In recent times, I have been surrounded by more and more friends who are opening UK FCA accounts.
The UK FCA has always been known as the "strongest financial regulation". Unfortunately, there has been no channel to open FCA accounts in China for a long time. But as foreign exchange investment becomes increasingly popular, some high-quality FCA Securities firms are also beginning to enter the public's view. For example, my friends are all at EBCAccount opened by the group.
Coincidentally, the EBC Group has recently launched a free account opening activity. During this period, opening an FCA account at EBC can exempt all fees, including authentication fees and remittance processing fees.
So before opening an FCA account, let's evaluate from all dimensions, why is FCA called the strongest regulatory authority?
As shown in the following figure, I took some time to make a detailed summary, which basically covers the financial regulatory agencies that are most easily accessible to us in our transactions.
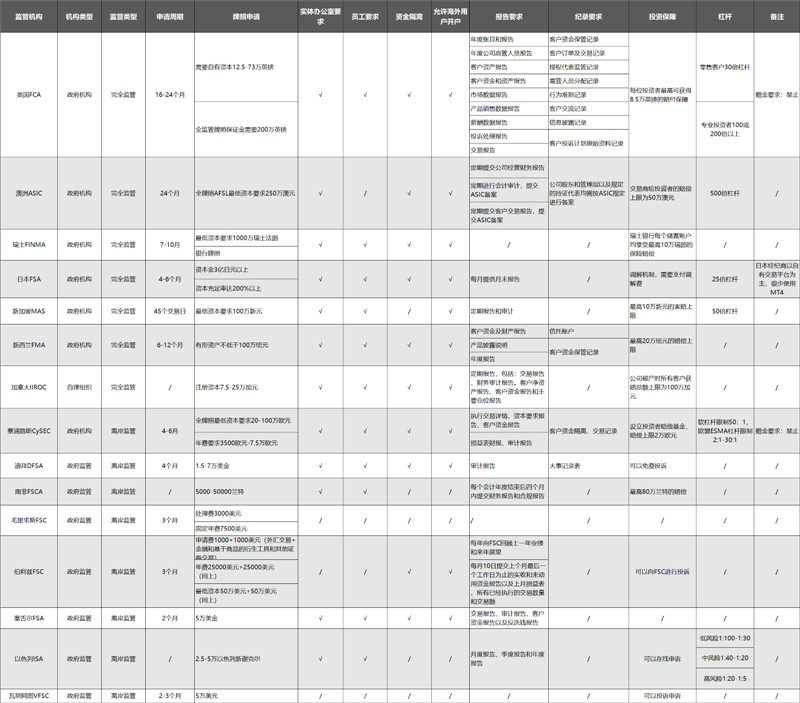
Some people may question why there is no US NFA. Firstly, there are very few NFA licensed institutions, which can be said to be uncommon; Secondly, there is no NFA account opening channel in China, so it is not within the scope of our current discussion.
I have compared this list based on application thresholds, reporting and record requirements, leverage requirements, etc. Additionally, I have compared investment protection plans of major regulatory agencies.
There are also two dimensions, including the implementation of regulation and investment protection, which I did not reflect on this table because there is no specific standard for the implementation and execution status. I will intersperse these dimensions in the analysis.
1、 Application Threshold:
The application threshold includes the application period and application fee.
In my opinion, top-level regulation must have a very high application threshold. Because regulation itself is a screening process, low thresholds often lead to mud and sand, making it easy for users to fall into the trap of false platforms. There are two common dimensions, one is the application cycle, and the other is the application fee.
1. From the perspective of application cycle:
The cycles of FCA in the UK and ASIC in Australia are the longest, taking around 2 years each.
In contrast, other fully regulated licenses generally last between 6 and 12 months, while offshore regulatory licenses typically only last between 2 and 3 months, making it much easier to pass.
So, in terms of application time, Australian ASIC=UK FCA> Switzerland FINMA=New Zealand FMA> Japan FSA=Cyprus CySEC> Others.
2. From the perspective of application fees:
① Switzerland has a higher FINMA, which requires holding a banking license in addition to a minimum capital requirement of 10 million Swiss francs
② The full FCA license in the UK is approximately £ 2.125 million to £ 2.73 million
③ Japan's FSA is also relatively high, with a capital of over 300 million yen, equivalent to around 1.7562 million pounds;
④ The Australian AFSL application requirement is equivalent to £ 1.3395 million
⑤ Other fully regulated licenses are generally below $1 million, while offshore regulation is as low as around $20000 to $50000
So, in terms of application fees, Switzerland FINMA> UK FCA> ASIC Australia=FSA Japan> other
Of course, it is not enough to only look at these two dimensions, but also to consider some implicit factors.
