In the financial market, people have always been most enthusiastic about investing in stocks. And in this digitalized world of wealth, the stock exchange is in the spotlight. It allows investors and funds from all over the world to jointly write the wealth legend of this era. In China, there are a lot of such stages, the most notable of which are the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges. Now let's take a good look at the introduction and trading rules of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE).

History of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange
Its full name is Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE), which was established on December 1. 1990. as one of the two major stock exchanges in China. As the second stock exchange in China, its establishment marked an important step in China's capital market. Its creation provided more financing and development opportunities for Chinese enterprises and promoted the rapid development of China's capital market.
In early 1990. Shenzhen Development Bank (SZD) conducted a Stock Split operation. Subsequently, its stock price experienced a sharp rise after the stock split. This rise reflected market investors' enthusiasm for the stock and optimistic expectations about future market prospects. However, this market enthusiasm also led to a certain degree of market disruption, including problems such as excessive speculation and increased market volatility.
And when Stock Prices are volatile and abnormal market behavior occurs, it is necessary that regulators take measures to maintain the stability and healthy development of the market. For example, the regulation of the stock market should be strengthened to ensure the transparency and fairness of information disclosure, as well as to prevent market manipulation and fraudulent behavior.
Therefore, against the background of the stock split and the sharp rise in the price of SZD shares, the regulators realized the importance of regulating the market. In order to strengthen market regulation to help protect the interests of investors, ensure the healthy development of the market, and enhance the stability and trust of the market, Shenzhen formally set up a leading group on the securities market on July 2 1990 and began preparations for the establishment of a stock exchange.
By December 1. 1990. the Shenzhen Stock Exchange opened for trial operation and began centralized trading of Shenanda shares, with 8.000 shares traded. On this basis, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange officially opened in 1991. This laid the foundation for the standardized development and expansion of China's securities market and was also an important step in the gradual maturation and internationalization of China's financial market.
In the context of the time, both the market and the regulators were debating the positioning of the securities exchange market, the shareholding system, and the market mechanism. Yu Guogang, the founder of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE), and his team formulated the regulations and rules of the SZSE by studying and learning from foreign experiences and combining them with the actual situation in China, which provided a solid foundation for the establishment of the market.
Nowadays, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange provides a trading platform for a wide range of securities varieties to meet the needs of investors. It also meets the need for market regulation and supervision, including regulating the behavior of listed companies, ensuring the transparency of information disclosure, and providing education and risk warning services for investors.
It has grown rapidly since its inception, taking the lead in achieving the quadruple system of computerized trading, paperless settlement, satellite communication, and lobby-free operation, which has enhanced trading efficiency and accuracy. In addition, it has provided opportunities for different types of enterprises to raise capital and grow by launching the SME and GEM markets. It promotes the diversity and vitality of China's capital market and the development of innovative enterprises.
And it also actively promotes financial innovation, develops new types of financial products and services, and cooperates with international markets to improve market competitiveness and internationalization. Through these efforts, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE) plays an important role in China's capital market, contributing to the continued growth and prosperity of the Chinese economy.
At the same time, the successful development of the SZSE has provided a strong impetus for the growth of Shenzhen from a small fishing village to a cosmopolitan city. Shenzhen's GDP has grown from 180 million yuan in 1978 to 2.69 trillion yuan in 2019. making a huge leap forward and demonstrating the rapid rise of Shenzhen's economy.
What does the SZSE do?
| Functional Category |
Main Duties |
Main Services |
| Trading Platform |
Trade various securities |
Pooled and continuous bidding |
| Listing Review |
Reviewing IPOs and securities offerings |
Verify listing eligibility. |
| Market Regulation |
Prevent misconduct in transactions. |
Promoting market stability |
| Information Disclosure |
Monitor listed companies' disclosures. |
Protecting investors' right to know |
| Investor Protection |
Offer investor education and risk warnings. |
Guide investments and protect rights. |
Shenzhen Stock Exchange Listing Rules
The Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE) Listing Rules set out the requirements for listing on the SZSE, including financial, legal, and governance criteria. There are also specific guidelines for listing, including specific steps, processes, documents, and review processes.
