The Forex fundamentals are the backbone of understanding how the largest and most liquid financial market in the world operates. With daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion, the Forex market is a central part of global financial systems. Unlike stock markets, which are typically structured around central exchanges, the Forex market operates over-the-counter (OTC) and is decentralised. This means currencies are traded directly between participants — including banks, brokers, hedge funds, corporations, and individual traders — across a vast global network.
Understanding Forex fundamentals is crucial for anyone looking to engage in Forex trading. These fundamentals provide the framework for understanding how global economic, political, and social factors influence the movement of currency pairs. More than just trading tools, these fundamentals encompass a wide range of variables, including interest rates, inflation, political events, and central bank policies. Grasping these elements is key to making informed, strategic decisions in the ever-evolving Forex market.
This article will delve into the core principles of Forex fundamentals, offering a comprehensive view of the factors driving currency movements, the role of economic indicators, and the impact of geopolitical events. Armed with this understanding, traders can navigate the complexities of the Forex market and build a solid foundation for successful trading.
Forex Fundamentals' Basics: Currency Pairs and Exchange Rates
A fundamental concept of the Forex fundamentals is the idea of currency pairs. Every currency in the Forex market is traded in relation to another, meaning currencies always come in pairs. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro is the base currency, and the US dollar is the quote currency. The exchange rate tells traders how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.

Understanding currency pairs is essential to Forex fundamentals because fluctuations in the exchange rate are the primary indicators that drive trading decisions. These changes are often caused by a combination of economic fundamentals that reflect the relative strength of the economies behind the currencies involved. When a country's economic outlook improves, its currency tends to appreciate, while poor economic performance can lead to depreciation.
A deeper understanding of Forex fundamentals also involves knowing the distinction between major, minor, and cross-currency pairs. Major currency pairs include the US dollar and are highly liquid, making them ideal for both beginners and seasoned traders. Minor pairs and cross-currency pairs, however, involve less liquid currencies and can be more volatile, which presents both greater risk and reward for traders. Knowing which currency pairs to focus on is a crucial aspect of these fundamentals.
Forex Fundamentals' Key Factors: Economic Data and Geopolitical Events
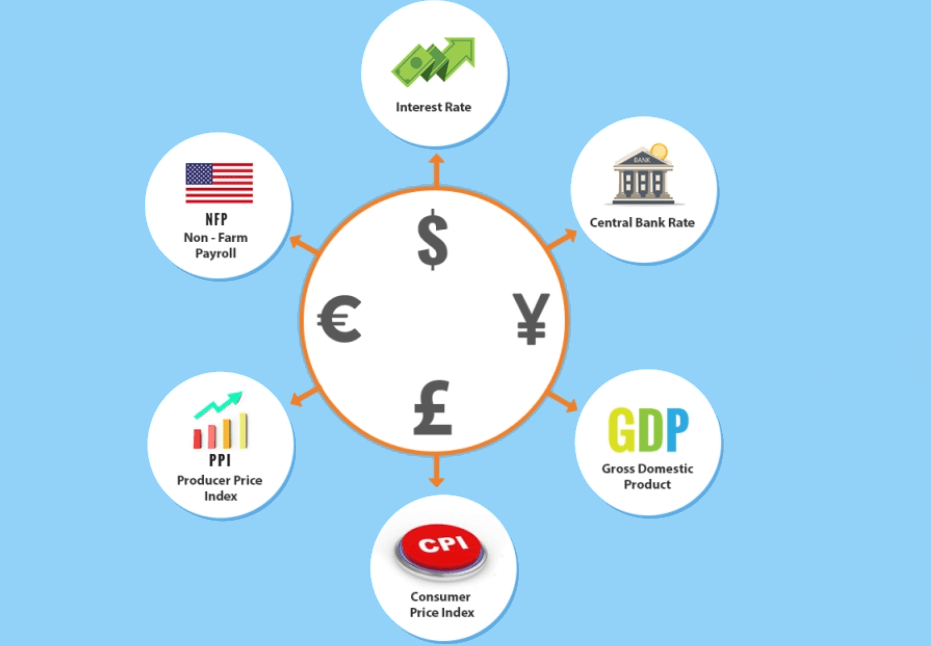
Economic fundamentals play an essential role in understanding the Forex market. Economic data provides vital insights into the health of a nation's economy and directly influences the relative value of its currency. Key economic reports, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, employment statistics, and trade balances, offer traders a window into how strong or weak an economy is, which in turn affects its currency's value.
