At 2am Beijing time on July 28th, the Federal Reserve released its latest interest rate resolution as scheduled. In line with market expectations, this meeting will continue to raise interest rates by 75 basis points, raise the federal funds rate range to 2.25% -2.5%, and continue the previously established process of shrinking the balance sheet.

The website of Foreign Policy magazine in the United States reported on July 28th that in response to inflation, the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates by 75 basis points twice in a row. This move is intended to bring the United States back on track, but it has also caused a chain reaction around the world.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) evaluated the impact of interest rate hikes in developed economies on emerging markets and developing economies in its latest World Economic Outlook report released on July 26th. The increase in borrowing costs, the decrease in credit liquidity, the strengthening of the US dollar, and the slowdown in economic growth will cause more countries to fall into difficulties
Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and other countries have been deeply affected. Liliana Rojas Suarez, senior researcher of the Center for Global Development, a US think tank, said in an interview with Foreign Policy that other countries are likely to become the next victims. Argentina, El Salvador, Egypt, Tunisia and Türkiye have already shown warning signs.
According to CNBC analysis, the Federal Reserve's aggressive rate hikes will hit the global economy in three ways:
One is to trigger a global recession.
Kenneth Rogoff, a famous economist, pointed out earlier this year that the recession in the United States, especially the recession caused by repeated interest rate hikes, will curb global import demand and cause serious damage to financial markets.
The second is to trigger a chain reaction from other countries' central banks.
Kasten Brzeski, head of macro research at Dutch International Group, said that it is expected that the Fed's aggressive rate hike will have an impact on European policymakers. "This clearly means that we may see a stronger US dollar and a weaker euro... The weaker euro increases inflationary pressure, which is truly worrying
The third is to trigger a decline in profits.
Guy Steele, head of emerging markets and credit research at Societe Generale in France, pointed out that in addition to the global economic recession, investors should also be wary of a decline in profits.
US Central Bank
Federal Reserve officials are hawking heavily: Inflation cannot cool down, interest rate hikes cannot stop
After raising interest rates by 75 basis points last week, Federal Reserve officials intensively released "hawks" during the day, downplaying the possibility of the central bank's monetary policy shift and pouring cold water on the market.
The Federal Reserve's "Eagle King" and St. Louis Fed President Brad stated that modern central banks have more credibility than central banks in the 1970s, and the Federal Reserve and European Central Bank can reduce inflation while avoiding a recession and achieve a "relatively soft landing". Brad stated that with high inflation, the central bank still needs to raise interest rates significantly. Data shows that consumer prices in the United States rose 9.1% year-on-year in June, and inflation is running at its fastest pace since 1981. He said, "I think inflation in the second quarter was higher than I expectedSince this situation has occurred, I believe that the interest rate hike will have to be slightly higher than what I previously mentioned
Neel, Governor of the Minneapolis Federal ReserveKashkari stated that the market has overly anticipated that the Federal Reserve will soon retreat on the path of austerity. San Francisco Federal Reserve Chairman Daley stated in a media interview that the Federal Reserve wants to achieve a 2% inflation targetThere is still a long way to go, and we must fulfill our promise to continue raising interest rates well. This year, FOMC Voting Committee and Chicago Fed Chairman Evans expects the Federal Reserve to decide to raise interest rates by 50 basis points at its September meeting.
According to the Zhishang Exchange's interest rate observation tool (FedWatchAccording to the Tool survey, the probability of a 50 basis point interest rate hike in September is 58%, and the probability of a 75 basis point interest rate hike is 42%. It is expected that by the end of the year, the federal funds rate will rise to 3.25% to 3.5%, the highest level since early 2008. The market expects that if tightening measures lead to a recession in the US economy, the Federal Reserve will initiate a rate cutting cycle next summer.
European Central Bank
Doubts about raising interest rates by more than 1 percentage point:
The European Central Bank's monetary policy meeting in late July raised the three key interest rates in the eurozone by 50 basis points to ensure that the medium-term Inflation rate in the eurozone is below the 2% target. This is the first rate hike by the European Central Bank since 2011. After this interest rate hike, the Eurozone deposit mechanism interest rate has ended its negative interest rate for the first time since June 2014. The interest rate of treasury bond of countries with high debt, such as Italy, Greece, Portugal, Spain and other countries, rose in response, which had an immediate contraction effect on their economies.
The money market briefly predicted on Tuesday that the European Central Bank will be forced to halt operations before the rate hike reaches 100 basis points. By contrast, the money market remained betting until July 21st that the overall rate hike would exceed 200 basis points. The European Central Bank raised interest rates by 50 basis points last month, marking the first rate hike since 2011.
