When following financial news, we often see discussions about interest rates, such as 'How many times does the US Federal Reserve plan to raise interest rates this year' or 'Our central bank has decided to keep interest rates unchanged'. Although these interest rate adjustments may seem professional, they are in fact closely related to our investments and loans. In particular, the high-frequency term 'interest rate cut' can have a profound impact on your financial situation. Today, we're going to take a closer look at interest rate cuts and their impact on the economy and investments.
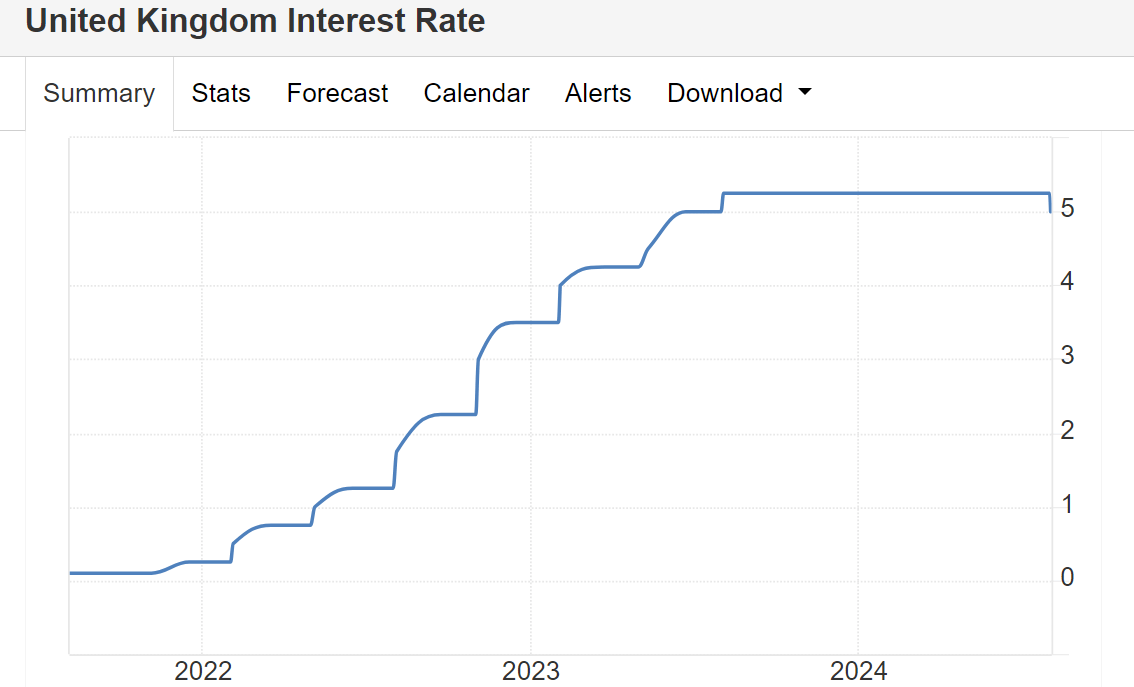 What is Interest Rate?
What is Interest Rate?
It refers to the central bank lowering its benchmark interest rate, the monetary policy rate. The benchmark interest rate is the reference rate for interbank lending and borrowing and also determines the lending and deposit rates of commercial banks. As a monetary policy tool, interest rate cuts regulate economic activities by adjusting interest rates to affect the money supply in the market.
The central bank implements interest rate cuts through a variety of monetary policy tools. Firstly, it adjusts the benchmark interest rate, such as the federal funds rate, which directly affects the borrowing costs of commercial banks and passes on this change to consumers and businesses by adjusting the lending and deposit rates of commercial banks. Secondly, the central bank regulates the supply of money in the market through open market operations. For example, purchasing government bonds can increase the supply of money in the market, thus driving down interest rates.
In addition, the central bank can also influence market liquidity by adjusting reserve requirements. Lowering reserve requirements releases more funds for commercial banks to lend, thus increasing the supply of money in the market. At the same time, lowering the discount rate makes it cheaper for commercial banks to borrow from the central bank, encouraging banks to borrow and lend more, further driving down market interest rates.
By lowering interest rates, the central bank aims to stimulate economic growth. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing and encourage businesses and consumers to borrow and spend more, thereby boosting economic activity. In addition, it helps to reduce the unemployment rate as economic growth may push businesses to increase investment and hiring, thus creating more jobs.
