What are Securities?
2024-01-12 Summary:
Summary:
Securities symbolize an investor's ownership or debt link to financial interests or assets—a tradable financial instrument in the market. This includes stocks, bonds, etc., issued and traded for financing and capital optimization.
In the 17th century, Europe's great age of navigation, the East India Company, as a pioneer of overseas colonial expansion, can be said to be infamous. However, his appearance brought a new face to the old financial family: securities. Many people seem to know about it, but they can't tell. Here we will come to understand, from various aspects, what are securities?
 What are Securities?
What are Securities?
It is a financial instrument that represents a financial interest or debt. It is a negotiable document that can be traded on the financial markets and represents a relationship in which the holder has a certain interest or debt in the issuer (usually a company or government). Simply put, it is a document used to prove that you are entitled to a certain interest.
It is for everything from small checks, IOUs, and certificates of deposit to large stocks and bonds. Even food stamps and postage stamps, which were once all the rage, are two of them. It is a tradable financial asset that can be bought and sold in the market, and the price at which it is traded depends on supply and demand and various factors in the market. These financial instruments allow investors to participate in the capital market and gain capital appreciation or, in some cases, a fixed return.
At the beginning of the East India Company, the Dutch people lent money to the company out of their own pockets. The company made notes and promised dividends, and these notes were the world's first securities. As the East India Company continued to expand overseas, it was only in 1609 that an institution was born that specialized in serving its buying and selling—the Stock Exchange.
In terms of types, it can be categorized into financial and physical ones. Financial instruments are financial instruments that can be bought and sold on the financial markets and represent specific financial interests. For example, stocks, bonds, ETFs, warrants, and convertible bonds all fall into this category, and the instruments are usually in electronic form to facilitate listing and trading on the SEHK.
Physical ones are paper securities that exist in physical form and represent ownership of a physical asset. In the past, investors usually held physical objects such as paper stock certificates or bond certificates. With the continuous development of electronic information technology, it has gradually become paperless. The paper pioneers of the East India Company hundreds of years ago can only lie obediently in the museum for posterity.
By nature, it can be categorized into priced and priceless. Priceless refers to financial instruments that cannot be freely traded and transferred in the market and are usually issued directly by the issuer to a specific individual or organization. Its face value and value may not be easily determined, nor can it be bought and sold in the market to generate income. Similar to certificates of deposit, IOUs, etc., which cannot be circulated in the market,.
Valuable is to have a certain amount of coupon that can bring the holder a certain amount of income, such as the stock, bonds, and so on. It is a financial instrument that can be traded and transferred in the market with a determined face value and value. Investors can buy it to obtain capital gains or interest, the market for trading, or its price fluctuations in the market.
In China, it belongs to the typical imported products, the earliest foreign stocks. The stock exchange is also opened by the foreigners of the Shanghai Stock Exchange. It was not until the establishment of the Shanghai Stock Exchange in 1990 that China's securities market flourished. In a nutshell, it is the most important financing channel. It bridges the gap between capital raisers and investors and is an indispensable and important member of the financial family.
