Crude oil is the lifeblood of the global energy market, powering everything from cars to factories. But not all crude oil is the same. Its value, ease of refining, and environmental impact depend on its specific characteristics.
For beginners, understanding the different types of crude oil is essential for grasping how the oil industry works and why some oils are more sought after than others. This guide breaks down the major types, their features, and their importance in the world economy.
Crude Oil Examples
Crude oil is a naturally occurring, unrefined petroleum product composed of hydrocarbon deposits and other organic materials. Extracted from the earth, it is processed in refineries to produce fuels like petrol, diesel, and jet fuel, as well as raw materials for plastics, chemicals, and more.
Types of Crude Oil
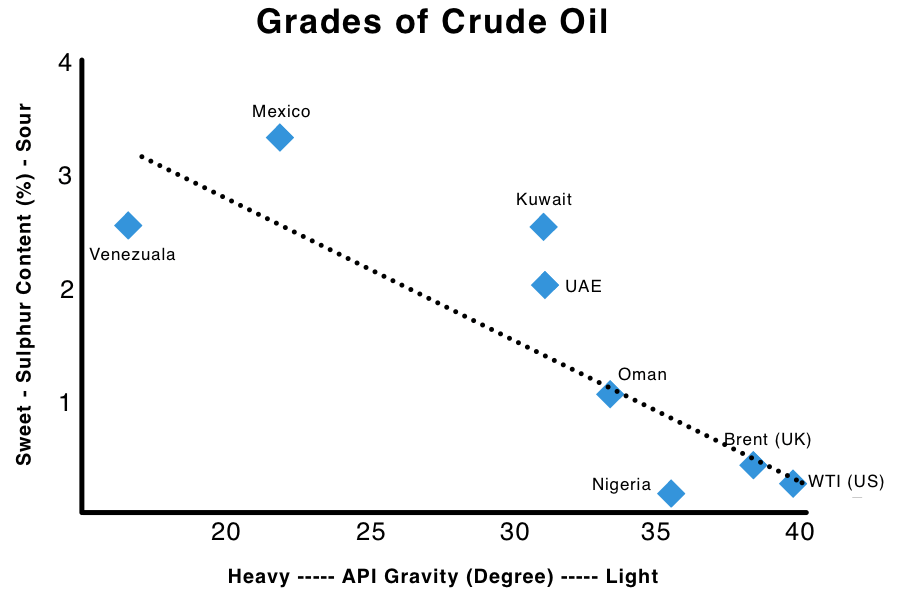
Crude oil is classified based on two main properties: density (how heavy or light the oil is) and sulphur content (how “sweet” or “sour” the oil is). These characteristics determine how easy the oil is to refine and what products can be made from it.
1. Light Crude Oil
Characteristics: Low density, high API gravity (typically 31–45°), low viscosity, and low sulphur content.
Examples: Brent Crude (North Sea), West Texas Intermediate (WTI, USA).
Uses: Highly valued for producing large amounts of high-quality petrol, diesel, and jet fuel.
Market Value: Commands premium prices due to its ease of refining and high demand for its refined products. Brent Crude often trades at $80–$100 per barrel, while WTI is slightly lower, depending on market conditions.
Economic Importance: Countries producing light crude enjoy higher revenues and stronger market positions.
2. Heavy Crude Oil
Characteristics: High density, low API gravity (below 22°), high viscosity, and often higher sulphur content.
Examples: Oil sands (Alberta, Canada), Orinoco Belt (Venezuela).
Uses: More challenging and costly to refine, often used for products like fuel oil and asphalt.
Market Value: Sells at a discount compared to light crude, often trading at $30–$50 per barrel due to higher refining and transport costs.
Processing: Requires complex and energy-intensive processes such as hydrocracking and sulphur removal, making it less environmentally friendly.
3. Sweet Crude Oil
Characteristics: Contains less than 0.5% sulphur.
Examples: Brent Crude, WTI, Bonny Light (Nigeria).
Uses: Easier and cheaper to refine into clean fuels, making it highly desirable for producing petrol and diesel that meet strict environmental standards.
Market Value: Generally more expensive than sour crude due to lower processing costs and higher demand.
4. Sour Crude Oil
Characteristics: Contains more than 0.5% sulphur.
Examples: Dubai Crude (Middle East), Maya (Mexico), Kuwait Export.
Uses: Requires additional processing to remove sulphur, which can be costly and environmentally taxing.
Market Value: Sells at a discount to sweet crude, but demand is rising as refineries become more advanced and capable of handling sour grades.
5. Medium Crude Oil
Characteristics: API gravity between 22.3° and 31.1°.
Examples: Oman, Bonny Light (Nigeria), Flotta (UK).
Uses: Falls between light and heavy crude in terms of refining complexity and product yield.
Market Value: Priced between light and heavy crude, offering a balance of quality and cost.
How Is Crude Oil Named and Classified?
Crude oils are often named after their geographic origin, such as Brent (North Sea), WTI (Texas), or Dubai (Middle East). These names also serve as global benchmarks for oil pricing and trading.
The classification of crude oil is further refined by its chemical properties, such as API gravity and sulphur content, which influence its suitability for different refining processes and end products.
Why Do These Differences Matter?
Refining Efficiency: Light, sweet crudes are easier and cheaper to refine, producing more valuable fuels with less environmental impact.
Market Pricing: Light, sweet crudes command higher prices, while heavy, sour crudes are discounted due to higher processing costs.
Environmental Impact: Sweet crudes are cleaner to process, while sour and heavy crudes require more energy and produce more pollutants.
Global Trade: The type of crude oil a country produces affects its economic standing and its relationships in the global energy market.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of crude oil is crucial for anyone interested in the energy sector. Light, heavy, sweet, and sour crudes each have unique characteristics that affect their value, refining process, and impact on the environment.
As the world continues to evolve its energy mix, knowing these differences helps investors, policymakers, and consumers make informed decisions in a complex global market.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.