After a two-and-a-half-year cycle of interest rate hikes, the Fed finally announced an interest rate cut and a one-time 50 basis point cut, which undoubtedly became one of the most important events of the year in the financial world. While many people were vague about the news, everyone realized that the potential impact of the Fed Rate Cut would be far-reaching and wide-ranging. Next, we will discuss the purpose of the Fed rate cut and its impact on the international financial markets so that we can better seize market opportunities.
 The Purpose of the Fed Rate Cuts
The Purpose of the Fed Rate Cuts
The Federal Reserve refers to the central bank of the U.S. The Fed rate cuts refer to the U.S. Federal Reserve System's lowering of its benchmark interest rate in order to stimulate economic growth and increase employment. By lowering the cost of borrowing, interest rate cuts are intended to encourage consumers and businesses to increase spending and investment, thereby boosting economic activity. In times of economic slowdown or risk of recession, interest rate cuts are seen as an effective monetary policy tool to help boost market confidence and maintain financial stability.
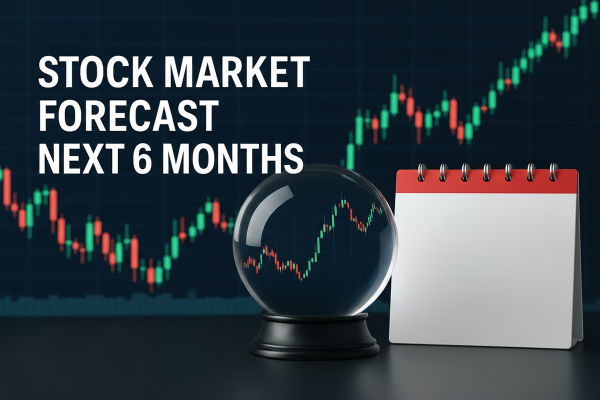
On September 18. 2024. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell announced a 0.5 percentage point cut in the policy rate, a cut that reflected the complexity of the current economic environment. Firstly, inflation has been effectively controlled over the past few months, providing room for a rate cut; secondly, the economy is at risk of a potential recession, and the rate cut is intended to boost economic growth by lowering borrowing costs and stimulating consumption and investment. This policy is intended not only to boost market confidence but also to stave off a possible economic slowdown by maintaining a strong labor market.
However, despite the need to cut interest rates, the current U.S. economy as a whole is still performing well, with GDP growth remaining at 3.1% and is expected to continue to achieve positive growth in 2024. This suggests that the purpose of this Fed rate cut is not only to deal with a potential recession but also to maintain sustained economic growth and labor market stability. Through moderate interest rate cuts, the Fed hopes to stimulate economic vitality while ensuring market resilience and long-term health.
Currently, the Fed's top priority is to achieve maximum employment and price stability. Therefore, this interest rate cut is designed to stimulate economic activity by reducing borrowing costs and encouraging consumption and investment, thereby creating more jobs. In the current economic environment, the Fed rate cuts are seen as a necessary measure to keep the labor market strong in the face of inflationary pressures and a potential economic slowdown. This policy not only helps ease the financing burden on businesses but also encourages consumers to spend more, further boosting economic growth.
Although inflation in the United States has eased over the past few months, it still puts pressure on consumers' cost of living and affects their purchasing power. To address this challenge, the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts have become a key policy tool aimed at lowering the cost of borrowing, thereby stimulating consumption and investment.
By making loans and credit more affordable, interest rate cuts not only encourage consumers to spend more but also promote capital investment by businesses, which in turn boosts overall economic growth. This strategy hopes to further control inflation and keep the economy on a healthier track to improve people's living standards.
At the same time, the U.S. economy is also facing the risk of a potential recession, so cutting interest rates is seen as an effective preventive measure. It can stimulate economic activity and prevent recession due to economic slowdown. By lowering interest rates, the Fed hopes to increase the resilience of the economy so that it can better adapt and bounce back in the face of external shocks. This policy will not only help boost consumer and business confidence but also promote investment and consumption, thereby providing support for economic growth and ensuring its stability in an uncertain environment.