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Equity | Investor's ownership in a company. | A-share, U.S. stock |
| Bond | Investors earn from borrowing. | Government bonds, corporate bonds |
| Investment Funds | Investor-managed portfolio. | Stock funds, bond funds |
| Options | Right to buy/sell asset at future set price. | Stock options, futures options |
| Futures Contracts | Promise to deliver asset at set future price/time. | Commodity futures, financial futures |
| Commodity Options | Trade commodities at agreed future prices. | Gold Options, Crude Oil Options |
| financial derivatives | Derivative contracts: options, futures, etc. | Interest rate swaps, currency swaps |
| Convertible Bonds | Convertible under specific conditions. | Convertible bonds |
| Initial Public Offering | First stock offering for business. | IPO (Initial Public Offering) |
| Local Government Bonds | Bonds used by local governments to raise funds | Specialized local government bonds. |
Functions of Securities
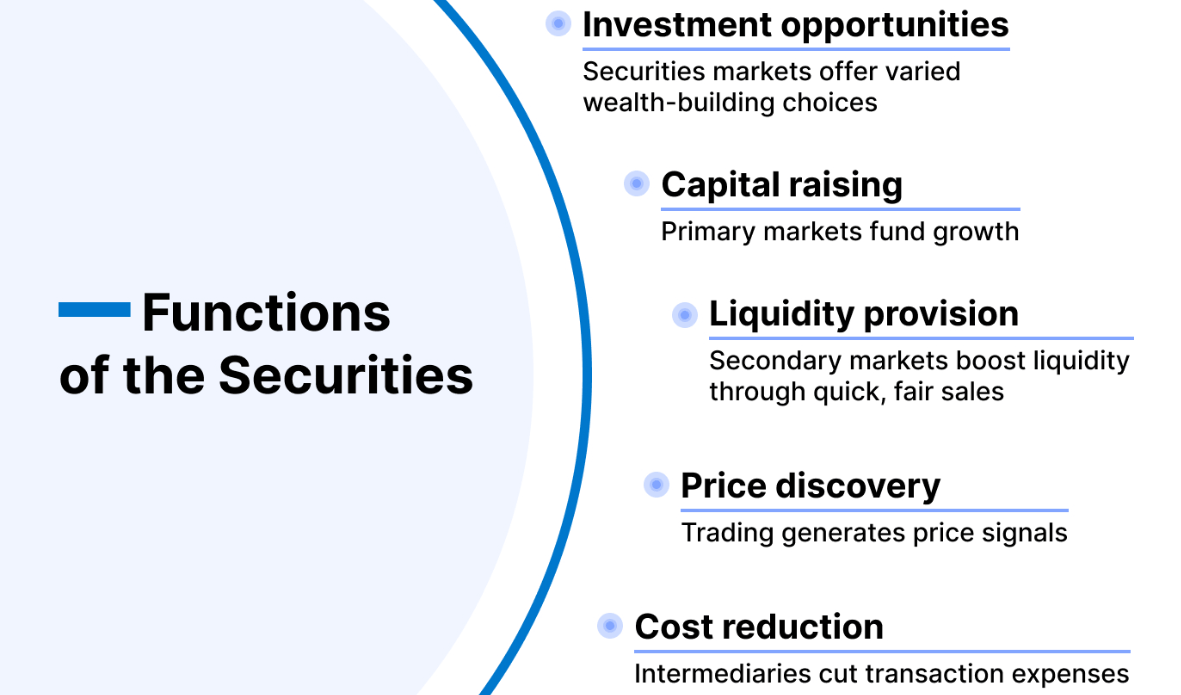
It has two main functions: one is to raise finance, and the other is to optimize the allocation of capital. It provides access to finance through the issuance of shares or bonds, which helps to incentivize innovation and promote economic growth. Investors are willing to invest in companies that have the potential and the ability to innovate, thus promoting new technologies and business models.
Through it, individual and institutional investors are also able to share in the profitability and value-added opportunities of companies. This helps spread wealth so that more people can share the fruits of economic growth and promote wealth distribution in society. After successful financing, the scattered and idle money in society is integrated through it and used for enterprise development or national construction to achieve the optimal allocation of capital.
It has an extremely wide range of financing options for governments, businesses, and other entities. A company can raise finance by issuing shares or bonds to raise capital for business expansion, investment projects, or debt repayment. And governments can raise capital for nation-building by issuing Treasury bonds and other forms of financing.
Again, as a financial instrument, it provides investors with a wide range of investment choices, including stocks, bonds, funds, and so on. Wealth enhancement and asset allocation are achieved through participation in various investment activities. Whether you are a billionaire or a senior loser, you can invest in it to share the profits of enterprises and gain capital gains or interest income.
Moreover, trading venues such as the SEHK increase the liquidity of assets. Holders can buy and sell in the market at any time, realizing the rapid liquidity of funds. Freedom to adjust their asset allocation and more flexible management of assets. This trading activity also helps to form prices, which are constantly adjusted by supply and demand in the market and investors' responses to information, reflecting the market's view of the value of the business.
Because of the diversified investment choices given to investors, it is not only possible to invest in different industries, companies, or regions, thereby reducing the impact of specific risks on the portfolio. It also offers a variety of derivative contracts, such as futures and options, to help investors manage risk. These instruments can be used to hedge against risks such as price fluctuations, interest rate fluctuations, and so on.
