Is Public Companies Worth Investing In?
2024-01-19 Summary:
Summary:
Public companies are traded on stock exchanges and require investment analysis considering industry traits, supply chains, core strengths, financial metrics, and company disclosures. Choose growth-oriented companies after comprehensive understanding.
The phrase "public company," whether from TV series, movies I watched as a child, or the novels I read growing up, always felt very powerful. In the stock market, public company stocks represent many influential companies, making it a challenging task for many to choose the right ones to invest in. This article will provide a summary of public companies and offer insights on how to analyze whether they are worth investing in.
What is Public Company?
It refers to a business that has been listed (or listed) on a stock exchange. Listing is when a company's shares (or other Securities) are listed on a stock exchange, its shares are publicly traded on the stock exchange, and investors can become shareholders of the company by purchasing these shares. One of the main purposes of going public is to provide companies with access to financing while also providing a market for investors to buy and sell shares.
A company is not listed if it has $10 million in capital. But if the company wants to expand, it needs to go public, and it can sell 8 million shares. If someone buys those 8 million shares, the company can use that money to do other things to expand.
And in fact, if the company wants to go public, it is not so simple; it also needs to meet some conditions to apply. It must meet a series of regulations and standards set by the exchange to ensure the financial health, transparency, and compliance of the company. These regulations may involve requirements for financial reporting, corporate governance, information disclosure, market capitalization, liquidity, and more.
At the same time, the company's ownership structure needs to comply with relevant regulations, and there may be a minimum share disclosure requirement. That means having a stable shareholder structure and avoiding excessive concentration of holdings. There is also usually a clear governance structure, including a board of directors, senior management, etc., to ensure compliance and the effective operation of the company.
The company's shares are listed on stock exchanges, such as NASDAQ, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), etc., and ownership is sold to investors through a public offering of shares. This provides a relatively high level of liquidity, allowing investors to buy and sell these stocks with relative ease. They can buy and sell these shares through the stock exchange and become shareholders of the company to share the profits and interests of the company.
After listing, the company will be subject to the supervision of the stock exchange and relevant regulatory authorities. This includes complying with certain financial and regulatory requirements to protect the interests of investors. For example, the company is responsible for providing regular financial reports and other necessary information to investors and securities regulators in order to maintain transparency and enable investors to understand the company's operations.
Going public is not only a means for a company to raise money but also to show the public company's business status and prospects. However, listing also requires compliance with a range of regulations and faces scrutiny from investors and the market. If there is a violation or if the financial situation does not meet the standards set by the exchange, it is possible to be asked to delist.
The status of a public company usually depends on a number of factors, including market capitalization, performance, and industry status. The market value of a company is the total market value of its shares, which is an important indicator to measure the size of a company. Companies with a large market capitalization usually have a more prominent position in the market. A company's financial performance, including revenues, profits, and growth rates, has a significant impact on its position. Good performance usually reflects the competitiveness and health of the company.
A company's position in its industry is also critical. In the same industry, the leading company may have a larger market share and a higher status. Multinational companies or companies with an important position in international markets may enjoy higher visibility and status on a global scale.
A company's governance structure and transparency also have an impact on its standing, and companies that follow good governance practices are generally more trusted by investors and the market. A company's ability to innovate and technological leadership can be key factors in certain industries, affecting its position and market position.
| Type of Shareholder | Type of shareholding | Specification |
| Major Shareholders | Ordinary Shares | Company founders, management, etc. |
| Institutional Investor | Preferred Shares | Funds, insurance companies, etc. |
| Retail Investor | Ordinary Shares | Individual investors |
| Employee Stock Ownership Plan | Ordinary Shares | Employee shareholding |
| Other Special Classes of Shares | Special Classes of Shares | Unique financial or governance needs. |
How to Analyze if a Public Company Worth Investing In?
If you want to know whether a company is worth investing in, you need to interpret it from six perspectives. Remember that a company's valuation is a discount to the company's future cash flows, and the stock price is largely dependent on the market's expectations of the company's future performance. Therefore, as a retail investor, it is necessary to deeply understand the development prospects of the company.
To see whether the stock of the public company is worth investing in, the first step is to lock in the industry and have a comprehensive understanding of the industry in which the company is located. One depends on the characteristics of the industry; the second depends on whether the industry is cyclical; and the third is the stage of the industry.
The characteristics of the industry are to determine whether it belongs to the industry of complete market competition, oligopoly industry, or monopoly competition industry. For example, electronics, panels, automobiles, etc. belong to the industry of complete market competition; oil belongs to the industry of oligopoly; nuclear power, aerospace, etc. belong to the industry of monopoly competition. In different industries, investors focus on completely different.