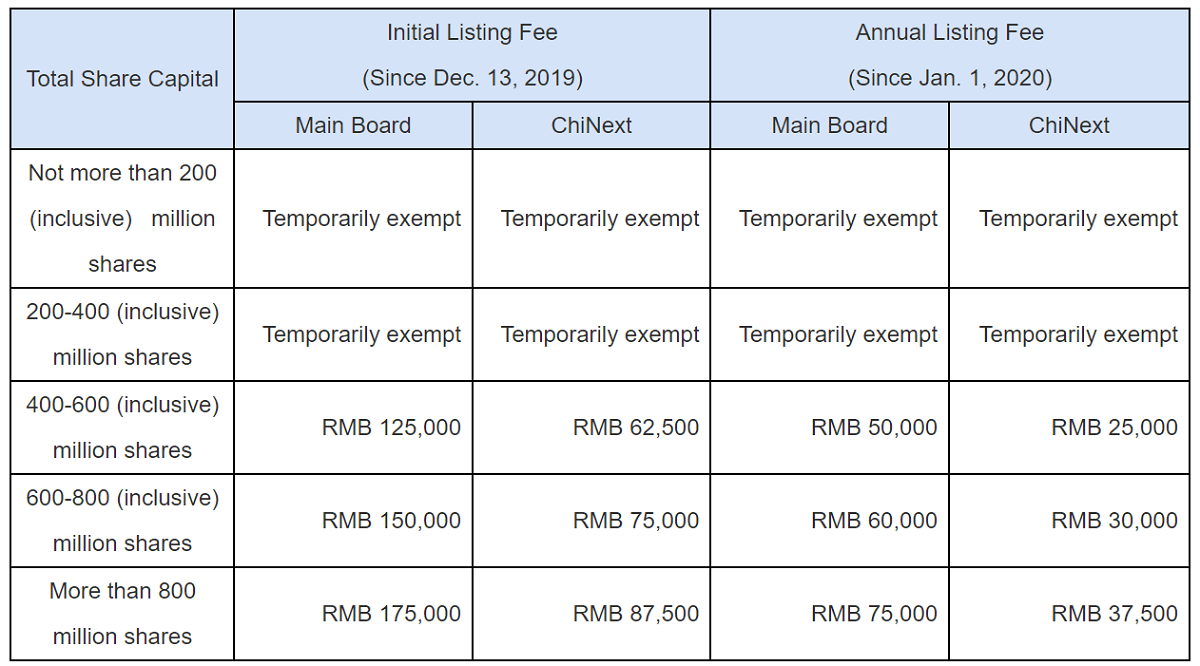
Generally speaking, listed companies are required to meet certain financial standards when applying for listing, and these standards vary according to different boards (Main Board, GEM, and New Third Board) to ensure the quality and stability of listed companies. For example, companies listed on the Main Board are required to have stable profitability and are usually required to be consistently profitable with a certain level of net assets and market capitalization. In addition, companies are also required to have a long operating history and strong operational strength to ensure their stable performance in the market.
GEM listing, on the other hand, focuses on supporting innovative companies and requires companies to perform faster in terms of net profit and operating income growth. It also puts more emphasis on the innovation ability and development potential of enterprises, which may be relatively lenient in terms of operating history and profitability but more demanding in terms of expectations for future development.
However, both pre- and post-listing companies need to fulfill a series of requirements to ensure market stability and investor interests. These requirements include a sound corporate governance structure, fulfillment of the requirements on the number of shareholders and shareholding distribution, timeliness and accuracy of information disclosure, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
In other words, listed companies need to establish a sound corporate governance system, including a board of directors, a supervisory board, independent directors, and an audit committee. It also needs to establish effective internal control and risk management mechanisms to ensure compliance and the sound operation of the company. A certain number of shareholders and equity distribution requirements also need to be met to ensure market liquidity and stability.
Moreover, listed companies are required to disclose information relating to the company's financial, operational, and material matters in a timely and accurate manner. The Exchange has strict regulatory requirements on information disclosure by listed companies to ensure information transparency and protect investors' right to know. Companies need to comply with the requirements of the Company Law, the Securities Law, and other relevant laws and regulations before listing.
