What challenges will the British economy face in the post Elizabeth II era? This is a highly controversial topic recently. The UK is currently facing many difficulties, such as high unemployment, high inflation, the energy crisis, the change of government, the rise of interest rates in the British pound and the death of the Queen who has been in power for 70 years. Under various difficulties, where will the UK economy and the pound go in the future? How will the fate of this old economic powerhouse be interpreted?

The situation in the UK has been turbulent this week, with the pound plummeting on Monday and rebounding slightly on Tuesday. Yesterday, the British government launched the largest tax reduction policy combination since 1972, hoping to use strong and proactive fiscal policies to boost the country's declining and long-term economic situation. The tax reduction measures introduced this time involve company tax, personal income tax, and property tax. However, contrary to expectations, a series of tax reduction policy combinations not only failed to stimulate economic stability and recovery, but also caused huge fluctuations in the UK financial market. Major asset classes were sold off due to expected rapid weakness, and asset prices under the "three kills" of stocks, bonds and foreign exchange showed significant overshoot.
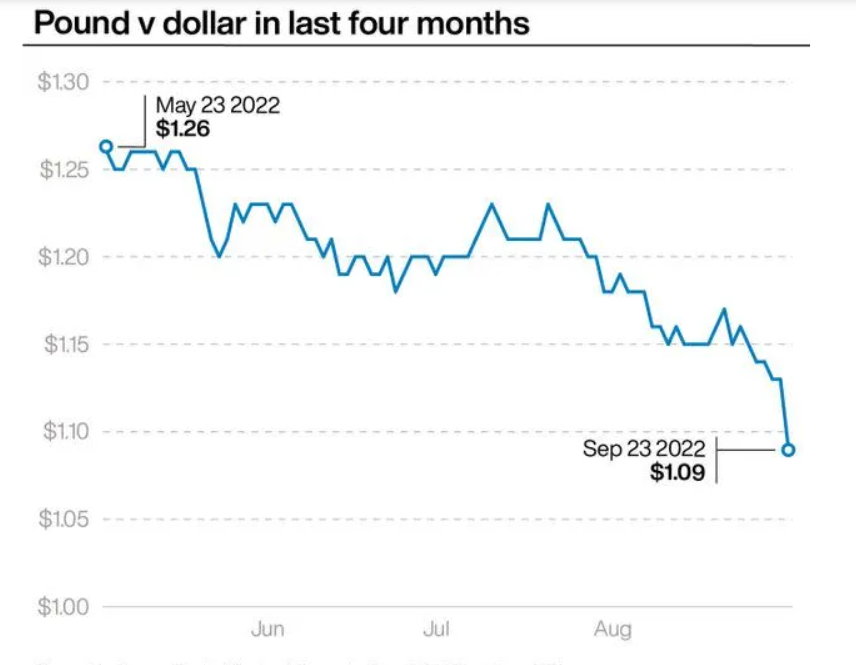
The trend of sterling against the US dollar over the past four months
On September 22nd, the Bank of England announced a 50 basis point interest rate hike, raising the benchmark interest rate to 2.25% to cope with the rising inflation hub. Relatively speaking, the Bank of England has been criticized by the market for its slow pace of rate hikes and timid wait-and-see attitude. The so-called tax reduction policy combination proposed by the British government, disregarding the deteriorating fiscal situation, not only fails to reflect the stabilizing role of macroeconomic regulation policies in countercyclical regulation, but also leads to issues such as resonance in the financial market, deep price dips, continuous depreciation of the pound, and high inflation.
A series of problems, such as the death of the Queen, the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the energy crisis, the haze of Brexit, and high inflation, have formed a strong negative interference to the UK's economic growth. The British government has to face the deteriorating economic situation, find ways to reduce inflation, and cope with the rising dissatisfaction of the public to ensure the support rate of the new government. Therefore, it has to take a risk and launch a tax reduction stimulus plan that exceeds expectations.
The British government's plan is to use tax reduction policies, especially for businesses and the wealthy, to increase the marginal consumption propensity of the residential sector, while enhancing the investment willingness of enterprises, in order to achieve the policy goal of stimulating economic stability. However, the key to the problem lies in the adequacy of the policy reserve toolbox for proactive fiscal policies to be effective. However, at present, the British government is facing the dilemma of "ammunition shortage". The measures of tax reduction and energy subsidies will further expand the gap between fiscal revenue and expenditure, which needs to be made up by issuing treasury bond. It can be said that there is no financial basis for large-scale tax reduction and energy subsidies in the UK.
At present, there is another focus in the market, that is, the coming into power of the new British Prime Minister Truss. After she took office, she immediately launched the "three axes", namely, tax reduction, pro US and residence in Ukraine, which triggered a lot of thinking in the market.

First of all, Truss' policies and measures are very similar to Thatcher's iron fist measures. Thatcher made efforts at the supply side at that time, which strongly suppressed the trade union forces that hindered the performance of British competitiveness and improved the vitality of the British market. Today, Truss is also taking measures at the supply side to improve the core competitiveness of the UK, and also adopts the development model of "small government and large market".
In addition, developed countries basically have very mature management and operation systems, so even if the national leadership changes many times, it will not affect the operation mode of its functional departments. The layout of Truss is also to improve the vitality of its operation mechanism.
On the other hand, fearing the rise of China's national power and the increase of its influence, developed countries are very radical in the international market, strengthening the role of the Big government in external circulation, while at home they pay more attention to improving market power. Therefore, Truss's new micro initiatives deserve the market's continued attention.
Secondly, the UK economy is linked to the US economy, so the impact of the US dollar on the UK economy is greater than that of the British pound. The relationship between the UK and the US is closely related to the economic performance of the offshore and onshore US dollars. Nowadays, the Federal Reserve's interest rate hike has led to the market evading high-quality liquidity, leading to significant declines in sterling, the UK stock market, and bond markets. Even US stocks and US corporate bonds may experience weakness. Global capital converges in the highly liquid US debt market. Therefore, when the global economy went down in the previous stage, Britain and the United States gained the favor of global financial capital by virtue of their status as international financial centers, and the economy dominated by the service industry followed the trend and was in a relatively strong position.
The industrial structure of the UK and its offshore US dollar business will make the position of the UK's financial center overly dependent on the performance of the US dollar. Therefore, there are still many macroeconomic issues in the UK. As for whether Truss' initiative can play the same role as Thatcher's initiative in today's environment, it remains to be further observed.
Overall, the current UK economic recession, financial market volatility, and increased future debt risks are a reflection of the Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes, global economic recession, and rising inflation in the UK. In fact, not only the UK, but also the world must bear the spillover effects of the Federal Reserve's tightening monetary policy, with some developing economies facing even greater pressure. The world macro-economy is facing a situation of "internal and external difficulties", and the macro policy based on the traditional Phillips curve is increasingly facing the challenges brought by its flattening. However, it is evident that the British government has not yet provided an effective solution, and the deep-seated contradictions in its domestic economy are still in a period of relief. The cost of the Bank of England's deep foreign exchange intervention will also be enormous, and the depreciation trend of the pound is difficult to fundamentally reverse in the short term.
Risk Reminder and Disclaimer: There are risks in the market, and investment needs to be cautious. This article does not constitute investment advice.