As shares issued by a company, they also serve as a symbol of ownership of the company and give shareholders certain rights, such as participation in shareholders' meetings and voting rights. Shareholders can participate in the affairs of the company through their voting rights, thus influencing the company's operations and decisions. There are also stocks and bonds, such as those in pension funds and pension plans, which are used in long-term savings and pension plans to support people in their retirement.
Companies have the option of listing and issuing shares on the stock markets of several countries, which promotes the free flow of international capital. At the same time, investors can participate in the economies of other countries by buying shares or bonds of multinational companies. This, in turn, enhances financial ties between countries and promotes the development of the global economy.
It can be said that its prosperity is usually closely related to the growth of economic activities. It can improve the efficiency of financing for businesses and promote investment, which in turn has a positive impact on the overall economy. Overall, it plays an important role in the capital market, providing an effective tool for companies to raise funds and investors to obtain returns, as well as promoting economic development and the rational allocation of capital.
 How it works
How it works
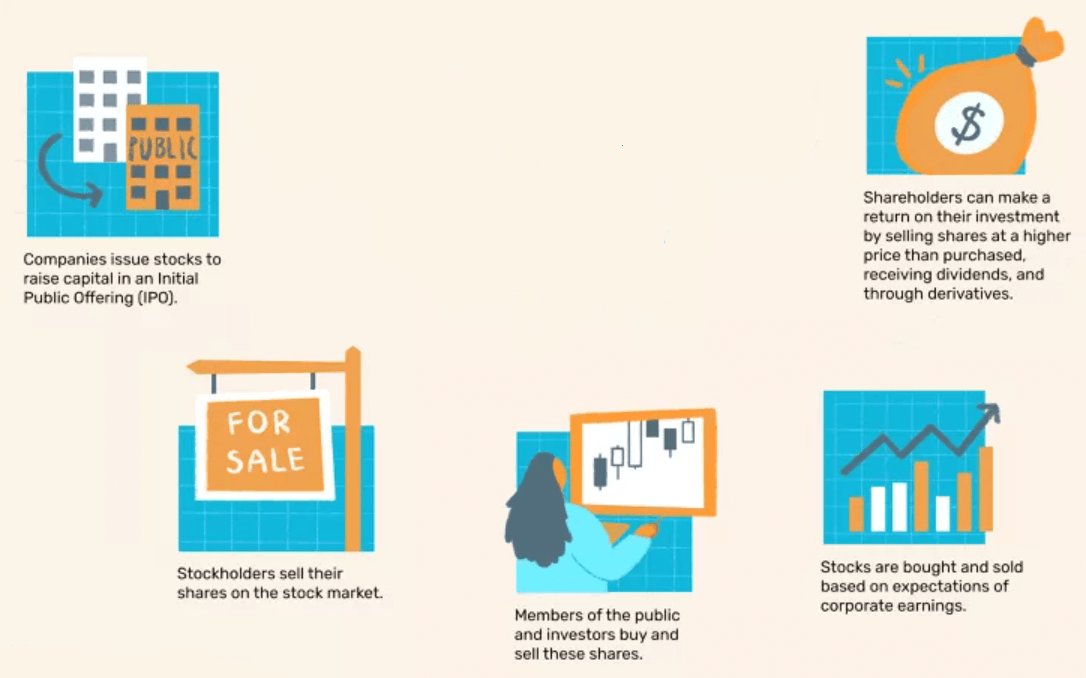
Its operational operation involves multiple participants and processes, such as the issuance stage, post-issuance, trading stage, and post-trading. At the issuance stage, the issuing entity, company, or government needs to raise capital, which can be raised through the issuance of shares or bonds. For example, an initial public offering (IPO) of a company or the issuance of bonds by a government are common issuance methods, and the shares will be listed on the stock exchange. Financial institutions, such as investment banks, act as underwriters to help the issuing entity complete the issuance of stocks or bonds.
After the issuance, investors can buy the newly issued stocks or bonds in the primary market. Investors can be either individuals, institutions (e.g., funds, pension funds, etc.), or other entities. The listed company maintains communication with investors through investor relations activities, answering questions, and providing information.
It is traded on the secondary market, where investors can buy and sell shares through the SECP. The SEC is the place where it is bought and sold, e.g., the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ, etc. Exchanges provide an organized market environment and ensure that buyers and sellers can find counterparties in the open market.
These trades will be made through a broker, which acts as an intermediary between the investor and the market. Brokerage firms provide trading platforms, offer buying and selling services, and execute investor orders. The investor, in turn, buys and sells through them and makes a profit from it.
