Futures Position Profit and Loss Calculation
The daily mark to market system must calculate the funds that may be required to meet the daily liquidation conditions, and establish corresponding dynamic cash flow reserves throughout the entire investment period. The daily mark to market system generally includes two aspects: calculating floating profits and losses and calculating actual profits and losses:
1. Calculate the floating profit and loss of futures positions. The settlement institution calculates the floating profit and loss of members' open positions based on the settlement price of the day's transactions, and determines the amount of margin payable for open positions.
The calculation method is:
Floating profit and loss=(settlement price on the day - opening price) × open interest × contract unit - handling fee.
If the account experiences floating losses and the amount of margin is insufficient to maintain the open position contract, the settlement institution will notify members to make up the difference before the next day's market opening, that is, increase the margin, otherwise the position will be forcibly closed. If the account is a floating profit, the profit portion cannot be raised unless the open contract is closed and the floating profit is converted into actual profit.
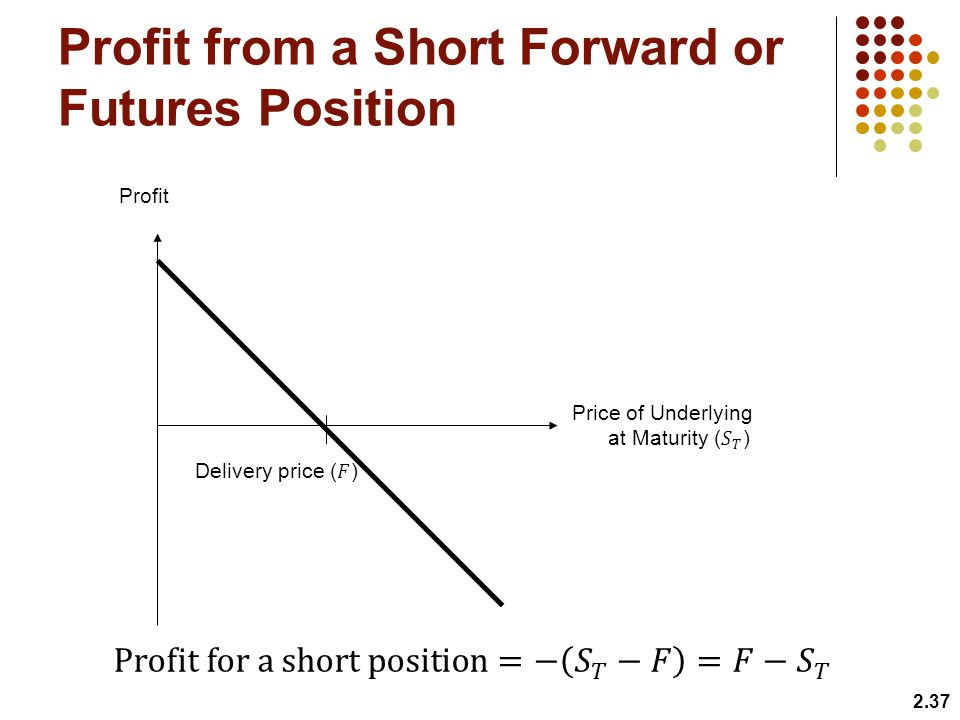
2. Calculate the actual profit and loss of futures positions. The profit or loss achieved by closing the position is called the actual profit or loss.
The calculation method for the actual profit and loss of bulls is:
Profit/Loss=(closing price - buying price) × open interest × Contract unit - handling fee
The calculation method for short selling profit and loss is:
Profit/Loss=(selling price - closing share) × Quantity to be stored × Contract unit - handling fee
In addition, comparing the settlement systems used in futures and stock trading can provide a better understanding of the daily mark to market system of futures. The daily clearing (mark to market) system adopted in futures trading makes the clearing method and cash flow of futures different from stock trading. When futures prices change over time, credit profits, debit losses, profits, and losses accumulate sequentially, and at any given time point, each futures margin account has a net profit or net loss; Stocks are simply held until the time of purchase and sale before being liquidated, without any prior transfer of funds. According to this requirement, futures contracts have cash inflows and outflows every day, while stocks only have cash flows once on trading days.
The existence of the daily mark to market system and the implementation of the daily settlement system make it possible for futures traders to face significant negative cash flow risks when futures prices fluctuate violently. Futures investors have raised their requirements for fund liquidity for traders, while the daily mark to market system helps to avoid credit risks for funds.
【 EBC Platform Risk Reminder and Disclaimer 】: There are risks in the market, and investment needs to be cautious. This article does not constitute investment advice.