Firstly, there is the issue of institutional review. Most regulatory agencies submit application materials according to requirements and follow the process step by step.
But there are also individual institutions that have additional requirements, such as Swiss FINMA requiring a bank license.
However, mature regulatory agencies such as the FCA in the UK conduct layer by layer audits and background checks on the platform when reviewing corporate qualifications, making it more difficult for them to pass compared to other regulatory agencies.
The second issue is the freezing of funds. If you look closely, you will find that most regulatory agencies provide minimum funding requirements. Generally speaking, as long as the license plate is issued, the capital will become the operating capital of the platform, which can be used, but the financial constraint is actually limited.
So some platforms adopt an application fee+annual fee model, but generally the annual fee requirements are not high.
The most troublesome thing is actually the UK FCA, as it uses a margin model. This part of the funds is generally unusable and may even be requested by the FCA to be added, which greatly tests the platform's cash flow.
Overall, in terms of application threshold, FCA> in the UK; ASIC Australia=FINMA Switzerland> Japan FSA=New Zealand FMA> other
2、 Reporting and Recording Requirements:
Continuous supervision is the main responsibility of financial regulatory agencies.
Generally, platforms submit reports regularly and regulatory agencies review them. Of course, mature financial regulations such as the FCA in the UK will also conduct inspections through proactive inquiries, requiring platforms to explain some abnormal behaviors and phenomena, resulting in higher overall regulatory efforts.
In terms of the content of reports and records, the UK FCA is a unique entity, including 9+8 reporting and record requirements, which can be said to cover all aspects of financial regulation, and even supervise information such as complaint handling and customer communication. For example, if you have obvious violations in handling a complaint, or if you have misleading information in communicating with users, it will be judged as a violation by the FCA, and even corresponding penalties will be imposed.
In recent years, the FCA has almost suspended the issuance of licenses and cancelled a considerable number of non compliant licenses, which has increasingly high requirements for licensed institutions to operate in compliance.
Other comprehensive regulations generally include 3-5 items such as regular reports, audit reports, and customer reports, such as ASIC in Australia and FMA in New Zealand. Some regulations also require proof of fund segregation. Although the intensity and scope are not as strong as those of FCA, the prevention of general risks is still relatively effective.
FINMA in Switzerland does not have very clear requirements for reporting and recording reports, but it will conduct regular evaluations of licensed institutions. Generally, large institutions conduct evaluations once a year, medium institutions conduct evaluations every 2-3 years, and small institutions generally only conduct temporary evaluations, with some uncertainty. So, when trading on FINMA licensed platforms in Switzerland, try to choose a larger platform as much as possible.
If it is offshore supervision, except for CySEC in Cyprus, there may not be clear requirements for report disclosure, and the overall safety factor is also low.
Overall, in terms of reporting and recording requirements, as well as ongoing supervision, FCA> in the UK; ASIC Australia=FMA New Zealand> Cyprus CySEC=Canada IIROC=Switzerland FINMA> other
3、 Investment Guarantee
There are many institutions that provide investment protection.
In addition to the UK FCA's FSCS compensation plan of up to £ 85000, which we are most familiar with, there is also an Australian ASIC providing compensation protection up to AUD 500000, and a Swiss FINMA providing insurance compensation of up to CHF 100000 per savings account.
But to be honest, at least from my knowledge and understanding, when it comes to financial compensation, most people's first reaction is the UK FCA. This is because FCA has always been an industry benchmark in the implementation of financial compensation.
The exact number is unknown, but since 2001, the FSCS program provided by the FCA in the UK has roughly helped around 4.5 million people, with compensation amounts of at least £ 26 billion. This is all that we can actually feel.
Recently, in order to rescue Credit Suisse, Swiss FINMA chose to fully write down ATI bonds. Simply put, FINMA approved the restructuring plan without consulting creditors in advance, which resulted in investors of AT1 bonds bearing all losses.
Although FINMA has policy considerations in doing so, as an investor, my intuitive impression is that investment risks have increased, which is in contrast to the implementation of FCA's compensation. That's why I said that compensation is not based on standards, but on implementation.
So, in terms of investment protection, I believe it is the UK FCA> Others.
4、 Lever
Providing different leverage based on user types is actually a very important dimension for measuring financial regulation. Because it involves the dimension of user protection, it not only requires the development of specialized classification standards, but also separate supervision.
In recent years, top regulatory agencies have been very cautious in their leverage, generally only allowing up to 500 times. If your platform allows leverage of 1000 or even 2000 times, 99.9% is offshore supervision.
