Hedging is also called "hedging trading", that is, when buying or selling in the spot market, the same commodity is bought and sold in the futures market in the opposite direction and in the same quantity. Even if the market price changes and causes spot losses, the losses can be minimized due to the opposite operations in the futures market. This hedging based on spot and futures, which minimizes investment risk, is known as hedging.
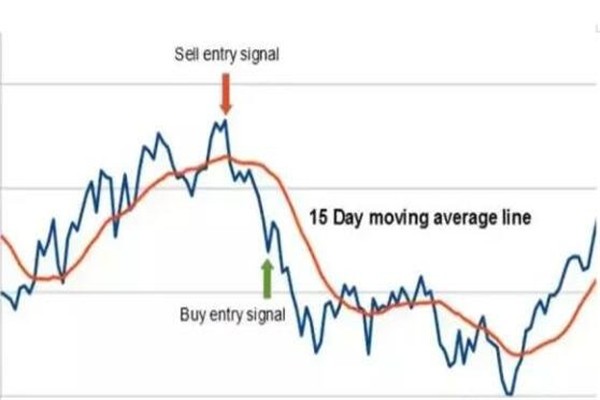
Under normal circumstances, the trend of the spot market and futures market is basically the same due to the same supply and demand relationship. If the price of the same commodity rises in the spot market, it will also rise in the futures market. If the price falls in the spot market, the price in the futures market will also fall. If investors operate in opposite directions in these two markets, even if there is an investment loss in one market, The basic principle of hedging can also be compensated for by the profits of another market.
In the spot market of commodities such as corn, sugar, and copper, in order to avoid or offset the risks caused by factors such as spot price fluctuations, one can simultaneously sell the existing goods and buy futures contracts with opposite but equivalent quantities in the futures market. By closing or selling out futures contracts at an expected time, the risk of price fluctuations in the spot market can be avoided. Stock index futures belong to financial futures, which is a classification of commodity futures. The principle of hedging mentioned above can also be applied. Buying futures contracts in the opposite direction and in the same quantity as those in the spot market can make up the losses of another market with the profits of one market, so as to avoid risks. Unlike physical commodities such as corn and sugar in commodity futures, spot in stock index futures refers to the stock price index.
