The Indian Stock Market is one of the most dynamic and diverse financial hubs in Asia. With its rich history and significant impact on the global economy, it offers ample opportunities for investors. For those new to investing or just starting to explore the world of Indian finance, understanding the basics, the key indices, and the market's regulations is essential.
This article will take you through these foundational aspects, providing insights into how the Indian stock market operates, its unique features, and the key sectors that drive its growth.
Indian Stock Market's Basics for Beginners
The Indian Stock Market primarily comprises two key exchanges: the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). Together, these platforms facilitate the trading of equities, derivatives, and commodities, providing liquidity and transparency to the market. The NSE is the largest in terms of trading volumes, while the BSE, one of the oldest in the world, continues to play a significant role in the Indian financial landscape.
Over the years, the Indian Stock Market has evolved into a highly sophisticated entity. From its early days in the 19th century, when informal trading occurred in Mumbai, the market has seen various phases of modernisation and regulation. The establishment of the NSE in 1992 marked a significant turning point, providing electronic trading that enhanced efficiency and reduced risks.
Today, the Indian Stock Market is an attractive destination for global investors, thanks to its robust financial infrastructure, improved transparency, and increasing market depth.
As of today, the market continues to experience remarkable growth. Investors are increasingly looking towards the Indian stock market, particularly in light of the country's growing economy and expanding consumer base. The market's development reflects India's overall economic progress, driven by its young workforce, burgeoning middle class, and technological advancements.
Indian Stock Market's Key Indices and Sectors
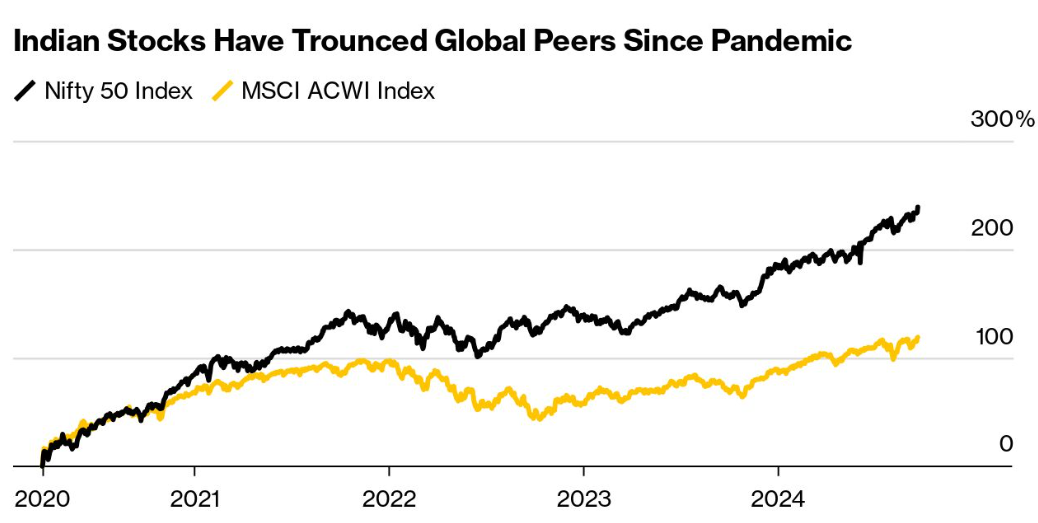
Having established the foundational structure of the Indian Stock Market, it's essential to delve deeper into how the market reflects the country's economic pulse. While the exchanges themselves provide the platform for trading, the key indices, such as the Nifty 50 and Sensex, offer a snapshot of the overall market performance. These indices, alongside the various sectors, play a pivotal role in determining market sentiment and guiding investment decisions. Two of the most well-known indices are the Nifty 50 and the Sensex.
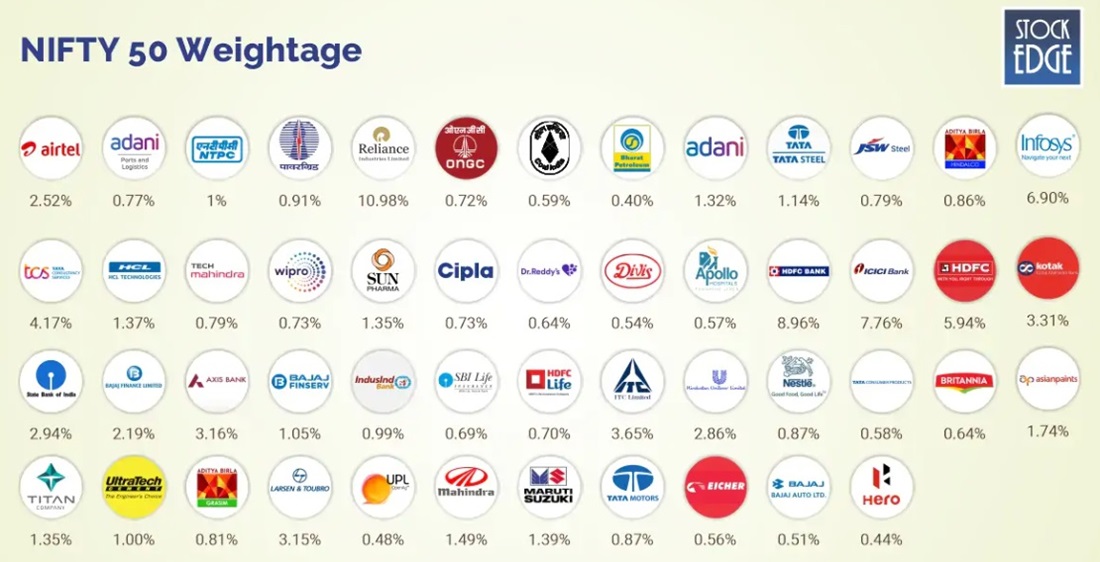
The Nifty 50 is composed of 50 of the largest and most actively traded stocks on the NSE. These companies span across various sectors, from technology to pharmaceuticals, and their collective performance reflects the broader market trend. The Sensex, which is composed of 30 of the most prominent companies listed on the BSE, is another barometer of the market's health, widely used by investors and analysts to gauge the overall economic sentiment.