EU New Regulation MiFIDAfter the announcement of II, the use of leverage has become more restrained, and even stated that leverage will be limited to around 1:30 in the future. So many foreign exchange platforms, and even some large platforms, in order to avoid the new EU regulations, have transferred their business and users to other regulatory licenses.
There are two "unpleasant" aspects to the EU's new regulations:
① Different leverage ratios should be given based on customer trading experience, which means that platforms and regulatory agencies should classify customers;
② The leverage is too small, and many retail investors feel that 30 times the leverage is too small to meet their trading needs.
So, only by providing different levers based on user types can we balance the function of user protection while regulating.
At present, only the UK FCA, Cyprus CySEC, and Israel ISA regulatory agencies provide different leverage based on user classification, with only the UK FCA providing complete regulation.
So, in this regard, the UK FCA> Cyprus CySEC=Israel ISA> Others.
The above is a comprehensive evaluation of major regulatory agencies, with scores of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1 in descending order. I have roughly drawn a table where the UK FCA is undoubtedly the strongest regulatory agency.
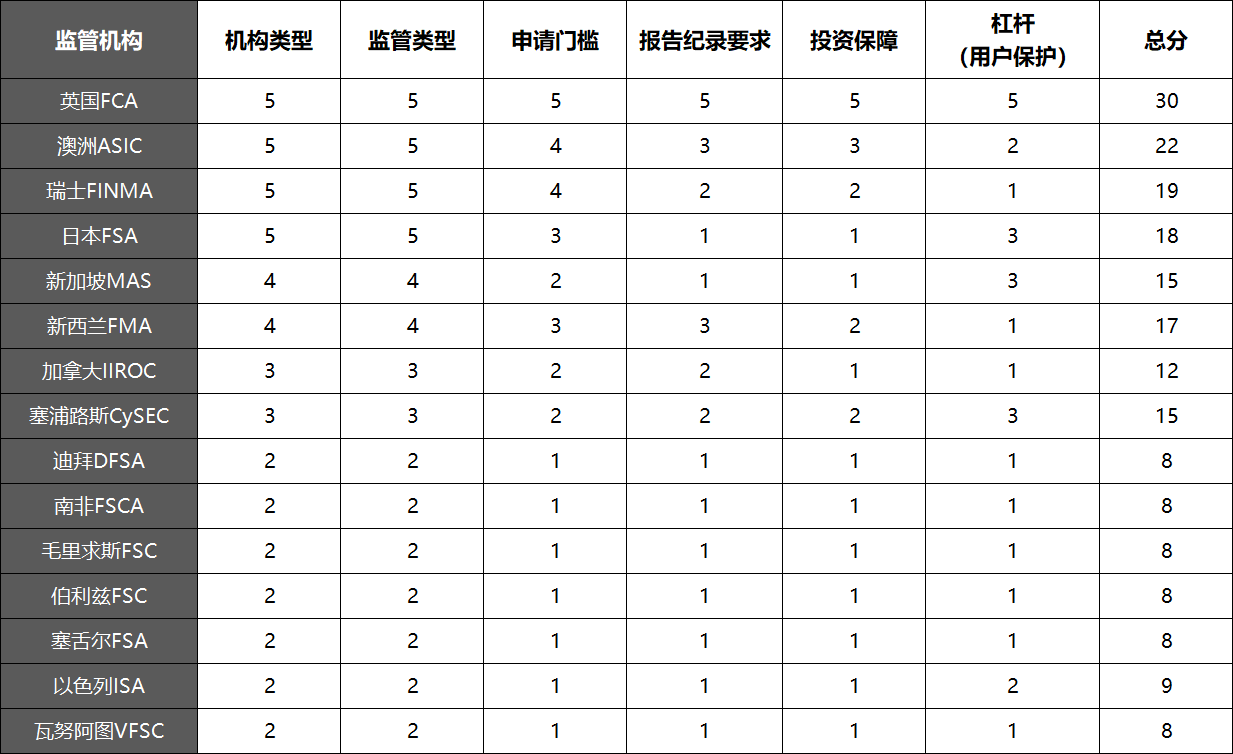
Of course, as I mentioned at the beginning, the evaluation criteria are thousands of people and faces.
Some people will also pay attention to the countries where regulatory agencies are located, such as those in the UK and the United States, which are definitely much better than some countries with weak financial industries. From this perspective, the FCA in the UK, the oldest financial country, also has an advantage.
As far as I know, EBC Group is also the only one in China that wants to open a formal FCA account and enjoy more than 100 times the leverage.