Once a transaction is completed, it involves clearing and settlement. Clearing is the financial confirmation of a transaction, while settlement is the delivery of securities and funds, the transfer of ownership of which is formalized in the clearing process. A central clearing agency (e.g., a clearing house) plays a key role in this process, ensuring that payments and deliveries are completed by both parties.
The market is regulated by regulators to ensure that it is fair, transparent, and free from manipulation. Regulators typically establish rules and regulations that govern issuers, brokers, and investors. At the same time, listed companies are required to disclose financial and business information on a regular basis in accordance with regulations to maintain the transparency of the market. Information such as economic indicators and company news is communicated to investors through various channels, which not only affects their decision-making but is also crucial to the proper functioning of the market.
Securities Company
It is an important type of institution in the financial system, mainly engaged in brokerage, trading, custodianship, research, investment banking, and other businesses. As a financial institution specializing in this type of business, its main responsibility is to provide securities trading and investment services to its clients.
It provides brokerage services by assisting clients in buying and selling transactions of stocks, bonds, funds, and other varieties, acting as an intermediary between investors and the exchange. It allows investors to buy and sell stocks, bonds, funds, and other financial instruments in the market and provides trading platforms and services to enable investors to execute buying and selling transactions.
Some firms also provide investment banking services, including corporate finance, merger and acquisition advisory, restructuring, and stock issuance, to offer a wider range of financial services to their clients. They work with corporations to assist them in raising funds in the capital markets. They also participate in corporate financing activities and help companies raise capital by underwriting new share issues and bond issues.
Some companies set up asset management departments to provide professional asset management services to their clients, including fund management and wealth management. Help clients manage their investment portfolios to achieve their financial goals. This includes risk management, portfolio analysis, and asset allocation.
Also provides custodial services to clients, i.e., the safekeeping of their assets. This includes managing clients' stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments to ensure the safety and transparency of transactions. Financial counseling services are also provided to help clients plan their financial goals for investments, retirement, education funds, and other areas.
Many firms have specialized research teams that analyze market trends, corporate performance, etc. They provide clients with research reports and analyses on market trends, corporate performance, etc. to help them make more informed investment decisions. They can also provide financial planning services for individual and institutional clients to help them develop comprehensive financial planning and investment strategies.
They require risk management when trading and investing to ensure the interests of their clients and the firm itself. This includes the management of market risk, credit risk, and other aspects. They also need to follow national and regional financial regulations and comply with the relevant rules and regulations. This is to ensure that its business is legally compliant and to protect the rights and interests of its clients.
Overall, securities firms play multiple roles in the financial market, connecting investors, companies, and the capital market, and are vital to the effective allocation of capital and the normal operation of the market. When selecting a firm, investors should consider factors such as the firm's reputation, service quality, fee structure, etc., and ensure that it is registered with the relevant regulatory bodies and operates legally.
| No | Securities companies | Stock Code | Market share |
| 1 | VPS Securities JSC | VPS | 17.65% |
| 2 | SSI Securities Corporation | SSI | 10.76% |
| 3 | VNDirect Securities Corporation | VND | 7.08% |
| 4 | Ho Chi Minh City Securities Corporation | HCM | 5.53% |
| 5 | Mirae Asset Securities Vietnam Joint Stock Company | MAS | 5.46% |
| 6 | Techcom Securities JSC | TCBS | 5.01% |
| 7 | Vietcap Securities Joint Stock Company | VCI | 4.82% |
| 8 | MB Securities JSC | MBS | 4.77% |
| 9 | KIS Vietnam Securities Corporation | KIS | 3.32% |
| 10 | FPT Securities JSC | FPTS | 3.14% |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.

How AI is Transforming the Future of Trading?
See how AI transforms trading with advanced data analysis, automation, and real-time insights, boosting accuracy and market efficiency for traders.
2024-10-29
How to Profit from AI Bots in Trading
Learn how to use AI bots in trading to enhance performance and generate income. Discover strategies for maximizing profits in the financial market.
2024-10-28
Best Currency Pairs for Forex Trading
Maximize your forex trading success by choosing the best currency pairs. Learn why USD, EUR, and JPY are among the most traded and profitable pairs
2024-10-24





