In technical analysis, candlestick patterns play a crucial role in identifying potential market reversals. Among them, the inverted hammer candlestick pattern is a key signal that suggests a possible shift from a bearish to a bullish trend. Understanding how to correctly identify and use this pattern can help traders improve their decision-making and enhance their trading strategies.
The inverted hammer pattern forms after a downtrend and is characterised by a small real body at the lower end of the candle, along with a long upper shadow. It signals that buying pressure is increasing, despite initial selling attempts, indicating a potential reversal if confirmed by subsequent bullish price action. This pattern is often compared to the hammer candlestick, but unlike the hammer, the inverted hammer has its long shadow at the top.
What is the Inverted Hammer Candlestick Pattern?
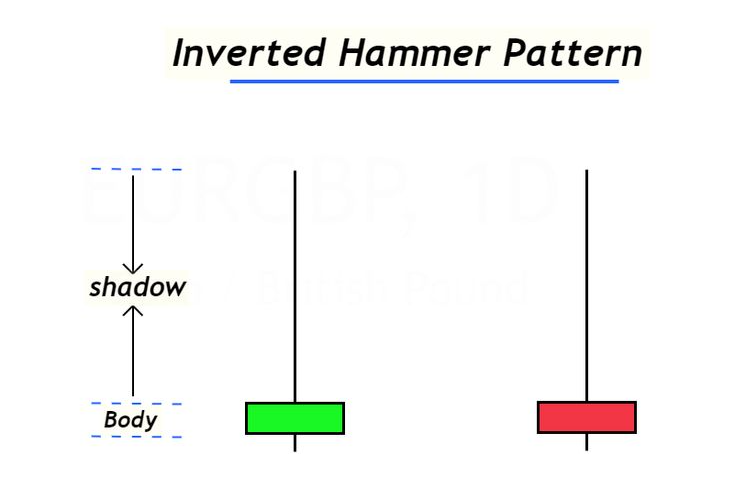
The inverted hammer candlestick is a bullish reversal signal that indicates a weakening downtrend and the potential for an upward price movement. This pattern is widely used in Japanese candlestick charting and is favoured by technical traders for identifying possible market reversals from bearish to bullish trends.
The pattern consists of a long upper shadow and a small real body near the bottom of the candle. It suggests that buyers attempted to push the price higher during the trading session, but sellers initially resisted. However, if the next candle confirms the bullish move, it strengthens the reversal signal. This confirmation usually comes in the form of a bullish engulfing candle or a strong green candle with high volume.
How to Use the Inverted Hammer Correctly
To maximise the effectiveness of the inverted hammer candlestick pattern, traders should follow a structured approach:
Confirm the Downtrend: Ensure that the inverted hammer appears after a clear downtrend, as the pattern has little significance in an uptrend or sideways market.
Wait for Confirmation: Do not enter a trade immediately after spotting the inverted hammer. Look for a confirmation candle in the next session, such as a bullish candle with strong momentum or a gap-up opening.
Check Volume: Higher trading volume on the inverted hammer or the confirmation candle strengthens the reliability of the signal.
Use Support and Resistance Levels: Identify key support levels where the inverted hammer appears. If the price bounces from a strong support zone, it increases the chances of a successful reversal.
Combine with Other Indicators: Supplement your analysis with the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), or moving averages to validate the strength of the reversal.
Set Entry and Exit Points:
Entry: Consider entering a buy trade once the confirmation candle closes above the high of the inverted hammer.
Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss below the low of the inverted hammer to minimise risk.
Take-Profit: Aim for a take-profit level at the nearest resistance zone or use a risk-reward ratio (e.g., 2:1) to lock in gains.
Avoiding Common Mistakes with the Inverted Hammer
While the inverted hammer pattern is a useful trading signal, relying solely on it for trading decisions can be risky. Common pitfalls to avoid include:
Trading Without Confirmation: Entering a trade based on the inverted hammer alone without waiting for bullish confirmation can lead to false signals.
Ignoring Other Technical Indicators: Combining the pattern with trendlines, support levels, and oscillators enhances its accuracy.
Neglecting Risk Management: Proper risk management, including stop-loss orders and position sizing, is essential to protect capital from market fluctuations.
Misinterpreting the Pattern: If the inverted hammer appears in an uptrend, it could be mistaken for a shooting star, which signals a potential bearish reversal rather than a bullish one.
Reliability and Frequency of the Inverted Hammer
The inverted hammer candlestick is a relatively reliable pattern, but its effectiveness varies depending on market conditions. Key points to consider:
It is more significant when appearing after a strong downtrend.
The pattern's reliability improves when confirmed by subsequent bullish price action and increased trading volume.
Frequency depends on market volatility, timeframe, and asset class, with higher occurrences in shorter timeframes due to frequent price fluctuations.
Institutional traders may require additional confirmation, such as a break above a key resistance level, before considering the signal valid.
Real-World Example of the Inverted Hammer in Action
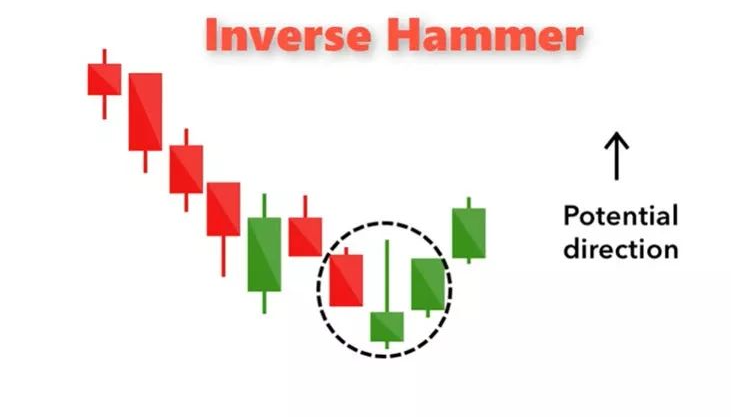
A real-world example of an inverted hammer pattern can be seen in stock market corrections or forex trading. For instance, if a currency pair like GBP/USD has been in a steady downtrend and an inverted hammer appears near a strong support level with increased volume, followed by a bullish engulfing candle, this could signal a reversal. Traders using technical analysis would look for confirmation before entering a long position.
Conclusion
The inverted hammer candlestick pattern is a valuable tool for traders seeking to identify potential bullish reversals in downtrending markets. While the pattern can offer strong trading signals, it should always be used alongside other technical indicators and risk management strategies to enhance reliability. By mastering its identification and applying proper trading strategies, traders can improve their decision-making and increase their chances of success in the financial markets.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.