On the other hand, it may also boost investment and prevent deflation. Lower interest rates mean lower financing costs for businesses, encouraging more investment projects and business expansion. At the same time, an increase in the money supply helps prevent a sustained fall in the price level (deflation) and keeps the economy healthy.
Interest rate cuts are usually implemented when the economy is weak, inflation is low, or there is a need to stimulate economic growth, as it provides several economic benefits. Firstly, it reduces the cost of borrowing and encourages businesses and consumers to spend more, thereby stimulating economic growth. Businesses may expand their investments, and consumers may increase their spending, thus boosting overall economic activity. In addition, it reduces the cost of financing, which is particularly favorable to businesses in need of loans, helping them to sustain their operations and growth in times of economic downturn.
Second, the interest rate cut helps boost the stock market. A low interest rate environment reduces the returns on fixed income investments (e.g., bonds), and investors are more inclined to put their money into the stock market, pushing it up. Meanwhile, low interest rates encourage banks to provide more loans, increasing market liquidity and easing the liquidity crunch. In addition, households' disposable incomes increased as a result of lower borrowing costs, which further supported consumption and investment.
Of course, despite its economic stimulus effect, the interest rate cut also brings some potential downsides. A prolonged period of low interest rates may lead to the formation of asset bubbles, such as excessive price rises in the property and stock markets, thereby increasing risks in the financial market. At the same time, it lowers the interest rate on savings and reduces the real return to savers, which may affect the willingness of individuals to save, especially retirees who rely on savings income.
In addition, low interest rates may trigger inflation and increase demand pressure, thereby pushing up the price level. A low-interest rate environment in which banks have lower interest rates on both their loans and deposits may compress profit margins and have a negative impact on their profitability. Further, its effect may be limited if interest rates are already very low, which limits the scope for monetary policy regulation.
While interest rate cuts are an effective policy tool used to stimulate economic growth, they may also bring about side effects such as asset bubbles, inflation, and reduced returns on savings. Therefore, central banks usually weigh the need for economic growth against the potential risks in order to formulate an appropriate monetary policy.
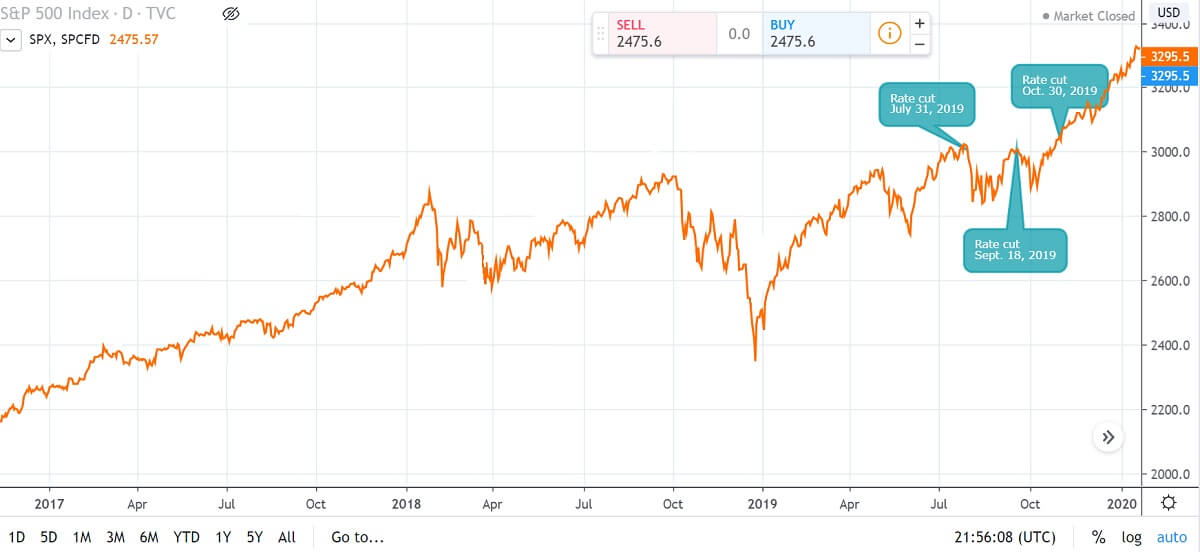
 What is the Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on the Stock Market?
What is the Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on the Stock Market?
Generally speaking, it helps to boost the stock market. However, the stock market's response is complex and affected by multiple factors, including the economic situation, market expectations, and investor behavior, so its impact is not a single outcome. Currently, there are very active forecasts and discussions on the Fed's interest rate cut.
