Index analysis in stocks is a crucial tool for understanding the performance of various sectors of the stock market. If you've ever looked at the news and heard about the "S&P 500" or the "FTSE 100", you've already encountered stock indices. But what exactly are they, and why do they matter for traders like you?
Understanding Stock Market Indices
In simple terms, a stock market index is a collection of stocks that represents a particular segment of the market. For example, the FTSE 100 includes the 100 largest companies listed on the London Stock Exchange. These indices are used as benchmarks to track how well a specific group of stocks is performing. When the index goes up, it generally means that the collective value of the stocks in that index is increasing, and vice versa when it falls.
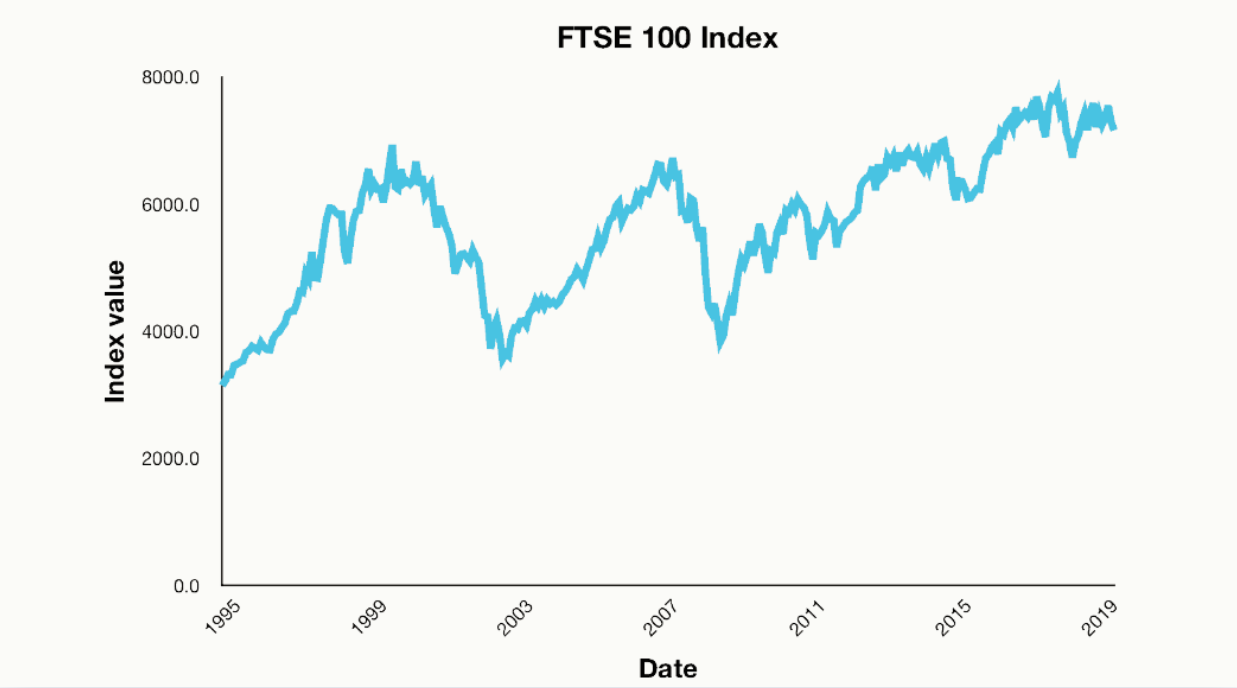
Indices provide a snapshot of market sentiment. They help traders gauge the overall health of a particular market or sector. For instance, the performance of the S&P 500 can give you a good idea of how the broader US stock market is doing. By tracking these indices, traders can assess whether the market is on an upward trend or experiencing a downturn, helping them make informed decisions about where to invest.
Types of Stock Market Indices
Not all indices are created equal, and understanding the different types is important when you're diving into index analysis. Broadly, indices can be grouped into three main types: price-weighted, market-cap-weighted, and equal-weighted.
Price-weighted indices: In a price-weighted index, the stocks with higher prices have more influence on the index's movements. A famous example of this is the dow jones industrial average (DJIA). While this method is straightforward, it doesn't necessarily reflect the actual size or economic impact of a company.

Market-cap-weighted indices: These are much more common and give more weight to companies with a larger market capitalisation. The S&P 500 is a prime example. In this type of index, the larger a company's market value, the more influence it has on the index's performance. This approach is seen as more representative of the overall market.
