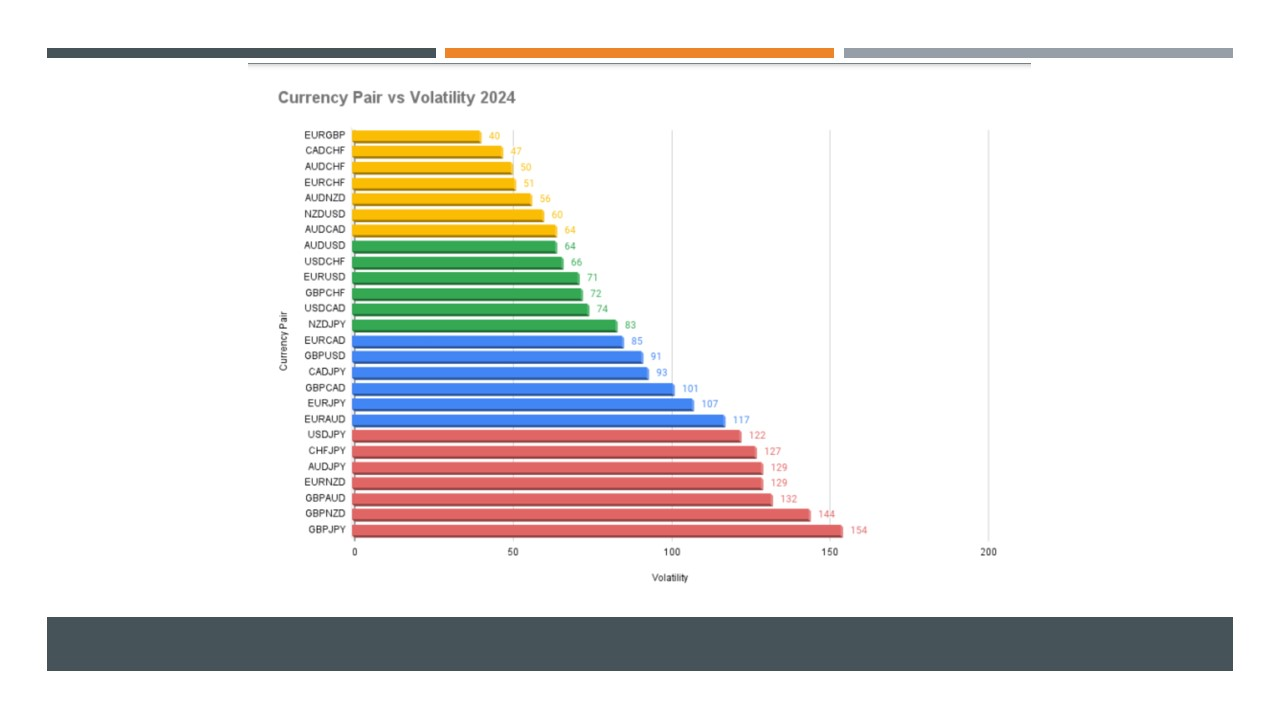
Volatility is a key term in forex trading that describes the degree of price fluctuations in a currency pair over time. Higher volatility means the price of a currency can change dramatically in a short period, while lower volatility indicates smaller and more gradual movements. While volatility offers traders opportunities for large profits, it also carries increased risks.
In the world of forex, volatility is often more pronounced in currency pairs that involve emerging market economies or countries facing political instability. Stable economies like those of the US, the Eurozone, or Japan tend to experience lower volatility because their currencies are supported by strong economic fundamentals. On the other hand, currency pairs involving countries with weaker economies, political uncertainties, or high inflation rates can experience more unpredictable and significant price swings.
While major pairs such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY are known for their lower volatility, some currency pairs are notorious for their large price movements, offering opportunities for traders willing to embrace the risks. Understanding the most volatile forex pairs is crucial for anyone looking to trade in the forex market and capitalise on market fluctuations.
How to Measure Forex Volatility
To successfully trade volatile currency pairs, traders often rely on tools that help them measure and understand volatility. The most used indicators are the Average True Range (ATR) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
The ATR measures the average range of price movement over a specified period, helping traders understand the degree of volatility in each market. A high ATR indicates larger price swings, while a lower ATR shows more stable conditions. This tool is essential for setting stop-loss levels and determining position sizes when trading highly volatile pairs.
The RSI is another useful tool that helps traders assess whether a currency pair is overbought or oversold. This can be particularly helpful in volatile markets where prices are prone to sudden reversals. If the RSI value is above 70. it may suggest that the currency is overbought and due for correction, while an RSI below 30 signals an oversold condition that could lead to a price rebound.
