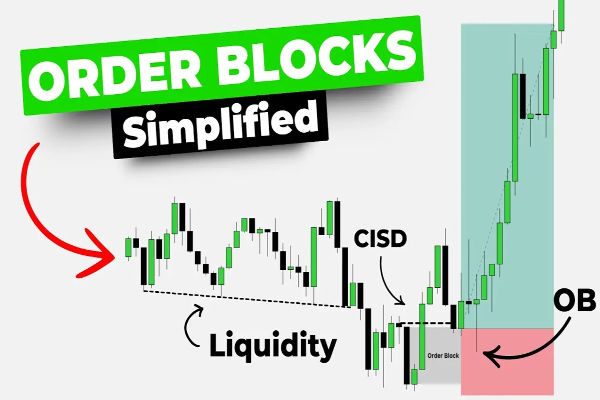
What is a Hedge Fund?
Hedge Fund refers to a fund that uses hedging trading methods, also known as a hedge fund or hedge fund.
It refers to financial funds that combine financial derivatives such as futures and options with financial organizations for the purpose of profit.
It is a form of investment fund, meaning "risk hedged fund". Hedge funds use various trading methods to hedge, swap, hedge, and earn huge profits. These concepts have gone beyond the traditional scope of risk prevention and revenue protection operations. In addition, the legal threshold for initiating and establishing hedge funds is much lower than that of mutual funds, further increasing their risk.

What are the Characteristics of Hedge Funds?
The high leverage of investment effects, the complexity of investment activities, the private placement of fundraising methods, and the concealment and flexibility of operations. Hedge funds have become synonymous with a new investment model. Based on the latest investment theories and extremely complex financial market operation techniques, fully utilize the leverage utility of various financial derivative products to bear high risks. Pursuing a high yield investment model. Hedge funds have the following characteristics.
Complexity
With the increasingly complex structure and constantly evolving patterns, various financial derivative products such as futures, options, swaps, etc. have gradually become the main operating tools of hedge funds. These derivative products were originally designed to hedge risks, but due to their low-cost, high-risk, and high return characteristics, they have become powerful tools for many modern hedge funds to engage in speculative behavior.
Hedge funds match these financial instruments with complex portfolio designs, invest based on market predictions, obtain excess profits when the predictions are accurate, or design investment strategies using the non equilibrium caused by short-term fluctuations in the market to obtain price differentials when the market returns to normal.
High leverage
A typical hedge fund often utilizes bank credit and uses extremely high leverage to expand investment funds several times or even dozens of times beyond its original fund volume, in order to achieve the goal of maximizing returns. The high liquidity of Securities assets in hedge funds allows them to easily use fund assets for collateral loans.
A hedge fund with a capital of only $100 million can lend billions of dollars by repeatedly mortgaging its securities assets. The existence of this leverage effect makes the net profit after deducting loan interest after a transaction much greater than the potential benefits of using only $100 million of capital to operate. Similarly, precisely because of the leverage effect, hedge funds often face a huge risk of excess losses when not operating properly.
Private Placement
The organizational structure of hedge funds is generally a partnership system. Fund investors enter the partnership with funds, providing most of the funds but not participating in investment activities; The fund manager enters the partnership with funds and skills, responsible for the investment decisions of the fund.
Due to the high level of concealment and flexibility required by hedge funds in their operations, the partners of hedge funds in the United States are generally limited to less than 100 people, with each partner contributing more than $1 million (different countries also have different regulations for hedge funds, such as controlling partners of Japanese hedge funds to less than 50 people).
Due to the fact that hedge funds are mostly private, they avoid the strict requirements of US law for public fund information disclosure. Due to the high risk and complex investment mechanisms of hedge funds, many Western countries prohibit them from publicly recruiting funds to protect the interests of ordinary investors.
In order to avoid high taxes in the United States and regulations from the Securities and Exchange Commission, hedge funds operating in the US market generally register offshore in low tax and loosely regulated areas such as the Bahamas and Bermuda, and are limited to raising funds from investors outside the United States.
Concealment
Hedge funds and securities investment funds targeting ordinary investors not only have significant differences in terms of fund investors, fundraising methods, information disclosure requirements, and regulatory level. There are also many differences in the fairness and flexibility of investment activities.
Securities investment funds generally have a clear definition of asset portfolios. There is a definite plan for the selection and proportion of investment tools, such as a balanced fund where stocks and bonds are roughly equal in the fund portfolio, and a growth fund where investments are focused on high growth stocks; At the same time, mutual funds are not allowed to use credit funds for investment, while hedge funds have no restrictions or definitions in these aspects. They can use all available financial instruments and portfolios to maximize the use of credit funds and seek excess returns higher than the market average profit.
Due to the high degree of concealment and flexibility in operation, as well as the leverage financing effect, hedge funds play an important role in speculative activities in modern international financial markets.
【 EBC Platform Risk Reminder and Disclaimer 】: There are risks in the market, and investment needs to be cautious. This article does not constitute investment advice.