Forex trading can seem intimidating at first, especially when faced with the seemingly complex world of charts and graphs. However, once you understand the basics, reading forex charts will become much less daunting. In fact, it’s one of the most essential skills you’ll need to navigate the currency markets effectively. Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to refine your skills, this guide will walk you through the key elements of reading Forex charts in a way that’s both engaging and easy to understand.
Understanding the Basics of Forex Charts
Let’s start with the foundation. A forex chart is essentially a visual representation of how currency pairs have performed over a specific period. Think of it as a storybook that tells you the history of a currency’s price movements. There are three main types of charts you’ll encounter: line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts.
Line charts are the simplest. They connect closing prices over time with a single line, giving you a clear, straightforward view of the overall trend.
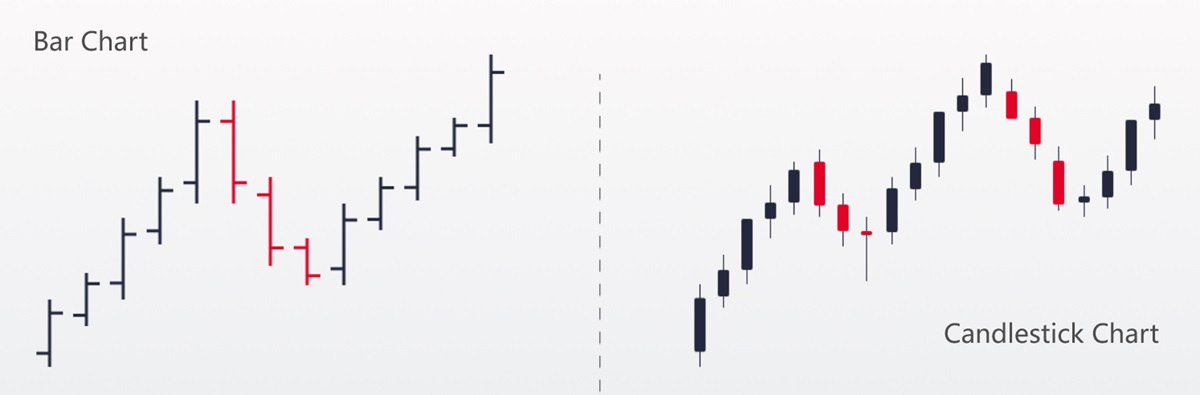
Bar charts provide a bit more detail. Each bar represents the opening, closing, high, and low prices for a specific time period.
Candlestick charts are the most popular among traders. They offer the same information as bar charts but in a more visually intuitive way, using “candles” to show price movements.
Every chart has two key axes: the price axis (vertical) and the time axis (horizontal). The price axis shows the value of the currency pair, while the time axis indicates the period you’re analysing—whether it’s minutes, hours, days, or even months. At the top of the chart, you’ll see the currency pair being traded, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, along with the timeframe you’re viewing.
How to Interpret Candlestick Patterns
If you’re serious about Forex trading, candlestick charts will quickly become your best friend. Each candlestick tells a story about price movement during a specific timeframe. Let’s break it down:
A candlestick has three main parts:
The body: This shows the opening and closing prices. If the body is filled (often red or black), it means the closing price was lower than the opening price. If it’s hollow (or green/white), the closing price was higher.
The wick (or shadow): These thin lines above and below the body represent the highest and lowest prices during that period.
Candlestick patterns can give you clues about market sentiment and potential price movements. For example:
A Doji (where the opening and closing prices are almost the same) suggests indecision in the market.
An Engulfing pattern (where one candle completely “engulfs” the previous one) can signal a potential reversal.
A Hammer (a small body with a long lower wick) often indicates a bullish reversal, while a Shooting Star (a small body with a long upper wick) can suggest a bearish reversal.
While these patterns are helpful, remember that they’re not foolproof. Always consider the broader market context before making decisions.
Using Technical Indicators to Analyse Trends
Once you’re comfortable with candlesticks, the next step is to incorporate technical indicators into your analysis. These are mathematical calculations based on price, volume, or open interest that help you identify trends, momentum, and potential entry or exit points.
Some of the most popular indicators include:
Moving Averages (MA): These smooth out price data to help you identify trends. For example, a 50-day MA shows the average price over the last 50 days.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): This measures the speed and change of price movements, helping you identify overbought or oversold conditions.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This shows the relationship between two moving averages and can help you spot changes in momentum.
Bollinger Bands: These show volatility and potential price levels where the market might reverse.
In addition to indicators, it’s important to identify support and resistance levels. Support is a price level where the currency tends to find buying interest, while resistance is where selling pressure often emerges. Drawing trendlines—lines that connect highs or lows—can also help you visualise the direction of the market.
Practical Tips for Reading Forex Charts Effectively
Now that you understand the basics, here are a few practical tips to help you read forex charts more effectively:
Choose the Right Timeframe: Your choice of timeframe depends on your trading style. If you’re a day trader, you might focus on shorter timeframes like 5-minute or 1-hour charts. For long-term investors, daily or weekly charts are more appropriate.
Combine Chart Analysis with Market News: Charts tell you what’s happening, but news and economic events explain why. Keep an eye on economic calendars and major news events that could impact currency prices.
Start Simple: Don’t overwhelm yourself with too many indicators or patterns at once. Begin with a few key tools and gradually expand your toolkit as you gain confidence.
Consistent Practice: Use a demo account to practise reading charts and making trades without risking real money. This will help you build confidence and refine your skills.
By understanding the basics of forex charts, interpreting candlestick patterns, and using technical indicators, you’ll be well-equipped to analyse the markets and make informed trading decisions. Remember, reading charts is both an art and a science—it takes time and practice to master. So, take it one step at a time, and soon enough, you’ll be navigating forex charts like a pro.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.