The announcement of the Fed rate cuts was aimed at boosting market confidence, a policy that is usually viewed positively by market participants as a sign of a healthy economy. This optimism helps boost the stock market and other asset prices, which in turn creates a more favorable investment environment. Rising investor confidence not only encourages them to spend and invest more but may also push businesses to increase their capital expenditure and expansion plans, thus further boosting economic growth. This positive cycle helps consolidate the economic recovery and drives the overall performance of asset classes to a positive level.
Interest rate cuts have significantly reduced borrowing costs, making it easier for businesses and consumers to obtain financing. Businesses can invest and expand at lower interest rates, boosting projects and innovation and increasing employment opportunities. Consumers, in turn, can enjoy more affordable loans for home purchases and consumption, stimulating the housing market and consumer spending. This two-way push enhances economic dynamism, contributes to overall economic growth, and boosts market confidence.
The Federal Reserve hopes to gradually adjust interest rates to a more neutral level through moderate interest rate cuts in order to achieve sustainable economic growth. The Fed's interest rate reduction policy aims to stimulate economic activity while keeping inflation within a manageable range, thus avoiding price increases due to overstimulation.
By fine-tuning interest rates, the Fed is able to provide a stable economic environment for investors and consumers, prompting them to be more confident in their borrowing and spending decisions. This balanced strategy not only helps maintain a healthy job market but also lays the foundation for long-term economic stability.
Overall, this Fed rate cut is designed to balance employment and inflation risks and guard against a potential recession while promoting economic growth and market confidence. Going forward, investors and economic analysts will pay close attention to the long-term effects of the rate cut and its impact on the economy. By cutting interest rates, the Fed is attempting to maintain economic stability and growth in the current complex economic environment.
 Impact of the Fed rate Cuts on the United States
Impact of the Fed rate Cuts on the United States
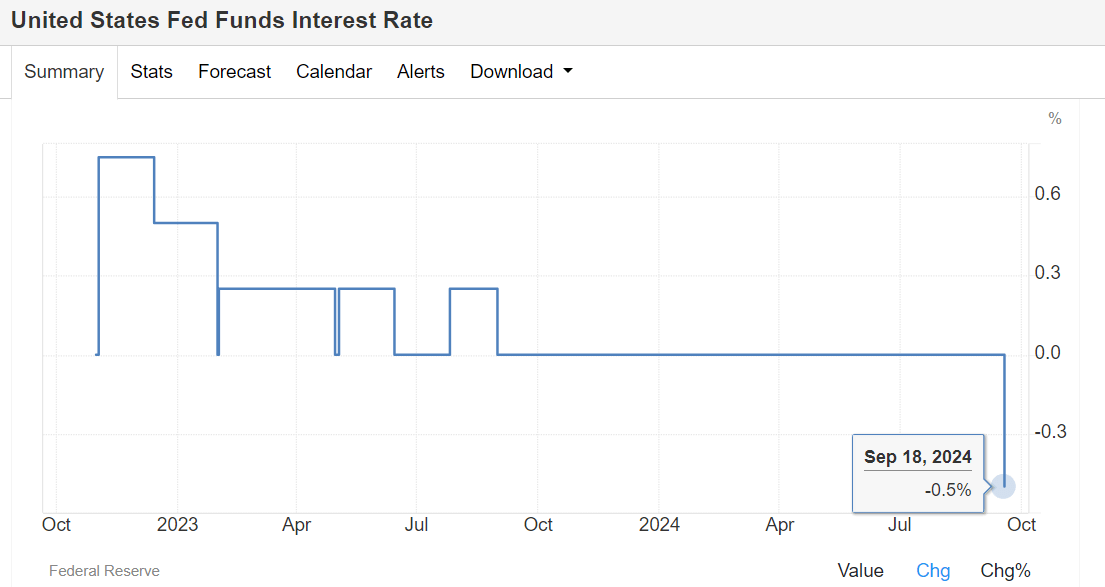
Although the aim was to promote economic growth, the stock market did not rebound as expected after the announcement of the Fed rate cuts but instead fell. As shown in the chart above, the Nasdaq index ended the day with a big drop after the Fed rate cuts. This was largely due to uncertainty in the market's expectations for future rate cuts, especially after Fed Chairman Powell stated that there would be no rush to cut rates further.
