The FTSE China A50 Index is one of the most widely recognised benchmarks for tracking the performance of China's domestic A-share market. Put simply, it represents the top 50 largest and most liquid A-share companies listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges. These are the shares that are traded in renminbi (RMB) and accessible mainly to Chinese traders, though international access has grown in recent years through various investment schemes.
Created by FTSE Russell, a global provider of financial indices, the China A50 Index offers a snapshot of how some of China's biggest companies are performing. It acts as a barometer for the health of China's onshore equity market and is frequently used by fund managers, traders, and analysts who want to keep an eye on Chinese markets.
If you're looking to gain exposure to China's economic momentum without diving into individual stocks, the A50 index is a strong place to start.
Composition and Selection Criteria
So, who gets to be in the FTSE China A50? The answer lies in size and liquidity. The index includes the 50 largest A-share companies based on market capitalisation. These companies are selected from the broader FTSE China A All Cap Index, which consists of a much larger pool of eligible stocks.
But it's not just about being big. The selected companies must also meet certain liquidity thresholds, meaning their shares are actively traded and relatively easy to buy or sell. This helps ensure that the index remains investable—especially important for ETFs and funds that track it.
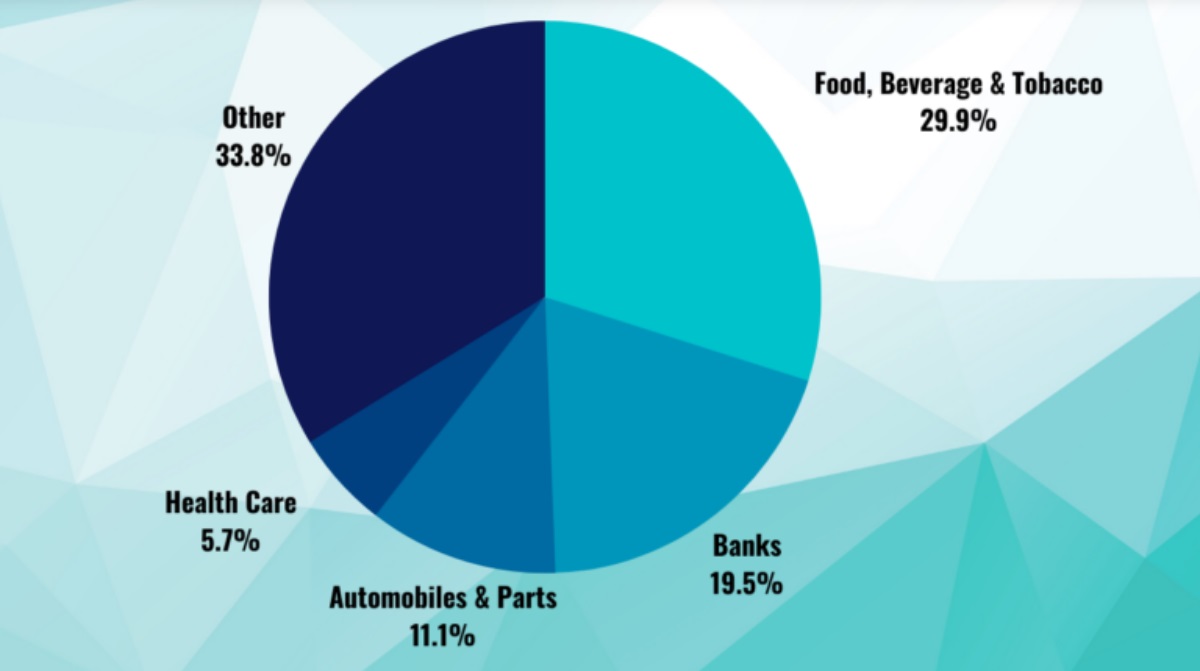
A key feature of the A50 is its balanced sector spread. While financial firms often make up a big portion of the index, you'll also find companies from technology, energy, healthcare, and consumer goods. The index is reviewed and adjusted quarterly to reflect shifts in the market, so it evolves over time as China's economy grows and changes.
Sector Representation and Weightings
If you peek inside the FTSE China A50. you'll notice it's heavily influenced by a handful of sectors—finance being the most dominant. This isn't surprising, given the size of major Chinese banks and insurance companies. Firms like ICBC, Ping An Insurance, and China Merchants Bank often feature prominently.
Beyond finance, consumer staples and industrials also play a key role, along with growing representation from tech and healthcare as China pivots towards innovation-driven growth. That said, the sector weightings are not equal. The index uses a market-cap weighting method, so larger companies have more influence over its movements than smaller ones.