For the specific impact of interest rate cuts on the stock market, market views are clearly divided. Some analysts believe that it will reduce the cost of financing and stimulate economic growth, thus driving the stock market up. On the other hand, there are also views that it may reflect signs of economic weakness, and if economic data fails to support the expectation, the stock market may fall.
It will have a positive impact on the stock market because lower interest rates reduce borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, thus boosting investment and consumer demand, which helps drive corporate earnings growth and push the stock market higher. At the same time, as interest rates fall, fixed-income assets such as bonds offer lower returns, and investors may shift their money to the stock market in search of higher returns, which also pushes the stock market higher.
It lowers the cost of financing for companies, allowing them to borrow at lower rates to invest and expand their businesses. This not only helps boost corporate profitability but also further drives up share prices. In a more stable economic environment, it usually has a positive effect on the stock market by promoting corporate growth and enhancing market liquidity. As such, it is often seen as a policy measure that favors the stock market.
And in the case of this rate cut forecast, if the Fed is cutting rates because they believe that rate hikes have been excessive and inflation is under control and the rate cuts are meant to stimulate the economy, this is usually seen as positive for the stock market. That's because lower interest rates can lower borrowing costs for businesses and improve corporate profitability, which can drive the stock market higher.
If it is because of slowing economic growth or even the risk of a recession, then the market may react poorly to this. Even if interest rates are lowered, lackluster economic growth and declining corporate profitability may cause the stock market to fall. The market may worry that it will not be effective in stimulating the economy or that the effects of a recession will be more severe than the benefits of a rate cut.
Moreover, the expectations of market participants are critical to the stock market's reaction. If the market generally expects the Fed to cut rates, the stock market may rise in advance of the announcement. In this case, by the time it is actually announced, the market may have already reflected the news in advance, resulting in an actual reaction that may not be as significant as expected. Investors should be aware that there may be a discrepancy between the market's expectation of it and the actual effect.
On the other hand, if the market anticipates it too optimistically but the economic data after the announcement fails to be as strong as expected, this may lead to a reverse correction in the stock market. In this case, the actual economic performance fails to support the market's optimistic expectations, and the stock market may fall due to disappointment. This suggests that the discrepancy between market expectations and actual economic data can have a significant impact on the stock market.
In addition, interest rate cuts usually change investors' risk appetite. In a low-interest rate environment, returns on fixed-income assets are lower, and investors may shift to riskier assets, such as equities, in search of higher returns. This shift usually pushes the stock market higher as the inflow of funds into the stock market drives up Stock Prices.
However, if it is due to a deterioration in the economic outlook, investors may be concerned about the state of the economy and may remain cautious about risky assets despite lower financing costs. In this case, the stock market may be negatively affected as the market becomes more pessimistic in its expectations of future economic growth.
What's more, it usually affects short-term interest rates quickly, but changes in long-term interest rates are not necessarily synchronized. While short-term interest rates will directly reflect the adjustment of the central bank's benchmark interest rate, long-term interest rates (e.g., yields on 10-year and 30-year bonds) are influenced by more economic expectations and market factors. As a result, there may not be an immediate and significant change in long-term interest rates, leading to a lagged or asymmetric adjustment in the yield curve of the bond market.
This lagged or asymmetric adjustment makes its impact on the bond market exhibit a delayed effect. Short-term bond prices may rise rapidly, while price adjustments for long-term bonds may be slower or different. This suggests that investors need to take these complex factors into account when assessing their impact on the bond market.
In conclusion, interest rate cuts do have an impact on the stock market, but this impact is not singular or direct. The stock market's reaction depends on the prevailing context, the general state of the economy, the market's expectations, and investor sentiment. Understanding these factors will help to better predict and analyze its actual impact on the stock market in order to make the right response.
 Investment Response Strategies to Interest Rate Cut
Investment Response Strategies to Interest Rate Cut
While it usually has a profound impact on the economy and investment markets, it does not always lead directly to expected changes in the economy or the stock market, and its effect depends on the overall state of the economy and the market's interpretation of it. In some cases, it may reflect a signal of an economic slowdown rather than the start of an economic recovery. Therefore, understanding how to react to interest rate cuts can help optimize your investment strategy and improve your chances of growing your wealth.
Interest rate cuts typically push up bond prices, making long-term bonds and high-quality corporate bonds noteworthy investment options. Long-term bonds outperformed during this period as their fixed interest payments became more attractive in a low interest rate environment, with significant relative price increases.