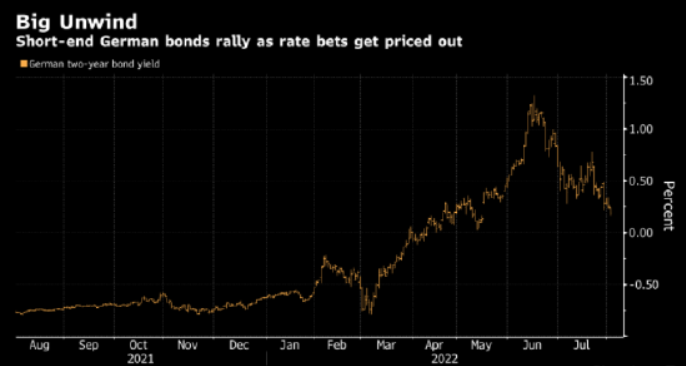
Traders are cutting their expectations for interest rate hikes due to market concerns that excessive tightening may lead to a recession in the eurozone. The record high inflation rate and the increasing possibility of energy disruptions in Russia could both lead to a depression in the 19 member eurozone.
Confidence in radical interest rate hikes has weakened, boosting European treasury bond. The yield of two-year German treasury bond fell to 0.17%, the lowest level since May 16. This sector also benefits from the demand for safe haven assets.
Bank of England
Or raise interest rates by 25 basis points, and the rate hike cycle may slow down:
James Morrison, an associate professor at the London School of Economics and Political Science, recently stated in a video interview with Xinhua News Agency that the US Federal Reserve's interest rate hike will inevitably have a negative impact on the world economy, which is one of the difficulties caused by the position of the US dollar in the international financial system for other economies and their policymakers.
According to data released by the Office for National Statistics on July 20th, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in the UK rose 9.4% year-on-year in June, reaching a new 40 year high. The Chief Economist of the Office for National Statistics, Fitzner, said that the surge in fuel and food prices has driven up inflation levels. Driven by metal and food prices, the ex factory prices of raw materials and manufactured goods continue to rise. The UK's CPI rose by 9% year-on-year in April and 9.1% in May, setting consecutive records for 40 years.
The British government will raise the energy Price ceiling in October, and the Bank of England estimates that the year-on-year CPI growth will exceed 11%. To curb high inflation, the Bank of England announced in June that it would raise its benchmark interest rate from 1% to 1.25%. This is the fifth rate hike by the Bank of England since December 2021.
Samuel Tombs, Chief Economist of Pantheon Macroeconomics in the UK, believes that YouGov's pricing of UK inflation expectations for 5-10 years fell again in July, from 4.0% in June to 3.8%. The full year expectation also decreased from 6.1% to 6.0%. Based on the data changes since the Bank of England's June interest rate decision, the possibility of a 25 basis point rate hike this week is greater than 50 basis points.
Bank of Australia
The pace of interest rate hikes may slow down, and behind the wave of tightening, the sound of "pigeons" rings:
After the July meeting of the Federal Reserve sparked hawkish policy speculation, another developed country central bank played a faint "dove voice" in the wave of interest rate hikes.
On August 2nd local time, the Australian Central Bank raised interest rates by 50 basis points for the third consecutive time, raising them to 1.85%. The cumulative rate hike since May has reached 175 basis points, and the tightening rate is the fastest since the 1990s.

The Bank of Australia will continue to raise interest rates in the coming months. Bank of Australia Governor Philip Lowe stated in a statement that further measures are expected to be taken in the process of normalizing monetary conditions in the coming months.
Despite the Australian central bank raising interest rates by another 50 basis points, the Australian dollar fell against the US dollar, falling below the 0.70 mark. The reason behind this is that the Australian Central Bank has given itself room to adjust the rate hike path when the economic outlook deteriorates, and policy makers may not follow the "predetermined path" to raise interest rates, implying that the pace of rate hikes may slow down.
This means that the Bank of Australia has reserved more flexibility for future policies. The Monetary Policy Committee expects to take further measures to normalize monetary policy in the coming months, but the policy has not taken a predetermined path, and the scale and timing of future interest rate hikes will depend on upcoming data releases.
In fact, compared to regions such as the United States, the eurozone, and the UK, the recession risk of Australia, a major commodity exporting country, remains relatively mild. The Bank of Australia predicts that Australia's GDP will grow by 3.25% in 2022 and 1.75% annually for the next two years. By comparison, the previous expectation was for a growth of 4.2% in 2022 and an annual growth of 2% for the next two years.
The global high inflation data has gradually led central banks around the world to lose patience and accelerate the pace of tightening. The Federal Reserve has already raised interest rates by 225 basis points in 2022. On July 13th, the Bank of Canada raised interest rates by 100bp beyond expectations, with a cumulative increase of 225bp in the first half of the year; The Bank of England also raised interest rates by 100bp in the first half of the yearSince 2022, more than 60 central banks have raised interest rates by at least 50 basis points at once. The global interest rate hike trend is becoming the main theme of the international financial market at this stage.