Enterprises in perfectly competitive markets need to pay attention to sales expenses because sales expenses are largely used to occupy the market. There is also a need to focus on the level of intelligence and refinement, as lower unit costs mean higher profit margins when companies cannot control the selling price.
For oligopolies and monopolies, it is necessary to pay attention to national policies. Taking China's nuclear power as an example, we should pay attention to the government's attitude towards nuclear power. After the Fukushima nuclear power plant accident, the Chinese government significantly reduced the speed of nuclear conversion for civilian nuclear power plants. Most of the plants are in Fujian and Jiangsu provinces, where feed-in tariffs and electricity directly affect China's nuclear revenues and profits.
Second, see whether it is a cyclical industry. It is generally believed that commodities are cyclical industries, while liquor, catering, food, beverages, etc., are non-cyclical.
The performance and stock prices of cyclical industries are volatile and follow certain rules. For example, Ganfeng Lithium and Tianqi Lithium declined because of the decline in the price of lithium resources. However, with the recovery of lithium resource prices, performance and stock prices can recover. The decline in the performance of non-cyclical industries is likely to be a problem for the sustainable development of the company. For example, the performance of a chain catering company has declined all the way, which may be really not good.
Look at the industry stage as an investor to clearly judge whether the company is an emerging industry, a mature industry, or a recession industry. An industry that the state supports, or one that the state is beginning to restrict. For example, the semiconductor and new energy industries are emerging industries, and the government has the power to develop them. Real estate, on the other hand, is an industry tightly controlled by the state.
This is not to say that only emerging industries and state-supported industries have investment opportunities, but there is a need to predict the mid-range of various industries. In fact, there are no more than three. One is the Matthew effect, which results in one family becoming dominant. The second is the balance of duopoly or multi-oligarchy. Third, it is relatively dispersed, and a hundred flowers bloom.
Whether it is a monopoly or a duopoly, investors have only a few options. Only when a hundred flowers blossom in an industry do you need to go through a lot of analysis to identify investment companies. If you want to have insight and then find a really high-growth enterprise, you must pay attention to the following stEPS:.
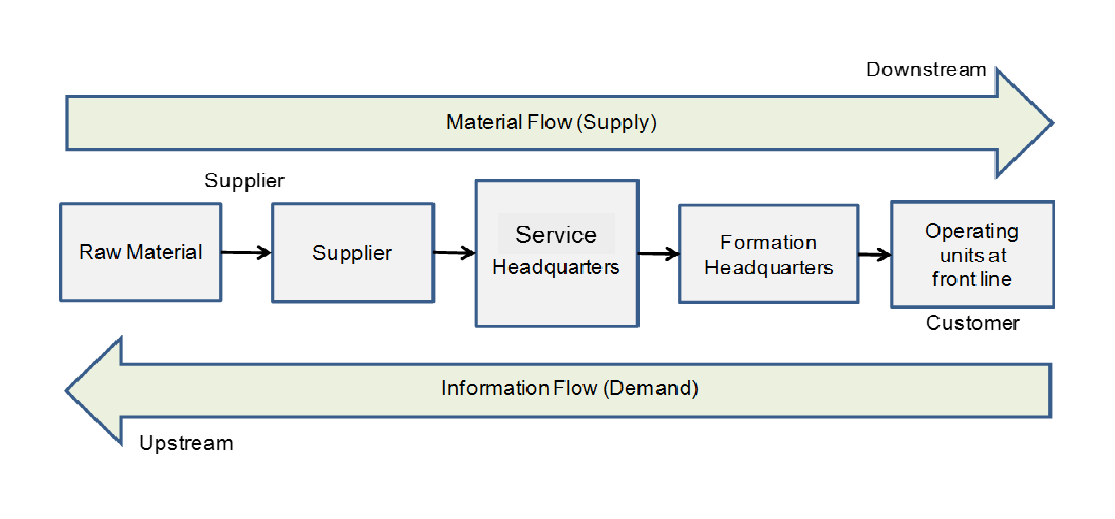 The second is to sort out the upstream and downstream relationships, mainly in terms of downstream customers and upstream supplier customers. To see the company's sales ratio to the top ten customers, whether it is concentrated on a few large customers or customers are very decentralized, When studying listed companies, having upstream and downstream premium capacity and pricing power is a very good plus for the company.
The second is to sort out the upstream and downstream relationships, mainly in terms of downstream customers and upstream supplier customers. To see the company's sales ratio to the top ten customers, whether it is concentrated on a few large customers or customers are very decentralized, When studying listed companies, having upstream and downstream premium capacity and pricing power is a very good plus for the company.