This structure means that if a big bank in the index has a rough day, it can noticeably drag down the overall performance. At the same time, if major players in the tech or energy sectors surge, they can help lift the index even if smaller constituents are struggling.
Performance and Historical Trends
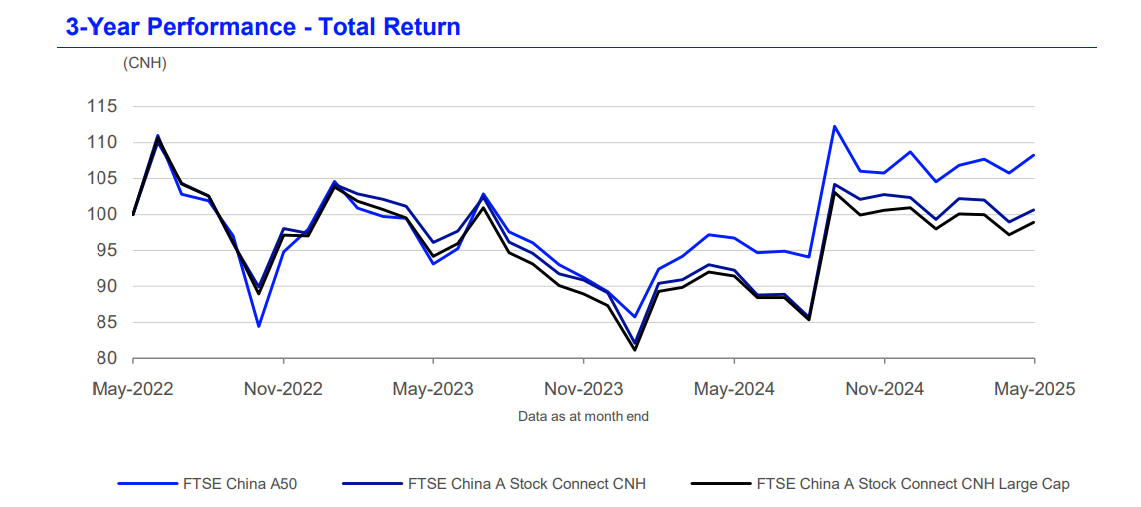
Like any stock market index, the FTSE China A50 has seen its fair share of ups and downs. Its performance is closely tied to China's economic conditions, government policy, and global trader sentiment toward Chinese markets.
Over the past decade, the index has experienced strong growth periods—often driven by economic stimulus, reforms, or a boom in sectors like technology or real estate. However, it's also faced setbacks, including market corrections, regulatory crackdowns, and global uncertainty.
One important thing to keep in mind is that the A50 behaves differently compared to offshore indices like the Hang Seng or MSCI China. That's because it focuses purely on the A-share market, which can be more volatile but also more directly linked to the Chinese economy.
For long-term traders, the A50 offers an interesting mix of growth potential and exposure to China's evolving corporate landscape. But it's not without risk—volatility and policy shifts can cause sharp swings, so it's important to keep a close eye on developments both inside and outside of China.
Comparison with Other Chinese Indices
It's easy to get lost in the sea of Chinese indices—CSI 300. SSE 50. Hang Seng Index, MSCI China… the list goes on. So how does the FTSE China A50 stack up?
Compared to the CSI 300. which covers the top 300 stocks across the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges, the A50 is more concentrated, focusing only on the top 50. This makes it less diversified but also more focused on the biggest and most influential companies.
The SSE 50 is another point of comparison—it also tracks large-cap stocks, but only from the Shanghai exchange. The FTSE China A50. on the other hand, includes stocks from both Shanghai and Shenzhen, giving it broader coverage.
Then there's the MSCI China Index, which includes offshore listings like Alibaba and Tencent that aren't part of the A-share market. The A50 is different because it stays strictly within China's mainland-listed shares, giving a more localised picture of China's economic drivers.
Each index has its purpose. If you're looking for pure exposure to China's onshore giants, the FTSE China A50 is a solid and widely-used benchmark that captures just that.
Conclusion
The FTSE China A50 Index stands out as a reliable benchmark for tracking the mainland's most influential A-share companies. Its structure offers both clarity and focus, reflecting shifts in China's economic priorities through its evolving composition. Whether you're exploring long-term investment opportunities or simply aiming to understand the forces driving China's markets, the A50 provides a valuable reference point. With its blend of market depth and sector diversity, it remains a strong indicator of how China's domestic market is performing—and where it may be headed next.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.








