Forex trading offers the potential for substantial earnings, but the actual salary of a forex trader can vary significantly based on factors such as experience, location, and the financial market they operate in. In countries with well-established financial systems, such as the United States, United Kingdom, Singapore, and Australia, forex traders can expect competitive salaries. These regions provide strong regulatory frameworks, liquid markets, and access to global financial networks, all of which contribute to the income potential for traders. However, while the earning prospects are appealing, it's important to recognise that the salary of a forex trader is not fixed and can fluctuate with market performance, making it both an opportunity and a risk.
Forex Traders: Opportunity vs. Risk
Nowadays, many people are drawn to forex trading due to the potential for high earnings, flexibility, and financial independence. Unlike traditional 9-to-5 jobs, forex trading offers the opportunity to earn based on market performance and personal skill, without a fixed salary cap. Additionally, traders can profit not only from their own trades but also from the activity of others through referral or affiliate programmes. This creates a potential for passive income, making forex trading particularly appealing for those seeking autonomy and the chance to be their own boss.
The flexibility of forex trading is another key attraction. Traders can work from anywhere in the world, choosing when and how much to trade. This makes it ideal for those who value time freedom and want to escape the rigid structure of office work. Furthermore, the allure of financial independence is strong, as successful traders have the potential to scale their business and earn without relying on traditional employment.
However, the high rewards come with significant risks. Forex trading is volatile, and the use of leverage can amplify both profits and losses. Without the right education, discipline, and risk management skills, traders can quickly face financial setbacks. Unlike a regular job, where income is predictable, forex trading offers no guarantees, and many newcomers find the emotional and financial challenges overwhelming. Ultimately, while forex trading offers great potential, it requires careful consideration and a strong understanding of the market before diving in.
Average Salary and Range of Forex Trader
While the potential for high earnings and the flexibility of forex trading are major draws, the actual income a trader can expect varies greatly depending on several factors, including their location, experience, and the markets they trade in. The countries where forex trading is most prominent—such as the United States, United Kingdom, Singapore, and Australia—offer unique advantages, including strong regulatory frameworks and well-established financial systems. These factors play a significant role in shaping the earning potential of traders. Let's now explore how the forex market in these countries impacts the salaries of traders and what makes these regions particularly attractive for those looking to succeed in the forex market.
United States: In the US, the average salary for a forex trader is $115.133 per year, with a range from $66.000 to $199.000 annually. According to Glassdoor, the average salary is $103.608 per year, with a broader range from $70.873 to $112.599. These figures reflect the high earning potential and the significant variation in salaries based on experience and location.
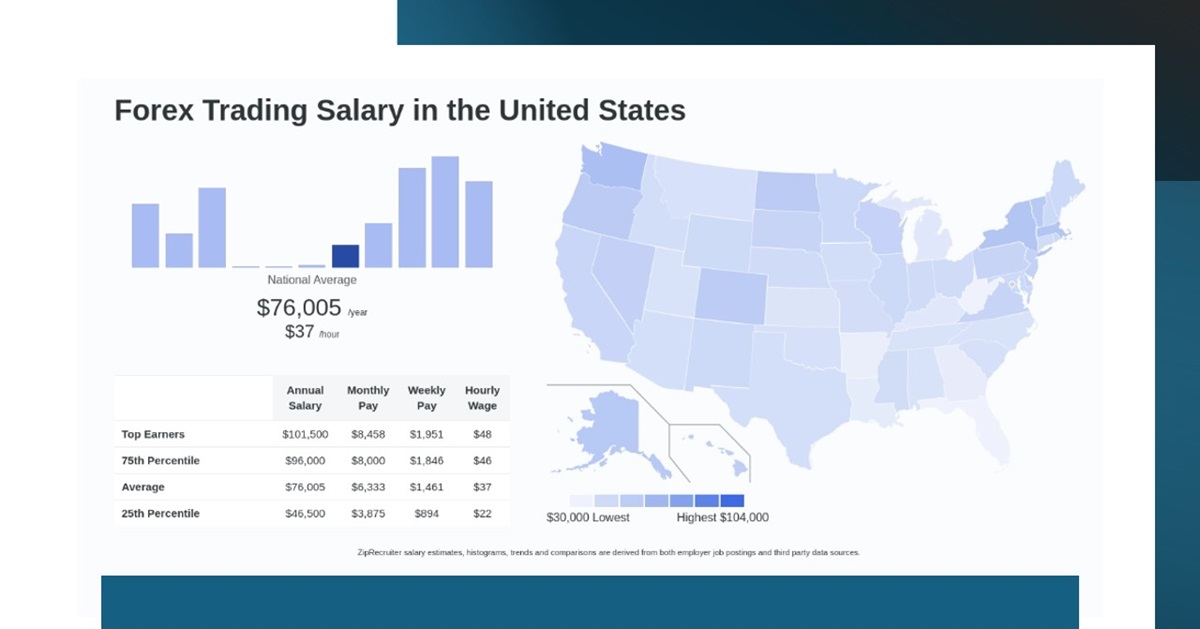
United Kingdom: In the UK, the average salary for a forex trader is £75.000 per year, with entry-level positions starting at £37.500 and the most experienced workers earning up to £90.000. Glassdoor reports an average salary of £138.832 per year, based on 33 salaries submitted anonymously. In London, the estimated total pay for a forex trader is £152.163 per year, with an average salary of £67.300.
Singapore: In Singapore, the average salary for a forex trader is S$198.000 per year, with a range from S$70.000 to S$200.500. Glassdoor reports an average additional cash compensation of S$45.500. Indeed indicates an average monthly salary of S$12.387. which translates to approximately S$148.644 per year. These figures highlight the high earning potential in Singapore, one of the world's major financial centers.
Australia: In Australia, the average salary for a forex trader is AU$87.543 per year. Glassdoor reports a slightly higher average salary of AU$119.831 to AU$135.000 per year, with a range from AU$64.953 to AU$164.235. These figures reflect the robust financial sector in Australia and the opportunities available for forex traders.
Other Factors that Affecting Forex Trader Salary
While location undoubtedly plays a major role in determining a forex trader's salary, it's not the only factor at play. As we've discussed, the financial environment of a region can significantly impact earning potential. Now, let's dive deeper into other crucial elements that influence a forex trader's income.
Among the other factors impact a forex trader's salary, experience is one of the most significant. As traders gain more time in the market, they develop better strategies and risk management skills that can lead to higher earnings. Experienced traders are more likely to understand the market's behaviour, make smarter decisions, and secure higher-paying roles or opportunities.
Another key factor is the trading strategy a trader uses. Whether they're a short-term, high-frequency trader or prefer a longer-term approach, successful strategies can lead to better profits. Traders who focus on certain markets or use advanced tools like technical analysis or algorithms often earn more, as their strategies can tap into specific opportunities for growth.
Last but not least, risk management is also critical to a forex trader's income. Traders who know how to manage their risks effectively, using tools like stop-loss orders or leveraging wisely, can protect their capital and maintain steady profits. Those who take on too much risk may see big rewards, but they also face greater chances of losses, which can cause fluctuations in their earnings.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.