These indices play a pivotal role in guiding investment decisions. A rising Nifty or Sensex often signals positive market sentiment, while a decline may indicate economic concerns. Investors, both domestic and international, watch these indices closely to assess the market's trajectory and identify potential investment opportunities.
The Indian Stock Market is also characterised by its diverse sectors, each contributing significantly to the country's economic growth. The IT sector, driven by giants like Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and Infosys, is a key player, positioning India as a global leader in outsourcing and technology services. The banking sector, which includes major institutions like HDFC Bank and State Bank of India (SBI), forms the backbone of the country's financial system, enabling credit and investment flows across the economy.
Pharmaceutical companies, such as Sun Pharma and Cipla, represent the pharmaceutical sector, a highly lucrative field, especially given India's position as the world's largest producer of generic drugs. The consumer goods sector, with stalwarts like Hindustan Unilever and Nestlé India, taps into the country's ever-growing consumer market. Lastly, the energy sector, including companies like Reliance Industries and NTPC, plays a crucial role in powering India's industrialisation and economic development.
Each of these sectors not only drives India's economic growth but also reflects the changing needs and aspirations of the population. With such a diverse range of industries, the Indian Stock Market offers numerous opportunities for investors to tap into the country's growth potential.
India Stock Market's Regulatory Framework and Trading Mechanisms
As we explore the key indices and sectors that define the Indian Stock Market, it becomes clear that the market's structure is underpinned by a combination of both traditional industries and emerging sectors. However, for investors to navigate this dynamic landscape successfully, it is equally important to understand the regulatory framework and trading mechanisms that govern the market. These systems ensure that the market operates smoothly, maintains investor confidence, and adapts to global standards. With the growing influx of foreign investments and technological advancements, India's regulatory environment continues to evolve, offering a secure and transparent platform for market participants.
The Indian Stock Market operates under a robust regulatory framework aimed at ensuring investor protection, market transparency, and the smooth functioning of exchanges. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), established in 1988. is the primary regulatory authority overseeing the operations of stock markets in India.
SEBI's primary objective is to protect the interests of investors, promote market transparency, and curb fraudulent practices. Over time, SEBI has introduced a range of reforms aimed at modernising the market, increasing corporate governance standards, and fostering greater investor confidence. Some of the key responsibilities of SEBI include regulating stock exchanges, enforcing securities laws, overseeing mutual funds, and ensuring that publicly listed companies disclose accurate financial information.
In addition to SEBI's oversight, the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) also play critical roles in the regulatory ecosystem. These exchanges set their own trading rules and ensure that market participants comply with established guidelines. The exchanges also offer the infrastructure needed to conduct trades efficiently and securely, from electronic trading platforms to clearing and settlement systems that reduce the risk of fraud.
The trading mechanisms of the Indian Stock Market have evolved significantly, particularly with the advent of electronic trading platforms in the 1990s. These systems replaced the earlier floor-based trading method and allowed for quicker, more efficient transactions. Today, India's exchanges operate on a fully automated trading system, where buy and sell orders are matched electronically, ensuring faster execution and minimal human intervention.
Moreover, the Settlement System—which ensures that trades are completed and the transfer of ownership occurs smoothly—is regulated by institutions like National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL). These organisations ensure that securities are transferred electronically, improving both efficiency and safety.
To enhance market efficiency and reduce systemic risks, in 2024. the SEBI has proposed significant changes to the trading mechanisms of the Indian securities market with the introduction of optional T+0 and instant settlement cycles, in addition to the existing T+1 settlement cycle. These new options aim to enhance market efficiency by reducing settlement times, thereby attracting and retaining investors. The T+0 settlement would complete on the same day for trades up to 1:30 PM, while the instant settlement would process trades on a real-time, trade-by-trade basis until 3:30 PM.
The new mechanisms are designed to increase investor protection by requiring funds and securities to be available prior to trading, thereby mitigating settlement risks and giving investors greater control over their assets. This approach also improves risk management for clearing corporations, as trades are backed by upfront funds and securities.
With the Indian stock market becoming increasingly attractive to investors, selecting the right stocks is key to capitalising on its growth potential. Below is a table of recommended stocks across different sectors based on their strong performance, market leadership, and future growth prospects.
To sum up, the Indian Stock Market is a vibrant, growing hub of investment opportunities, backed by a strong regulatory framework, diverse industries, and rapidly improving market mechanisms. For both seasoned investors and beginners, understanding the market's key indices, sectors, and regulations is essential for making informed investment decisions. With the right knowledge and careful stock selection, investors can tap into India's promising growth trajectory, capitalising on its key sectors such as IT, banking, pharmaceuticals, and energy. By monitoring market trends and focusing on high-quality stocks, investors can unlock the potential of one of the world's most exciting financial markets.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.