Together, these indicators help traders gauge the potential risk and rewards of trading volatile forex pairs, allowing for more informed decision-making.
Key Drivers of Forex Volatility
Several factors contribute to the volatility of certain forex pairs, with economic conditions, political events, and central bank policies playing pivotal roles. Emerging markets, where economies are more susceptible to changes in global conditions or internal instability, often experience more significant price movements.
Interest rates set by central banks are among the most important drivers of forex volatility. For example, when the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates, the US Dollar tends to appreciate, causing volatility in currency pairs involving the USD. Similarly, central bank policies in countries like Brazil or Turkey can create large swings in currency pairs such as USD/BRL or USD/TRY.
Political events also drive volatility. Elections, changes in government policies, or even political scandals can lead to sharp fluctuations in currency values. For instance, the value of the Turkish Lira (TRY) has historically been influenced by political instability in Turkey, contributing to high volatility in the USD/TRY pair.
Similarly, economic instability—such as high inflation, weak GDP growth, or trade disruptions—can create uncertain market conditions, causing currencies to fluctuate dramatically. Countries with economies highly dependent on commodities, such as New Zealand or south africa, can see their currencies rise or fall based on changes in global demand for their resources.
Top 10 Most Volatile Forex Pairs
Now, let's take a closer look at some of the most volatile forex pairs. These pairs are known for their large price swings, which can create both risks and opportunities for traders.
USD/TRY (US Dollar / Turkish Lira)
The USD/TRY pair has earned a reputation for extreme volatility. The Turkish Lira has been susceptible to drastic swings due to political instability, economic challenges, and fluctuating inflation rates. As a result, traders can expect frequent and significant price movements in this pair, especially in response to news events or changes in Turkey's economic policies.
USD/ZAR (US Dollar / South African Rand)
The South African Rand is another currency that is known for its volatility. Influenced by South Africa's reliance on commodity exports, the USD/ZAR pair can experience dramatic swings based on changes in global commodity prices, particularly gold and platinum. Additionally, economic instability and political events in South Africa contribute to volatility in this pair.
USD/BRL (US Dollar / Brazilian Real)
Brazil's economic conditions and political landscape make the USD/BRL pair highly volatile. The Brazilian Real is sensitive to changes in commodity prices (particularly oil and soybeans) and fluctuations in investor sentiment. Political scandals, such as corruption scandals involving Brazilian politicians, can further amplify volatility in this pair.
GBP/JPY (British Pound / Japanese Yen)
The GBP/JPY pair is often characterised by large price movements due to the differences in economic conditions between the UK and Japan. The British Pound can be influenced by the country's economic reports, such as GDP growth and inflation data, while the Japanese Yen is affected by Japan's monetary policy and global risk sentiment. This combination of factors creates substantial volatility, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty.
GBP/AUD (British Pound / australian dollar)
The GBP/AUD pair is impacted by economic conditions in both the UK and Australia, as well as the global trade relationship between the two nations. The Australian Dollar is also sensitive to commodity prices, especially those linked to mining and agriculture, which can cause sharp fluctuations when global demand changes.
EUR/TRY (Euro / Turkish Lira)
Similar to the USD/TRY pair, the EUR/TRY pair is highly volatile due to Turkey's economic and political instability. The Euro can also be influenced by broader economic events within the Eurozone, adding an extra layer of volatility when major news affects the region.
USD/MXN (US Dollar / Mexican Peso)
The USD/MXN pair sees significant volatility, especially in response to trade relations between the US and Mexico, as well as changes in oil prices. As an emerging market currency, the Mexican Peso is more prone to fluctuations, particularly during times of economic or political uncertainty.
USD/INR (US Dollar / Indian Rupee)
The Indian Rupee (INR) tends to be volatile due to India's dependence on imports for oil and other goods, which exposes the currency to global market fluctuations. Political instability, inflation, and trade imbalances in India can also influence the volatility of the USD/INR pair.
NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar / US Dollar)
The New Zealand Dollar is highly affected by global commodity prices, particularly agricultural exports like dairy. As a result, fluctuations in global demand for these products can create significant volatility in the NZD/USD pair, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
AUD/JPY (Australian Dollar / Japanese Yen)
The AUD/JPY pair often experiences volatility driven by changes in global risk sentiment. The Australian Dollar, which is influenced by commodity exports, can swing in response to changes in global demand, while the Japanese Yen is a safe-haven currency that reacts to shifts in global market risk.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.