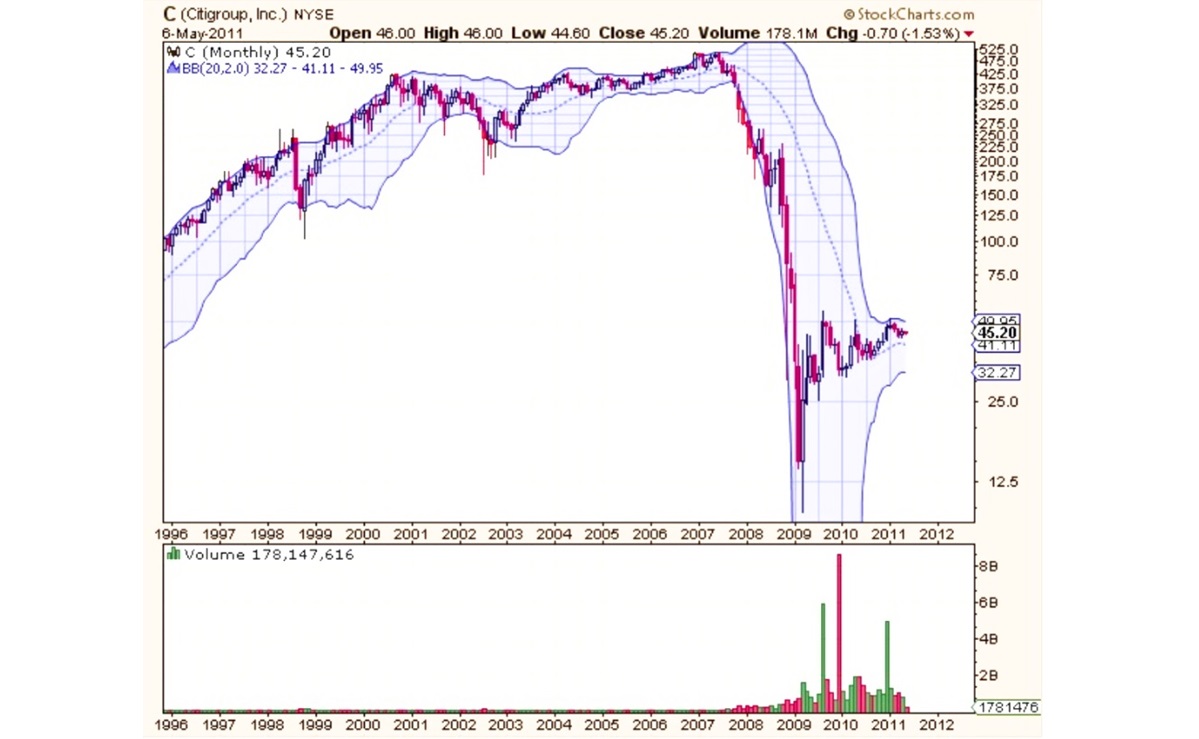
Reverse stock splits aren't an everyday occurrence, but they do pop up from time to time. A few well-known examples include companies like Citigroup, which underwent a 1-for-10 reverse stock split in 2011 after its stock price plummeted during the global financial crisis. Similarly, the tech company AIG performed a 1-for-20 reverse stock split in 2009 to raise its stock price after the financial crisis.
 While reverse stock splits are often associated with struggling companies trying to boost their image or meet listing requirements, they aren't always a sign of impending doom. In some cases, a reverse stock split can be part of a larger strategy to improve the company's market position or to prepare for a significant corporate event like a merger or acquisition.
While reverse stock splits are often associated with struggling companies trying to boost their image or meet listing requirements, they aren't always a sign of impending doom. In some cases, a reverse stock split can be part of a larger strategy to improve the company's market position or to prepare for a significant corporate event like a merger or acquisition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a reverse stock split is a corporate strategy that changes the way a company's stock is structured. While it doesn't increase the value of a shareholder's overall investment, it can improve the stock's price and market perception. For companies, it's often a way to meet listing requirements or make the stock more attractive to institutional traders.
However, traders should always approach a reverse stock split with caution. While it may seem like a positive move at first glance, the real impact on stock value depends on the company's performance and financial health. As with any investment, understanding the bigger picture is key to making informed decisions.
In the end, a reverse stock split might not be a cause for alarm, but it's certainly worth keeping an eye on. Whether you're a long-term trader or just getting started, understanding how reverse stock splits work can help you navigate the complexities of the stock market with a bit more confidence.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 While reverse stock splits are often associated with struggling companies trying to boost their image or meet listing requirements, they aren't always a sign of impending doom. In some cases, a reverse stock split can be part of a larger strategy to improve the company's market position or to prepare for a significant corporate event like a merger or acquisition.
While reverse stock splits are often associated with struggling companies trying to boost their image or meet listing requirements, they aren't always a sign of impending doom. In some cases, a reverse stock split can be part of a larger strategy to improve the company's market position or to prepare for a significant corporate event like a merger or acquisition.