The decision to cut rates triggered mixed reactions in the market, reflecting investors' mixed views on the economic outlook. Risky assets such as the equity market expressed dissatisfaction with the Fed's easing intentions, arguing that the rate cuts were insufficient and not effective in dispelling fears of a potential recession, thus affecting investor confidence and market performance.
Meanwhile, safe-haven assets such as gold have expressed concern about the risk of inflation that could be triggered by significant easing, with investors seeking safety while also feeling uncertain about the future path of monetary policy. This divergence reflects the market's cautious attitude towards the current economic environment, as well as multiple interpretations of future trends.
In addition, the Fed's decision to cut interest rates will have an impact on U.S. politics. In the run-up to the upcoming elections, the rate cut is seen as a favorable move for the ruling Democratic Party, aimed at boosting the economy and improving people's lives. In this context, the rate cut is not only an economic tool but also part of a political strategy.
Meanwhile, the Fed rate cuts will have different impacts on various sectors in the U.S. Certain sectors will benefit from it, especially real estate, fintech, consumer goods, construction, and clean energy, as well as dividend stocks, which will have more investment and market opportunities as a result of lower financing costs.
However, the banking sector could face a negative impact, with lower interest rates potentially compressing its profit margins. This disparity between sectors not only creates new opportunities for investors but also poses corresponding challenges, prompting them to be more flexible in their investment strategies to adapt to the changing market environment.
The US real estate market will benefit from interest rate cuts because they reduce borrowing costs and make it easier for homebuyers to obtain loans. This policy prompts consumers to be more willing to invest in real estate, thus stimulating demand for home purchases. With lower interest rates on loans, homebuyers are less stressed about their monthly payments, further increasing their purchasing power. This environment will not only boost new home sales but is also likely to drive activity in the secondary home market and overall provide positive growth momentum for the real estate sector, fueling the economic recovery.
Fintech companies such as Visa and PayPal will benefit from increased spending on the back of economic stimulus and the Fed rate cuts. Lower borrowing costs have made consumers more inclined to spend, fueling the growth of online payments and digital transactions, directly boosting transaction volumes and revenues for these companies. This trend not only strengthens their market position in the fintech space but also drives these platforms to innovate and expand new services to meet the rising demand for convenient payments, leading to continued business growth.
Interest rate cuts will stimulate the market for high-unit-priced consumer goods, such as cars and luxury goods, prompting consumers to be more willing to borrow for larger purchases. Lower borrowing costs enhance consumers' purchasing power, making them inclined to invest in new cars, luxury brands, and high-end appliances. This increase in consumption not only boosts sales in these sectors but is also likely to drive the overall economic recovery, with manufacturers and retailers increasing their inventories and production to meet growing demand, thus further boosting related industries.
The Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts will also significantly reduce borrowing costs, which will drive investment and development in the construction and clean energy sectors. For construction projects, businesses and developers will be able to raise capital at lower financing costs, boosting the development of new homes, infrastructure, and commercial buildings.
At the same time, clean energy investments will also benefit from more attractive financing conditions, especially in renewable energy projects such as solar and wind, where companies will be more willing to commit capital to achieve sustainable development goals. This will not only help accelerate the transition to a green economy but may also create more jobs and boost overall economic growth.
In an environment of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve, low interest rates have made fixed income investments less attractive, prompting investors to turn to the stock market, particularly dividend stocks. Such stocks offer stable cash flows and relatively high returns, attracting income-seeking investors. Lower borrowing costs make it more likely that companies will increase their dividend payments, further enhancing the attractiveness of dividend stocks. This increased demand not only pushes up share prices but also boosts market confidence, prompting investors to allocate their assets more aggressively to the stock market, which in turn drives economic growth.