If you focus on a few large customers, look at the strength of these large companies and whether they can maintain the stability of the company's future performance. For example, the largest customer of Njie shares is Ningde Times. As long as the Ningde Times or ternary lithium battery market is still growing, the future performance of Njie shares is foreseeable to be stable.
If the customers are too scattered, such as information system integration enterprises, China Software, Wave Tai Chi, etc., it is mainly for the parties and local governments to do system integration. The contract of each customer is relatively small and especially scattered, which is a common problem for system integration enterprises, resulting in high marketing costs and low gross profit.
After looking at the customer, then look at the company's supplier situation, which involves the company's procurement of raw materials. Focus on the price fluctuations of the company's raw materials and the company's premium ability upstream. If upstream raw material prices fluctuate greatly, then the company's future performance is likely to have relatively large fluctuations. For example, the panel industry has recently seen a sharp rise in the price of liquid crystal glass, which has led to an increase in the cost of the panel industry, which in turn has led to an increase in the cost of display TV screens.
To give another example, starting at the end of 2020. the global IC chip supply will be cut off due to the insufficient supply of fab capacity. In 2021. there was even news that the car plant could stop production due to a shortage of automotive chips. For example, Oriental LCD panel shipments are the first in the world, and it has strong bargaining power for upstream and downstream. It has even indirectly affected the supply-and-demand relationship in the market by controlling the output of the production line and the price of the panel.
The third is to find the core competitiveness, analyze a company, and understand the company's products and services. What is the business of the company? What is the function of each product? What is the sales revenue for each product? What proportion? How much does the core business contribute to revenue? Is it sustainable?
The product structure can be viewed on the company's official website. Taking the dry air concept as an example, open the official website of the dry air concept, find products and services, and you can directly see the detailed introduction of each type of product.
The fourth is to look at financial indicators, about which every mature investor has a different profile. Here are a few basic measures: one is the gross profit margin and profit margin; the second is the price-earnings ratio; and the third is the return on equity (Roe).
Looking at gross profit margin and profit margin, you can understand the profitability of public companies. If the scale of revenue is large but the gross profit margin is low, It indicates that the added value of the company's products is not high and that its future competitiveness is not strong. For example, foundry businesses and trading businesses have high incomes but low gross profits.
Regarding the P/E ratio, it is important to note that the comparison must be made within the industry. In the manufacturing industry, technology industry, foundry industry, and catering industry, the P/E ratio of different industries has a big difference.
When you look at the return on equity, you look at the annual return you can get after investing in the company. This is one of the most important indicators that Warren Buffett looks for when investing in his company. Generally speaking, Roe is greater than 10%, which is a minimum standard for investment targets. However, it should be noted that Roe indicators cannot be mechanically applied in the analysis, and specific problems should be analyzed to determine what causes the level of return on equity.
The fifth is about corporate announcements and research reports. There are many types of corporate announcements, including financial reporting, auditing, risk warning, additional issuance, and so on. The amount of information involved is huge and necessary to quickly understand a company.
The financial report will mark and interpret the reasons for the change of indicators, and this reason needs to be considered by ourselves. Because every enterprise will do earnings management through supply value changes, investment income, depreciation methods, investment real estate, measurement methods, income recognition progress, and so on, to adjust the financial indicators.
Looking at research reports is a quick way for investors to form a quick judgment, as well as to see what institutions think and rate the company's future. The more research reports there are, the more organizations are paying attention to the company. If a company does not research a few research reports a year, the status of such companies in the hearts of institutions can be imagined.
While many people want to understand a company quickly, analyzing a company can be complicated. It is necessary to comprehensively consider the company's financial situation, industry status, management team, market competitiveness, and other aspects of information. Investors must sharpen their eyes in order to find a public company with growth potential.
| Type | Content |
| Financial Report | Share financials for investor insight. |
| Audit Report | External audit boosts investor trust. |
| Risk Alert | Transparent risk disclosure minimizes investor uncertainty. |
| Increase Announcement | Stock increase impacts investors, monitor structure. |
| Results Announcement | Company's performance forecast influences investor confidence. |
| Notice of Shareholders' Meeting | Shareholders' meeting notice: engage in governance, exercise rights. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.

How AI is Transforming the Future of Trading?
See how AI transforms trading with advanced data analysis, automation, and real-time insights, boosting accuracy and market efficiency for traders.
2024-10-29
How to Profit from AI Bots in Trading
Learn how to use AI bots in trading to enhance performance and generate income. Discover strategies for maximizing profits in the financial market.
2024-10-28
Best Currency Pairs for Forex Trading
Maximize your forex trading success by choosing the best currency pairs. Learn why USD, EUR, and JPY are among the most traded and profitable pairs
2024-10-24