These requirements aim to ensure that listed companies have sufficient quality and regulation to protect investors' interests. Meanwhile, depending on different sectors and industries, the SZSE may have other specific requirements for listed companies, including the core competitiveness of the enterprise, its technological level, and market prospects.
Listing on the Main Board usually requires an enterprise to have stable profitability, strong market competitiveness, and a mature business model in the industry. In addition, financial indicators such as net assets and operating income of the enterprise need to reach a certain level. GEM focuses on innovative and growth-oriented companies, especially those with high technology and new business models. In addition to financial indicators, GEM also focuses on non-financial indicators such as an enterprise's technological level, R&D capability, and market prospects. The innovation ability and growth potential of an enterprise play an important role in the vetting of GEM listings.
Companies in different industries may face different regulatory requirements when listing on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. For companies in the high-tech industry, the regulatory focus may be on technology research and development and intellectual property protection to ensure the competitiveness of the company in the field of innovation. Companies in the manufacturing industry, on the other hand, may focus more on production and operational capabilities and quality management to ensure product quality and operational efficiency.
In addition, when applying for listings, companies need to pass the vetting of the SZSE to ensure the authenticity, completeness, and accuracy of the listing documents and information submitted. This rigorous vetting process helps to protect the interests of investors and ensure the transparency and reliability of market information, thereby maintaining the fairness and stability of the market.
 Shenzhen Stock Exchange Audit
Shenzhen Stock Exchange Audit
The listing rules of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange (SZSE) aim to maintain the fair, transparent, and orderly operation of the market and to protect the interests of investors. Listed companies are required to pass the SZSE's vetting before listing to ensure that all relevant listing conditions are met. After listing, companies must also continue to comply with these rules to safeguard the stability and standardization of the market and to maintain investor confidence and interests.
When submitting an application for an initial public offering (ipo), a company needs to appoint a sponsor to help prepare and submit the application. The sponsor must be a securities company with sponsorship qualifications, such as CITIC Securities, Huatai Securities, and Everbright Securities. The sponsor's role is to ensure that the company's IPO process runs smoothly and to protect the interests of investors and the market.
Sponsors play a key role in the entire IPO application process, including providing professional advice, assisting in the preparation of application materials, ensuring that the company complies with relevant laws, regulations, and regulatory requirements, as well as providing ongoing supervision of the company after listing. By performing its duties, the sponsor maintains the stability and fairness of the market and promotes the healthy development of the company and the capital market.
As for the SZSE, after receiving the filing materials submitted by the sponsor, it will conduct a preliminary review of the materials and give feedback within five working days. This process is the first step of the review procedure to ensure the completeness of the filing materials and compliance with the relevant requirements. If the materials are complete and meet the requirements, the Exchange will continue with the subsequent review process; if the materials do not meet the requirements, the Exchange may require the sponsor to make additions or modifications.
The Shenzhen Stock Exchange will conduct the first round of audit inquiries within 20 trading days after receiving an initial public offering (IPO) application. These are questions asked after a detailed review of the materials submitted by the issuer to ensure that the applicant meets the listing requirements. The purpose of this session is to assess the applicant company's business position, financial position, and the completeness and accuracy of information disclosure.
After receiving the first round of questions, issuers are required to respond to the questions within three months. During this period, issuers can communicate with the reviewers through the listing review system or the appointment channel to ensure that the review questions are answered in a timely and accurate manner. This process ensures an adequate exchange of information and improves the transparency and efficiency of the review.
The Shenzhen Stock Exchange may, if necessary, conduct secondary questioning after receiving the issuer's feedback on the first round of questioning. Secondary questioning is not required, but the SZSE may ask the issuer again when new or unresolved issues need to be addressed. This helps to ensure that the application materials and issuer information are sufficient and accurate.
Upon completion of the questioning process, the reviewers will issue an audit report based on the feedback and on-site inspection. This audit report is critical to the Listing Committee's deliberations as it provides a comprehensive assessment of the applicant and helps the Committee make the final listing decision. The quality and completeness of the audit report are critical to the accuracy and effectiveness of the entire listing review process.
The Listing Committee is an important part of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange's (SZSE) listing review process. The Listing Committee considers the audit reports submitted by the auditors and makes a decision on the IPO application based on the reports. The outcome of the Listing Committee's deliberations determines whether the company can continue to move forward in the listing process.