And while a low interest rate environment is likely to see a rise in demand for borrowing, driving growth in the lending business of U.S. banks, it could also have a negative impact on bank profitability. Specifically, low interest rates can compress a bank's net interest margin, which is the narrowing of the difference between the interest income a bank earns on its lending and the interest it pays to depositors. This narrowing of the net interest margin limits the scope for banks to make profits in their traditional lending business, which may lead to a decline in overall profitability.
To meet this challenge, banks need to adopt a variety of measures to maintain stable financial performance and meet shareholders' return expectations. Among them, adding other fee-based services, strengthening risk management, and diversifying revenue sources are important strategies. These adjustments will not only help banks make up for the losses from narrower spreads but also enhance their overall operational efficiency, thereby strengthening their resilience in a competitive financial market.
Overall, the Federal Reserve's policy of cutting interest rates aims to stimulate economic recovery, which is theoretically beneficial to most high-unit-priced products and the property market. However, the market's reaction is affected by the uncertainty of future policies. Investors need to closely monitor economic indicators and market dynamics in order to formulate investment strategies accordingly.
Impact of the Fed rate Cuts on Other Financial Markets
The United States, as an international financial giant, has a far-reaching impact on the global financial economy with its interest rate resolutions. This rate cut marks the first time the Fed has turned after four years of rate hikes, which may trigger a chain reaction of global capital flows and market volatility. This Fed rate-cutting cycle will not only affect investor sentiment but could also reshape the international financial landscape.
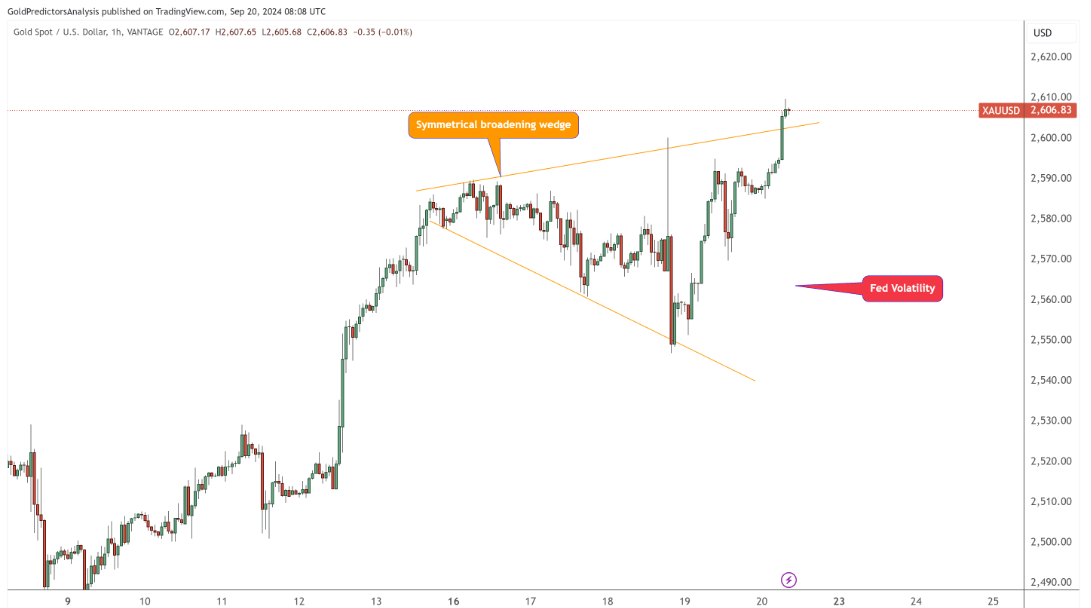
Interest rate cuts help improve liquidity in global capital markets, boost asset prices, promote the wealth effect, and further stimulate consumption and investment. When borrowing costs are lower, businesses and consumers are more willing to spend, which could boost demand for commodities, especially oil and metals, and thus push up their prices. As shown in the chart above, the price of gold has been fluctuating between the upper and lower levels of the wedge and breaking out to new highs since the Fed cut interest rates. This increased demand for commodities tends to drive a recovery in global commodity markets.