The initial motivation for the formation of stock index futures was to reduce systemic risk through hedging. Whether for ordinary investors, hedge fund companies, or investment institutions engaged in Block trade, hedging plays a great role. The reason why hedging can play such a significant role is mainly because the price trends of the futures market and the spot market tend to be consistent, and as the delivery period approaches, the price of futures contracts tends to converge with the spot price.
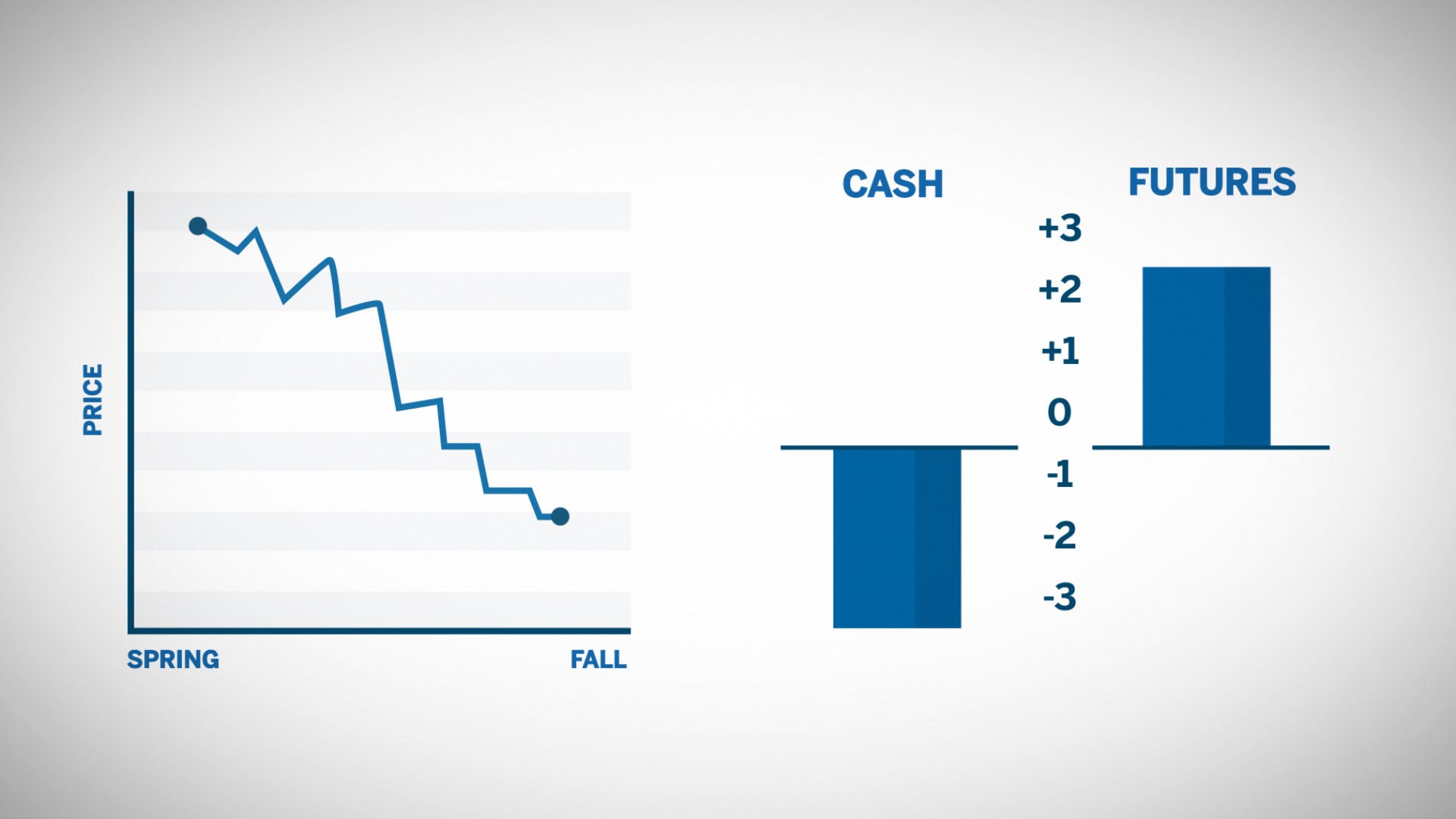
For the same commodity, futures contracts and their corresponding spot targets are the same, so the price trends of the two are basically consistent. Although the fluctuation range may not be completely consistent, the trends of the two are consistent. Due to the fact that futures contract prices represent the price of spot goods at a certain time in the future, an increase in spot prices will drive up futures prices, which in turn will further stimulate the rise in spot prices. Once the price deviation between the two shows a significant increase, a large number of risk-free arbitrageurs will seize the opportunity to enter. For example, taking sugar futures as an example, if the futures price is significantly lower than the spot price, investors will buy in the futures market and then sell in the spot market, thus engaging in risk-free arbitrage. The maturity and completeness of the futures market determine that the probability of risk-free arbitrage is extremely low, especially when the delivery period approaches, the prices of the futures market and the spot market will definitely tend to be consistent.
The operation of hedging is realized by investors' trading activities of a commodity in the futures market and the spot market in opposite directions and in equal quantities. This operation method can make up or offset the losses in one market by the losses in another market. By selecting the buying and selling timing and calculating the hedging ratio, the profit and loss ratio is optimized to help investors reduce investment risks while preserving assets.
【 EBC Platform Risk Reminder and Disclaimer 】: There are risks in the market, and investment needs to be cautious. This article does not constitute investment advice.