In addition, the low interest rate environment also made high-yield bonds (junk bonds) more attractive. While these bonds are riskier, they can provide relatively higher returns and a more stable income stream against a backdrop of falling interest rates. Investors can realize better returns in a low-interest rate environment by investing in these bonds.
During this period, the cost of corporate finance is lower, and many companies may increase their dividend distributions, thereby attracting the attention of investors. High-dividend stocks, particularly those companies that have been able to pay steady dividends despite the reduced interest rate environment, offer stable cash flows and relatively high returns. These stocks are able to provide investors with stable income in a low interest rate environment.
In addition, growth dividend stocks are also worth watching. These companies not only provide stable dividends but also show good growth potential over the period. Investing in companies that are expected to achieve business expansion and earnings growth in this environment can provide investors with capital appreciation opportunities.
Interest rate cuts usually result in lower real estate lending rates, which may boost demand in the property market. Lower lending rates make it less expensive to purchase a home, encouraging more homebuyers to enter the market, which in turn drives up property prices. This environment provides opportunities for real estate investors to achieve stable income and capital appreciation through real estate investment trusts (REITs) and direct investment in real estate.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are an indirect way of investing in real estate, allowing investors to share in the rental income and potential capital appreciation without the need to actually purchase the property. On the other hand, direct investment in real estate, such as purchasing rental properties or commercial properties, provides stable rental income and capital appreciation through property appreciation. Against this background, both types of investment may offer attractive returns to investors.
It is also likely to stimulate economic growth, which in turn will drive the stock market higher. In particular, sectors and companies that have benefited from low interest rates, such as technology companies and consumer goods companies, are likely to outperform. Technology companies usually have high growth potential, and interest rate cuts can help lower their financing costs, thus driving their share prices higher. Consumer goods companies are usually stable performers in times of economic uncertainty, as demand for their products is relatively unaffected by economic fluctuations.
If there is a need for a loan, opting for a floating rate loan may be a wise choice. During a period of interest rate cuts, the interest rate on a floating-rate loan will be lowered accordingly, thus reducing the repayment burden. This not only makes the cost of the loan more economical but also effectively reduces your financial stress. Utilizing this strategy can minimize the cost of borrowing in a low interest rate environment and bring more flexibility to your finances.
In a lower interest rate environment, certain asset classes may be exposed to higher risks, such as the possibility of increased volatility in the equity markets. To counter this risk, it is recommended that portfolios be adjusted to maintain an appropriate level of risk. This includes spreading risks through diversification and avoiding concentration of funds in a single asset class or sector, thereby protecting the portfolio from the negative impact of market volatility.
It may also lead to rising inflation, so investing in inflation-resistant assets such as gold and other real assets is an effective strategy to protect the value of investments. Real assets such as gold typically perform well in an inflationary environment because they maintain their purchasing power in real terms. By allocating to these types of assets, you can effectively hedge against the risks associated with inflation and ensure that the value of your investments remains stable when prices rise.
In a low-interest rate environment, businesses and individuals still need to maintain adequate liquidity despite lower financing costs. Building up adequate contingency reserves can help you cope with economic uncertainty and unexpected events, ensuring that you can respond quickly and maintain financial stability in the face of unforeseen challenges. Such liquidity reserves can help reduce reliance on additional financing and provide a cushion in times of market volatility.
Understanding the impact of interest rate cuts and adjusting your investment strategy can help optimize returns and reduce risk in a low interest rate environment. By focusing on the performance of equities, bonds, real estate, and inflation-proof assets and making decisions accordingly based on changes in interest rates, you can enhance your return potential while managing risk effectively. Timely portfolio adjustments not only capitalize on opportunities but also prepare for future economic changes.
Interest rate cuts and their impact on the economy and investment
| Perspective |
Positive Impact |
Negative impacts |
| Economic Growth |
Boosts consumption, investment, and growth. |
Can cause asset bubbles and overheating. |
| Stock Market |
Increased capital inflows drive stock markets up. |
Stocks may drop with economic weakness. |
| Bond Market |
Higher bond prices |
Lower returns and reduced attractiveness |
| Property Market |
Low loan rates boost home purchase demand. |
Prices may rise excessively, increasing risk. |
| investing strategies |
Increased investment in high-yield assets |
Risky assets are volatile; diversify. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.


 What is Interest Rate?
What is Interest Rate?
 What is the Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on the Stock Market?
What is the Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on the Stock Market?
 Investment Response Strategies to Interest Rate Cut
Investment Response Strategies to Interest Rate Cut