Looking again at the property market, although the Fed rate cuts may be good for domestic property stocks, the current property market remains in the doldrums, with sales and investment both falling sharply. The restoration of market confidence requires an overall improvement in the economy, and consumers will be willing to invest and spend only on the premise that employment and income are secure.
In addition, the Fed rate cuts will also enhance market liquidity and stimulate the rise in stock and bond prices. In a low-interest rate environment, investors seeking higher returns have turned to the stock and bond markets, attracting more capital inflows and further boosting the climb in asset prices. This trend is not only favorable to investors but may also trigger optimistic expectations of economic growth, contributing to overall economic recovery and development.
Interest rate cuts usually trigger a positive reaction in global financial markets, leading to a general rise in stock markets and a significant increase in investor confidence, which in turn pushes up demand for risky assets. However, interest rate cuts by the Fed could also exacerbate the risk of asset bubbles, particularly in equity and property markets, which could pose a threat to global financial stability.
For emerging markets in particular, a Fed rate cut would lower interest rate differentials with other countries, prompting capital to flow out of the United States and into emerging markets where interest rates are higher, thus easing capital outflow pressures. At the same time, the weakening of the United States dollar may also alleviate the depreciation pressure on emerging market currencies.
At the same time, the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts may trigger a concerted adjustment of global monetary policy, with other countries' central banks likely to follow the Federal Reserve's easing measures. Because the weakening of the dollar may prompt the central banks of other countries to adopt corresponding monetary policy easing to maintain exchange rate stability and promote their own economic growth. This chain reaction could trigger currency competition on a global scale, making it more challenging for central banks to respond to economic pressures, which would have far-reaching implications for the stability of international financial markets.
As a number of central banks, including the Federal Reserve, turn to easing, the global economy will shift from the previous pattern of raising interest rates to fight inflation to stimulating the economy through interest rate cuts. This shift will directly reduce borrowing costs and stimulate business investment and consumer spending, thereby boosting market confidence and driving global economic recovery. This effect is particularly evident in credit-dependent economies.
In addition, the depreciation of the United States dollar could lead to a relative appreciation of other currencies, and such exchange rate changes would have a direct impact on the earnings of multinational enterprises and the balance of trade. Specifically, a weaker dollar makes dollar-denominated goods more price-competitive in international markets, thereby stimulating United States exports and enhancing the international competitiveness of the manufacturing sector.
However, a weaker dollar also raises the cost of imported goods, increasing the expenditure burden on consumers and firms and affecting the consumption structure and corporate profits in the domestic market. Such changes may not only reshape the relationship between the United States and its major trading partners but may also prompt other countries to make adjustments in their monetary policies and trade strategies, creating new international trade dynamics.
In short, the Fed rate cuts not only affect the U.S. economy but also trigger a global chain reaction. Low interest rates attract capital into high-yield markets, pushing up asset prices and stimulating consumption. At the same time, central banks in other countries may take easing measures to maintain economic stability. These policy adjustments have reshaped financial markets and international trade patterns, and investors need to pay close attention to the Fed's dynamics in order to seize market opportunities.
Fed rate cuts' purpose and global market impact
| Purpose |
International Financial Market Impact |
| Lower borrowing costs to encourage investment. |
Boost global market liquidity and raise asset prices. |
| Boost employment and maintain labor stability. |
Attract capital to emerging markets, easing outflows. |
| Avoid recession by stimulating the economy. |
May prompt other central banks to adopt easing policies. |
| Boost investor confidence and promote recovery. |
May heighten global asset bubble risks, impacting stability. |
| Enhance livelihoods and support the ruling party. |
Affect international trade patterns and reshape relations. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.


 The Purpose of the Fed Rate Cuts
The Purpose of the Fed Rate Cuts Impact of the Fed rate Cuts on the United States
Impact of the Fed rate Cuts on the United States