After the listing committee's deliberations, the committee will report its review comments to the CSRC. The CSRC will review the Listing Committee's opinion and ultimately decide whether the application should be approved or not. This process is an important step in ensuring the quality and compliance of the listed company.
Once the SEC approves the listing application, the company can proceed with the final preparations for the issuance and listing. After going through the formal registration process with the SFC, the company is ready to issue shares and officially list and trade on the SZSE as planned. This process signifies that the company has successfully passed the listing audit and officially becomes a listed company.
 SZSE Trading Rules
SZSE Trading Rules
As one of the major stock exchanges in China, it has established a series of trading rules to regulate trading activities on its exchange. First of all, the SZSE provides investors with trading services in a wide range of securities, including stocks, bonds, funds (e.g., ETFs, LOFs, etc.), convertible bonds, and warrants. These rich securities varieties meet the needs of different investors and provide diversified investment choices.
It also provides two main trading methods: pooled bidding and continuous bidding. Aggregate bidding is a centralized aggregated trading method carried out during the opening and closing hours, which determines prices and turnover by centrally matching buy and sell orders; continuous bidding is a real-time trading method carried out outside the opening and closing hours, which aggregates buy and sell orders according to the real-time market quotes.
SZSE's trading hours are scheduled on trading days, usually from Monday to Friday, except for national holidays and closed days announced by the exchange. The morning trading hours are 9:15 to 9:25 for aggregate bidding and 9:30 to 11:30 for continuous bidding. Trading hours in the afternoon are continuous bidding from 13:00 to 14:57 and closing aggregate bidding from 14:57 to 15:00.
During the bidding process, the SZSE adopts the principle of price priority to ensure that the buy mandate with the highest bid and the sell mandate with the lowest bid are prioritized for trading, thus ensuring that trading is conducted at the price that is most advantageous to investors. In the case of the same price, the principle of time priority is adopted, according to the order of the time of the commission to prioritize the transaction. This means that early orders will be prioritized over later orders.
In order to control market volatility, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange offers trading varieties with price limits. For example, the price limit for Main Board stocks is usually 10%, while the price limit for GEM stocks is usually 20%. The benchmark for calculating the price limit is the closing price of the previous trading day, which is used as a reference point to determine the range of price fluctuations of the securities on that day.
In order to ensure market liquidity and stability, as well as to prevent excessive speculation and market manipulation, the Exchange may set a minimum trading unit or quantity limit per transaction for some varieties (e.g., GEM stocks). Such restrictions help to regulate market behavior and promote the healthy operation of the market.
One of the important costs that investors need to take into account when trading is the certain fees charged by the Exchange for trading activities, including trading commissions, stamp duty, transfer fees, and so on. For example, a commission of 0.1425% of the transaction price is paid when buying shares, as well as a transaction tax of 0.3% of the transaction price in addition to the commission when selling shares.
The trading rules of the SZSE are designed to ensure the fair, transparent, and orderly operation of the market and to protect the interests of investors. When buying and selling stocks, investors need to understand the relevant trading rules, including trading hours and restrictions on price fluctuations. This helps investors trade at the right time and avoid the risks associated with price fluctuations. At the same time, understanding the trading fees and rules can help investors better plan their investment strategies, control trading costs, and improve investment efficiency. By familiarizing themselves with the rules and regulations of the exchanges, investors can make more informed decisions in the market and improve their investment returns.
Introduction and Trading Rules of the Shenzhen Stock Exchange
| Content Category |
Brief Introduction |
Rules |
| Exchange Profile |
Established in 1990 |
Trade various securities. |
| Listing Review |
Review of IPOs and securities offerings |
Ensure compliance with standards. |
| Trading Hours |
Trading days are Monday through Friday. |
9:15am-11:30am, 13:00pm-15:00pm |
| Trading Methods |
Provide aggregated and continuous bidding. |
Centralized real-time trading |
| Trading Fees |
Collect trading fees and taxes. |
The commission is 0.1425%, and the tax is 0.3%. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 Shenzhen Stock Exchange Audit
Shenzhen Stock Exchange Audit SZSE Trading Rules
SZSE Trading Rules