For example, GDP growth shows the overall economic output of a country. A robust, growing economy usually strengthens the currency because it signals stability and growth. Conversely, a shrinking GDP indicates a contracting economy, which can cause a currency to lose value.
One of the most important Forex fundamentals is understanding how interest rates impact currency values. Central banks use interest rates to control inflation and stimulate economic growth. When a central bank raises interest rates, it makes the country's currency more attractive to investors because higher interest rates generally lead to higher returns on investments in that country's assets. As a result, the currency appreciates. Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, the currency may weaken, as investors move their capital elsewhere in search of higher returns.
In addition to economic reports, Forex fundamentals also include central bank policies. The Federal Reserve (US), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of England, and other central banks play a key role in shaping the value of currencies. These institutions influence currency markets through monetary policy decisions, such as changes to interest rates, quantitative easing, and other tools. A central bank’s stance on inflation and its outlook for future growth directly impacts how its currency behaves in the Forex market.
While economic fundamentals are at the heart of currency fluctuations, geopolitical events and market sentiment also have a profound effect on currency markets. Geopolitical events like elections, natural disasters, and international conflicts can cause dramatic shifts in currency values. These events often create uncertainty, which makes traders reassess the risks associated with a particular currency.
For instance, political instability or an unexpected election result can cause the currency of the affected country to drop as traders pull their investments out in search of safer assets. Market sentiment—the collective mood of investors—can also drive the market in the short term. Positive sentiment can cause currencies to appreciate, while negative sentiment can lead to depreciation. Understanding market sentiment is an essential part of Forex fundamentals because it reveals the psychological forces that shape price movements.
For example, during global crises such as trade wars or political instability, investors tend to flock to safe-haven currencies like the US dollar, Swiss franc, and Japanese yen. This can lead to the appreciation of these currencies, even when other economic indicators may not be particularly strong.
Forex Fundamentals' Function in Risk Management and Trading Strategy
The volatility and complexity of the Forex market make risk management a fundamental aspect of any trading strategy. Since currencies can fluctuate dramatically in response to economic fundamentals or geopolitical events, managing risk is critical to long-term success. Effective risk management ensures that you can protect your capital and avoid significant losses, especially when trading with leverage.
Traders can use a variety of tools to manage risk, such as stop-loss orders and take-profit orders, which automatically close a position at a predetermined price level. By using these tools, traders can limit their potential losses and lock in profits when the market moves in their favour. In addition, the use of position sizing helps traders determine how much of their trading capital to risk on each trade, ensuring that no single trade jeopardises their overall portfolio.
Risk-to-reward ratios also play a significant role in Forex fundamentals. Traders typically aim for a higher potential reward compared to the amount of risk they take. For example, if a trader risks 50 pips on a trade, they may aim for a reward of 150 pips, giving them a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:3. Maintaining a favourable risk-to-reward ratio is one of the cornerstones of a sound trading strategy.
Moreover, leveraging fundamental analysis in conjunction with technical analysis can provide a comprehensive view of the market, allowing traders to make more informed decisions based on both long-term trends and short-term volatility. A successful Forex trading strategy is built on a solid understanding of Forex fundamentals. By incorporating key economic fundamentals such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and employment figures, traders can make predictions about how currencies will move in response to these factors. Understanding the relationship between central bank policies and currency value is also vital in crafting a well-rounded strategy.
Traders who focus on Forex fundamentals typically look for long-term trends, but they also need to remain flexible in the short term, adjusting their strategies in response to new information. Combining fundamental analysis with technical analysis, which examines past price movements and Chart Patterns, can lead to more accurate predictions and better trading outcomes.
For example, a trader might identify a country with strong economic growth and rising interest rates, indicating a potential opportunity to buy that country's currency. On the flip side, if a country's economic indicators are weak and inflation is rising, the trader might consider selling its currency. The key to success in Forex trading lies in synthesising Forex fundamentals with market knowledge, risk management, and strategic planning.
In conclusion, understanding Forex fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to trade currencies successfully. The Forex market is driven by a complex web of economic fundamentals, central bank policies, geopolitical events, and market sentiment, all of which influence currency movements. By developing a deep understanding of these factors, traders can make informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and maximise their potential for long-term success.
Whether you're a novice trader or an experienced professional, mastering Forex fundamental is the first step toward becoming a successful participant in this fast-paced and dynamic market. By staying informed, adopting risk management strategies, and continuously adapting to new information, traders can unlock the potential of Forex trading and navigate its complexities with confidence.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.