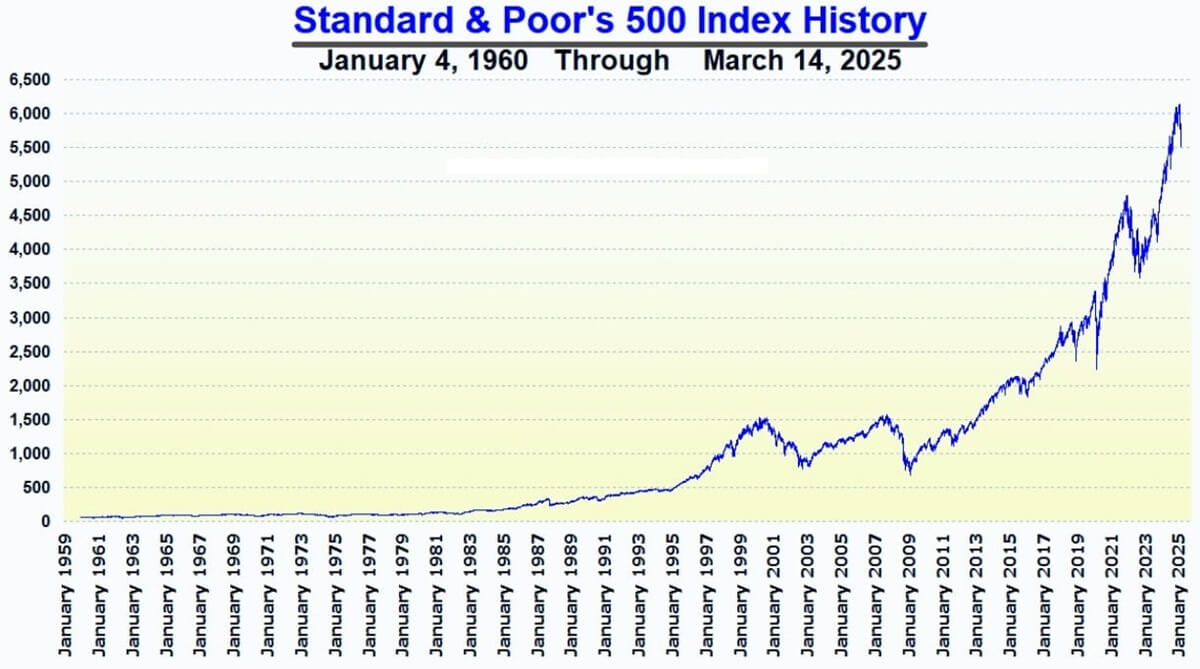 Equal-weighted indices: As the name suggests, in an equal-weighted index, each stock has the same impact on the index, regardless of its size or value. This method is less common but can be useful for tracking smaller stocks or sectors where size doesn't necessarily equate to importance.
Equal-weighted indices: As the name suggests, in an equal-weighted index, each stock has the same impact on the index, regardless of its size or value. This method is less common but can be useful for tracking smaller stocks or sectors where size doesn't necessarily equate to importance.
Each type of index offers different insights, and understanding the structure of an index can give you a clearer picture of what's driving its performance.
Methods of Index Analysis
When it comes to analysing stock indices, there are several methods traders use, each providing a unique perspective on market trends. The two most common approaches are technical analysis and fundamental analysis, but some traders also use quantitative methods to dig deeper.
Technical analysis: This method involves analysing historical price movements and trading volumes. Technical analysts use charts and patterns to predict where the market might move next. The idea is that past performance can give us clues about future trends. Technical analysis is particularly useful for short-term traders who are looking for quick movements in Stock Prices.
Fundamental analysis: Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on price patterns, fundamental analysis looks at the intrinsic value of companies and their underlying economic health. This could include analysing a company's earnings, revenue, growth potential, and broader economic indicators. When applied to indices, fundamental analysis might focus on the financial health of the companies within the index and how these factors contribute to the overall index's performance.
Quantitative methods: These are data-driven techniques that use mathematical models and statistical analysis to predict market trends. Quantitative analysis is often used by institutional traders and hedge funds who rely on sophisticated algorithms to analyse vast amounts of data. While not commonly used by individual traders, it is an increasingly popular tool for those looking for a more analytical approach.
By combining these methods, traders can get a fuller picture of index performance, making it easier to spot trends and opportunities.
Applications of Index Analysis in Trading
Index analysis can be incredibly useful when building a diversified investment portfolio. Many traders use indices as a benchmark, meaning they compare the performance of their own investments to that of an index. For example, if you have a portfolio that mirrors the performance of the S&P 500. you can easily see whether your investments are keeping up with the broader market.
Moreover, indices can also be used as a tool for passive investing. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track indices like the FTSE 100 or the NASDAQ-100 allow traders to buy into a basket of stocks that mirrors the index. This means you can gain exposure to a wide range of companies without having to select each one individually.
Another application of index analysis is in sector investing. Indices like the NASDAQ-100 are heavily weighted towards technology, while others may focus on energy or healthcare. If you believe a specific sector will outperform, you might invest in an ETF that tracks an index focused on that sector.
Challenges and Limitations of Index Analysis
While index analysis can be a powerful tool for traders, it's not without its limitations. For one, indices can sometimes fail to capture the full picture. For instance, market-cap-weighted indices, such as the S&P 500. give more weight to larger companies, meaning that smaller, but potentially more dynamic companies, can be underrepresented.
Another challenge is market volatility. Indices can be affected by broader economic conditions, and a sudden market shift can lead to significant drops, even if the underlying companies remain strong. Relying solely on index performance without considering the broader economic context can lead to poor decision-making.
Furthermore, index analysis doesn't always account for individual company performance. For example, a stock within an index might perform poorly due to company-specific issues, even though the overall index is doing well. This is why it's important to combine index analysis with other tools and methods, like fundamental and technical analysis, to get a comprehensive view of the market.
In summary, index analysis in stocks is an essential tool for understanding the market as a whole. By understanding the types of indices, methods of analysis, and how to apply this knowledge to your investment strategies, you can make more informed decisions. While it's not without its challenges, index analysis can provide valuable insights into market trends, helping you navigate the often complex world of stock trading. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, gaining a solid understanding of index analysis can be a game changer for your portfolio.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.




 Equal-weighted indices: As the name suggests, in an equal-weighted index, each stock has the same impact on the index, regardless of its size or value. This method is less common but can be useful for tracking smaller stocks or sectors where size doesn't necessarily equate to importance.
Equal-weighted indices: As the name suggests, in an equal-weighted index, each stock has the same impact on the index, regardless of its size or value. This method is less common but can be useful for tracking smaller stocks or sectors where size doesn't necessarily equate to importance.